SLLSFE2 June 2019 SN65HVDA1040B-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.2.1.1 Bus Loading, Length, and Number of Nodes
The ISO 11898 Standard specifies up to 1 Mbps data rate, maximum bus length of 40 meters, maximum drop line (stub) length of 0.3 meters, and a maximum of 30 nodes. However, with careful network design, the system may have longer cables, longer stub lengths, and many more nodes to a bus. Many CAN organizations and standards have scaled the use of CAN for applications outside the original ISO 11898 standard. They have made system-level trade-offs for data rate, cable length, and parasitic loading of the bus. Examples of some of these specifications are ARINC825, CANopen, CAN Kingdom, DeviceNet, and NMEA200.
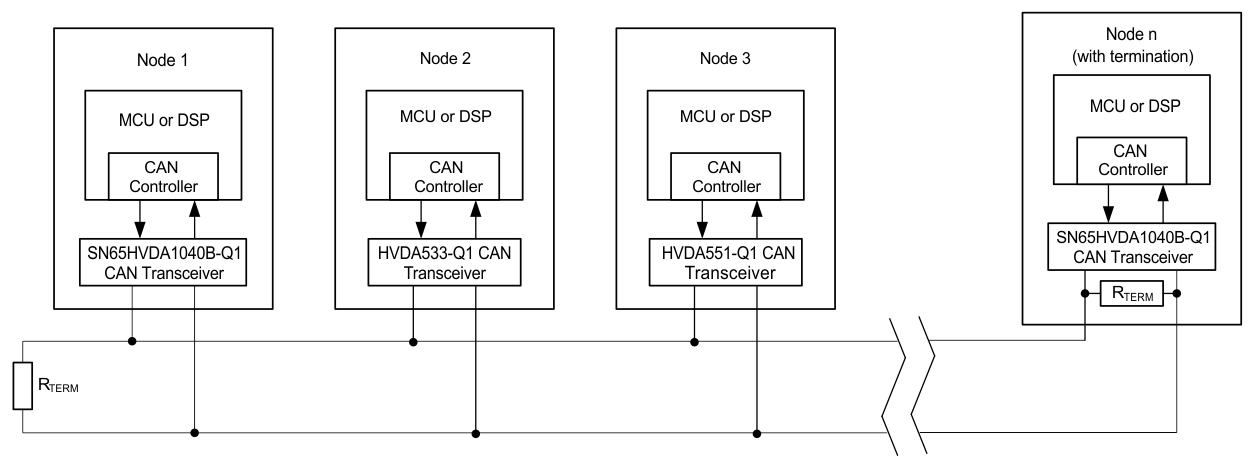 Figure 21. Typical CAN Bus Drawing
Figure 21. Typical CAN Bus Drawing A high number of nodes requires a transceiver with high input impedance and wide common-mode range such as the SN65HVDA1040B-Q1 CAN transceiver. ISO 11898-2 specifies the driver differential output with a 60-Ω load (two 120-Ω termination resistors in parallel) and the differential output must be greater than 1.5 V. The SN65HVDA1040B-Q1 device is specified to meet the 1.5-V requirement with a 60-Ω load, and additionally specified with a differential output voltage minimum of 1.2 V across a common-mode range of –2 V to 7 V through a 330-Ω coupling network. This network represents the bus loading of 90 SN65HVDA1040B-Q1 transceivers based on their minimum differential input resistance of 30 kΩ. Therefore, the SN65HVDA1040B-Q1 supports up to 90 transceivers on a single bus segment with margin to the 1.2-V minimum differential input voltage requirement at each node.
For CAN network design, margin must be given for signal loss across the system and cabling, parasitic loadings, network imbalances, ground offsets and signal integrity thus a practical maximum number of nodes may be lower. Bus length may also be extended beyond the original ISO 11898 standard of 40 meters by careful system design and data rate tradeoffs. For example, CANopen network design guidelines allow the network to be up to 1-km with changes in the termination resistance, cabling, less than 64 nodes and significantly lowered data rate.
This flexibility in CAN network design is one of the key strengths of the various extensions and additional standards that have been built on the original ISO 11898 CAN standard.