SNOSCP7A March 2013 – January 2016 LMX2485Q-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6 Register Maps
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTW|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTW|24
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
The critical pin is the high-frequency input pin that should have a short trace. In general, try to keep the ground and power planes 20 mils or more farther away from vias to supply pins to ensure that no spur energy can couple to them.
11.2 Layout Example
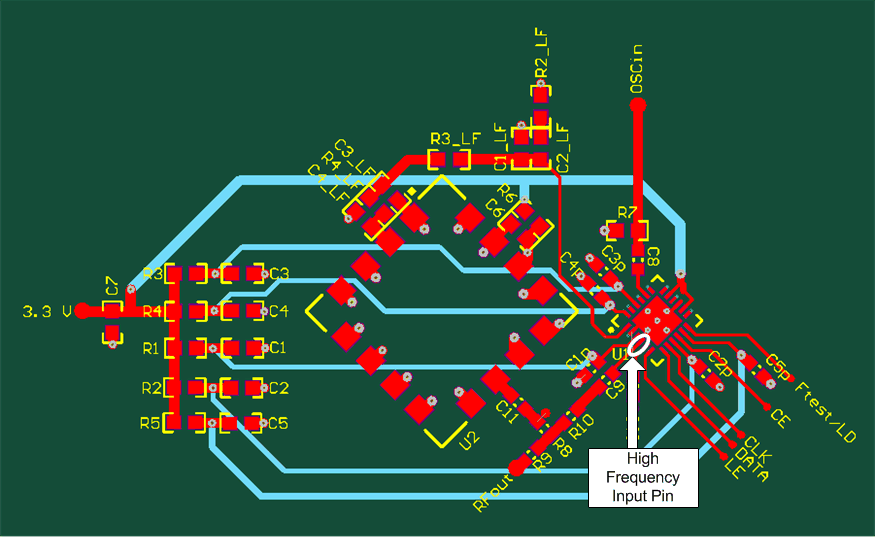 Figure 36. Layout Example
Figure 36. Layout Example