SNVSAH4C December 2015 – February 2018 LMR23610
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency Peak Current Mode Control
- 7.3.2 Adjustable Output Voltage
- 7.3.3 EN/SYNC
- 7.3.4 VCC, UVLO
- 7.3.5 Minimum ON-Time, Minimum OFF-Time and Frequency Foldback at Dropout Conditions
- 7.3.6 Internal Compensation and CFF
- 7.3.7 Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 7.3.8 Overcurrent and Short-Circuit Protection
- 7.3.9 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Output Voltage Setpoint
- 8.2.2.3 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.4 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.6 Feed-Forward Capacitor
- 8.2.2.7 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.9 VCC Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.10 Undervoltage Lockout Setpoint
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Orderable Information
7.3.8 Overcurrent and Short-Circuit Protection
The LMR23610 is protected from overcurrent conditions by cycle-by-cycle current limit on both the peak and valley of the inductor current. Hiccup mode is activated if a fault condition persists to prevent over-heating.
High-side MOSFET overcurrent protection is implemented by the nature of the peak-current-mode control. The HS switch current is sensed when the HS is turned on after a set blanking time. The HS switch current is compared to the output of the error amplifier (EA) minus slope compensation every switching cycle. See Functional Block Diagram for more details. The peak current of HS switch is limited by a clamped maximum peak current threshold IHS_LIMIT which is constant. So the peak current limit of the high-side switch is not affected by the slope compensation and remains constant over the full duty cycle range.
The current going through LS MOSFET is also sensed and monitored. When the LS switch turns on, the inductor current begins to ramp down. The LS switch will not be turned OFF at the end of a switching cycle if its current is above the LS current limit ILS_LIMIT. The LS switch will be kept ON so that inductor current keeps ramping down, until the inductor current ramps below the LS current limit ILS_LIMIT. Then the LS switch will be turned OFF and the HS switch will be turned on after a dead time. This is somewhat different than the more typical peak current limit, and results in Equation 9 for the maximum load current.
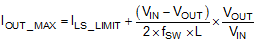
If the current of the LS switch is higher than the LS current limit for 64 consecutive cycles, hiccup current protection mode will be activated. In hiccup mode, the regulator will be shut down and kept off for 5 ms typically before the LMR23610 tries to start again. If over-current or short-circuit fault condition still exist, hiccup will repeat until the fault condition is removed. Hiccup mode reduces power dissipation under severe over-current conditions, prevents over-heating and potential damage to the device.