SNVS316H September 2004 – December 2014 LM2736
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 LM2736X (1.6 MHz) VBOOST Derived from VIN 5 V to 1.5 V / 750 mA
- 8.2.2 LM2736X (1.6 MHz) VBOOST Derived from VOUT 12 V to 3.3 V / 750 mA
- 8.2.3 LM2736X (1.6 MHz) VBOOST Derived from VSHUNT 18 V to 1.5 V / 750 mA
- 8.2.4 LM2736X (1.6 MHz) VBOOST Derived from Series Zener Diode (VIN) 15 V to 1.5 V / 750 mA
- 8.2.5 LM2736X (1.6 MHz) VBOOST Derived from Series Zener Diode (VOUT) 15 V to 9 V / 750 mA
- 8.2.6 LM2736Y (550 kHz) VBOOST Derived from VIN 5 V to 1.5 V / 750 mA
- 8.2.7 LM2736Y (550 kHz) VBOOST Derived from VOUT 12 V to 3.3 V / 750 mA
- 8.2.8 LM2736Y (550 kHz) VBOOST Derived from VSHUNT 18 V to 1.5 V / 750 mA
- 8.2.9 LM2736Y (550 kHz) VBOOST Derived from Series Zener Diode (VIN) 15 V to 1.5 V / 750 mA
- 8.2.10 LM2736Y (550 kHz) VBOOST Derived from Series Zener Diode (VOUT) 15 V to 9 V / 750 mA
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDC|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
The LM2736 device is a constant frequency PWM buck regulator IC that delivers a 750 mA load current. The regulator has a preset switching frequency of either 550 kHz (LM2736Y) or 1.6 MHz (LM2736X). These high frequencies allow the LM2736 device to operate with small surface mount capacitors and inductors, resulting in DC/DC converters that require a minimum amount of board space. The LM2736 device is internally compensated, so it is simple to use, and requires few external components. The LM2736 device uses current-mode control to regulate the output voltage.
The following operating description of the LM2736 device will refer to the Simplified Block Diagram (Functional Block Diagram) and to the waveforms in Figure 11. The LM2736 device supplies a regulated output voltage by switching the internal NMOS control switch at constant frequency and variable duty cycle. A switching cycle begins at the falling edge of the reset pulse generated by the internal oscillator. When this pulse goes low, the output control logic turns on the internal NMOS control switch. During this on-time, the SW pin voltage (VSW) swings up to approximately VIN, and the inductor current (IL) increases with a linear slope. IL is measured by the current-sense amplifier, which generates an output proportional to the switch current. The sense signal is summed with the regulator’s corrective ramp and compared to the error amplifier’s output, which is proportional to the difference between the feedback voltage and VREF. When the PWM comparator output goes high, the output switch turns off until the next switching cycle begins. During the switch off-time, inductor current discharges through Schottky diode D1, which forces the SW pin to swing below ground by the forward voltage (VD) of the catch diode. The regulator loop adjusts the duty cycle (D) to maintain a constant output voltage.
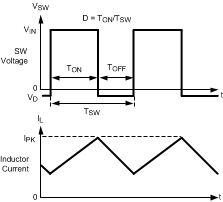 Figure 11. LM2736 Waveforms of SW Pin Voltage and Inductor Current
Figure 11. LM2736 Waveforms of SW Pin Voltage and Inductor Current
7.2 Functional Block Diagram
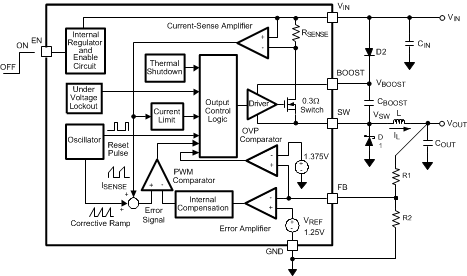
7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 Output Overvoltage Protection
The overvoltage comparator compares the FB pin voltage to a voltage that is 10% higher than the internal reference Vref. Once the FB pin voltage goes 10% above the internal reference, the internal NMOS control switch is turned off, which allows the output voltage to decrease toward regulation.
7.3.2 Undervoltage Lockout
Undervoltage lockout (UVLO) prevents the LM2736 device from operating until the input voltage exceeds 2.74 V (typ).
The UVLO threshold has approximately 440mV of hysteresis, so the part will operate until VIN drops below 2.3 V (typ). Hysteresis prevents the part from turning off during power up if VIN is non-monotonic.
7.3.3 Current Limit
The LM2736 device uses cycle-by-cycle current limiting to protect the output switch. During each switching cycle, a current limit comparator detects if the output switch current exceeds 1.5 A (typ), and turns off the switch until the next switching cycle begins.
7.3.4 Thermal Shutdown
Thermal shutdown limits total power dissipation by turning off the output switch when the IC junction temperature exceeds 165°C. After thermal shutdown occurs, the output switch doesn’t turn on until the junction temperature drops to approximately 150°C.
7.4 Device Functional Modes
7.4.1 Enable Pin / Shutdown Mode
The LM2736 device has a shutdown mode that is controlled by the enable pin (EN). When a logic low voltage is applied to EN, the part is in shutdown mode and its quiescent current drops to typically 30 nA. Switch leakage adds another 40 nA from the input supply. The voltage at this pin should never exceed VIN + 0.3 V.
7.4.2 Soft-Start
This function forces VOUT to increase at a controlled rate during start up. During soft-start, the error amplifier’s reference voltage ramps from 0 V to its nominal value of 1.25 V in approximately 200 µs. This forces the regulator output to ramp up in a more linear and controlled fashion, which helps reduce inrush current.