DLPS023C January 2012 – August 2015 DLPC300
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 I/O Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Crystal Port Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 Power Consumption
- 6.8 I2C Interface Timing Requirements
- 6.9 Parallel Interface Frame Timing Requirements
- 6.10 Parallel Interface General Timing Requirements
- 6.11 Parallel I/F Maximum Supported Horizontal Line Rate
- 6.12 BT.565 I/F General Timing Requirements
- 6.13 Flash Interface Timing Requirements
- 6.14 DMD Interface Timing Requirements
- 6.15 Mobile Dual Data Rate (mDDR) Memory Interface Timing Requirements
- 6.16 JTAG Interface: I/O Boundary Scan Application Switching Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2 Typical Application
- 8.3 System Examples
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
-
10Layout
- 10.1
Layout Guidelines
- 10.1.1 Printed Circuit Board Design Guidelines
- 10.1.2 Printed Circuit Board Layer Stackup Geometry
- 10.1.3 Signal Layers
- 10.1.4 Routing Constraints
- 10.1.5 Termination Requirements
- 10.1.6 PLL
- 10.1.7 General Handling Guidelines for Unused CMOS-Type Pins
- 10.1.8 Hot-Plug Usage
- 10.1.9 External Clock Input Crystal Oscillator
- 10.2 Layout Example
- 10.3 Thermal Considerations
- 10.1
Layout Guidelines
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ZVB|176
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11 Device and Documentation Support
11.1 Device Support
11.1.1 Third-Party Products Disclaimer
TI'S PUBLICATION OF INFORMATION REGARDING THIRD-PARTY PRODUCTS OR SERVICES DOES NOT CONSTITUTE AN ENDORSEMENT REGARDING THE SUITABILITY OF SUCH PRODUCTS OR SERVICES OR A WARRANTY, REPRESENTATION OR ENDORSEMENT OF SUCH PRODUCTS OR SERVICES, EITHER ALONE OR IN COMBINATION WITH ANY TI PRODUCT OR SERVICE.
11.1.2 Device Nomenclature
Figure 24 provides a legend for reading the complete device name for any DLP device.
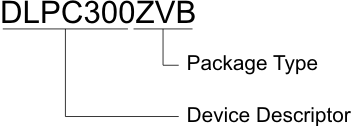 Figure 24. Device Nomenclature
Figure 24. Device Nomenclature
11.1.3 Device Marking
The device marking consists of the fields shown in Figure 25.
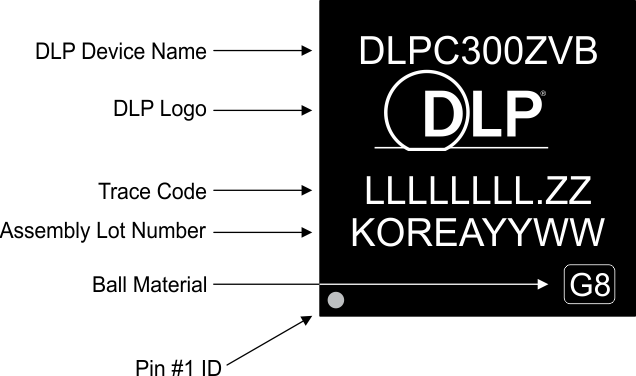 Figure 25. Device Marking
Figure 25. Device Marking
11.2 Documentation Support
11.2.1 Related Documentation
- DLP3000 0.3 WVGA Series 220 DMD data sheet, DLPS022
- DLPC300 Programmer's Guide, DLPU004
- DLP® 0.3 WVGA Chipset Reference Design
11.3 Community Resources
The following links connect to TI community resources. Linked contents are provided "AS IS" by the respective contributors. They do not constitute TI specifications and do not necessarily reflect TI's views; see TI's Terms of Use.
-
TI E2E™ Online Community TI's Engineer-to-Engineer (E2E) Community. Created to foster collaboration among engineers. At e2e.ti.com, you can ask questions, share knowledge, explore ideas and help solve problems with fellow engineers.
-
Design Support TI's Design Support Quickly find helpful E2E forums along with design support tools and contact information for technical support.
11.4 Trademarks
E2E is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
DLP is a registered trademark of Texas Instruments.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
11.5 Electrostatic Discharge Caution

These devices have limited built-in ESD protection. The leads should be shorted together or the device placed in conductive foam during storage or handling to prevent electrostatic damage to the MOS gates.
11.6 Glossary
SLYZ022 — TI Glossary.
This glossary lists and explains terms, acronyms, and definitions.