SBOS872A May 2018 – June 2018 OPA521
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGW|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGW|20
Orderable Information
8.2.2.1.2 High-Voltage Capacitor
The high-voltage capacitor (HV Cap) blocks the low-frequency mains voltage by forming a voltage divider with the winding inductance of the line coupling transformer. In many applications, a maximum reactive power (VA limit) on the HV Cap may be required. To meet this requirement, the HV Cap value is calculated by Equation 1.
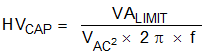
For a 240-VAC, 50-Hz application with a 10-VA limit, the maximum value for the HV Cap is shown in Equation 2.
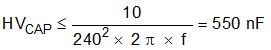
A 470-nF capacitor is frequently used in these types of applications. A metallized polypropylene electromagnetic interference and radio frequency interference (EMI/RFI) suppression capacitor is recommended because of the low loss factor associated with the dielectric, which results in minimal internal self-heating. Operating the capacitor at approximately 80% of its ac-rated voltage ensures a long component operating life. See Circuit Protection of this document for additional discussion on selecting the correct HV Cap value to withstand impulses on the mains.