SLLSFE2 June 2019 SN65HVDA1040B-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.2.1.2 CAN Termination
The ISO 11898 standard specifies the interconnect to be a twisted pair cable (shielded or unshielded) with 120-Ω characteristic impedance (ZO ). Resistors equal to the characteristic impedance of the line should be used to terminate both ends of the cable to prevent signal reflections. Unterminated drop lines (stubs) connecting nodes to the bus should be kept as short as possible to minimize signal reflections. The termination may be on the cable or in a node, but if nodes may be removed from the bus the termination must be carefully placed so that it is not removed from the bus.
Termination is typically a 120-Ω resistor at each end of the bus. If filtering and stabilization of the common-mode voltage of the bus is desired, then split termination may be used (see Figure 22 and Using SPLIT With Split Termination).
Care should be taken when determining the power ratings of the termination resistors. A typical worst case fault condition is if the system power supply and ground were shorted across the termination resistance which would result in much higher current through the termination resistance than the CAN transceiver's current limit.
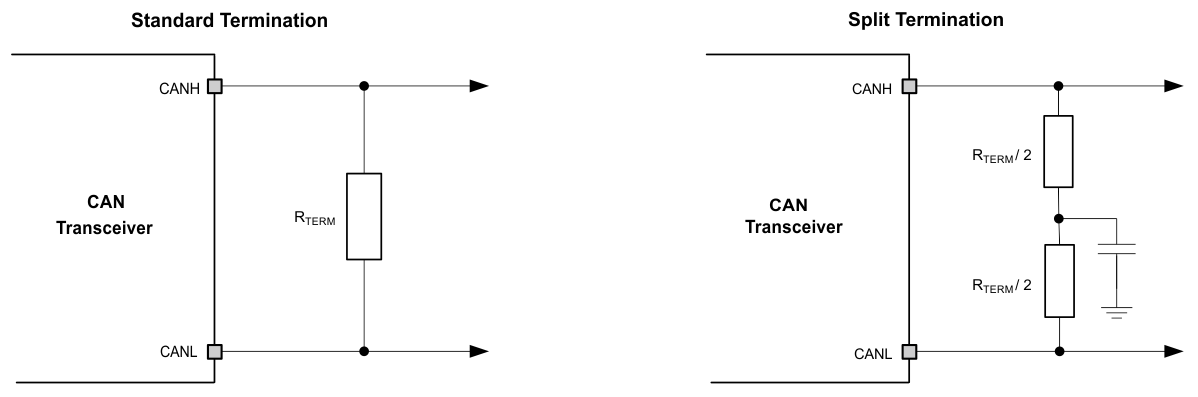 Figure 22. CAN Termination Schematic
Figure 22. CAN Termination Schematic