SBAS473E May 2009 – January 2018 ADS1013 , ADS1014 , ADS1015
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6 Register Map
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Shunt Resistor Considerations
- 9.2.2.2 Operational Amplifier Considerations
- 9.2.2.3 ADC Input Common-Mode Considerations
- 9.2.2.4 Resistor (R1, R2, R3, R4) Considerations
- 9.2.2.5 Noise and Input Impedance Considerations
- 9.2.2.6 First-order RC Filter Considerations
- 9.2.2.7 Circuit Implementation
- 9.2.2.8 Results Summary
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.5.3 Writing To and Reading From the Registers
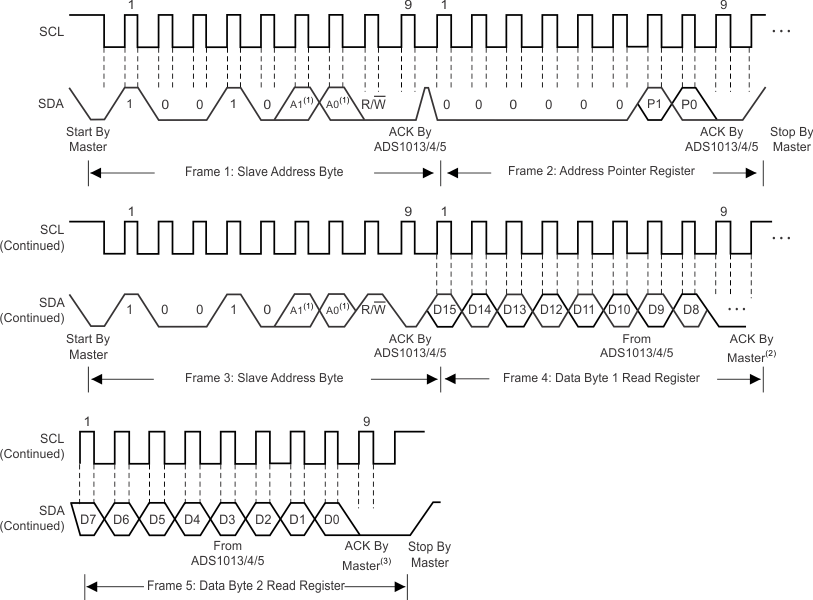
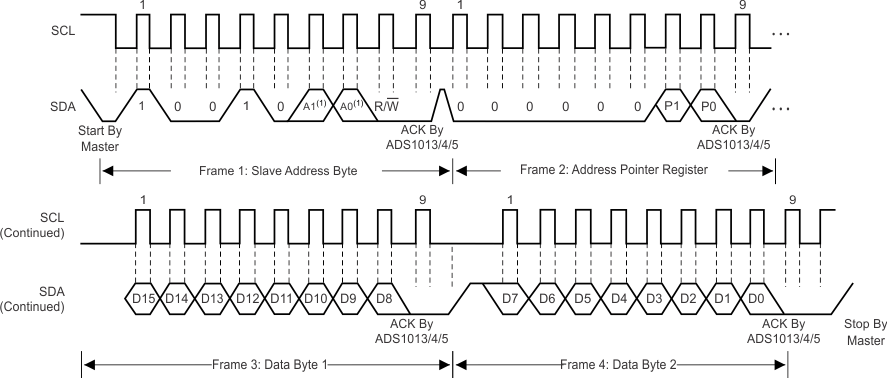
To access a specific register from the ADS101x, the master must first write an appropriate value to register address pointer bits P[1:0] in the Address Pointer register. The Address Pointer register is written to directly after the slave address byte, low R/W bit, and a successful slave acknowledgment. After the Address Pointer register is written, the slave acknowledges, and the master issues a STOP or a repeated START condition.
When reading from the ADS101x, the previous value written to bits P[1:0] determines the register that is read. To change which register is read, a new value must be written to P[1:0]. To write a new value to P[1:0], the master issues a slave address byte with the R/W bit low, followed by the Address Pointer register byte. No additional data has to be transmitted, and a STOP condition can be issued by the master. The master can now issue a START condition and send the slave address byte with the R/W bit high to begin the read. Figure 22 details this sequence. If repeated reads from the same register are desired, there is no need to continually send the Address Pointer register, because the ADS101x store the value of P[1:0] until it is modified by a write operation. However, for every write operation, the Address Pointer register must be written with the appropriate values.