SPRS958H March 2016 – November 2019
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Device Overview
- 2 Revision History
- 3 Device Comparison
-
4 Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 4.1 Terminal Assignment
- 4.2 Ball Characteristics
- 4.3 Multiplexing Characteristics
- 4.4
Signal Descriptions
- 4.4.1 Video Input Ports (VIP)
- 4.4.2 Display Subsystem – Video Output Ports
- 4.4.3 Display Subsystem – High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI)
- 4.4.4 Camera Serial Interface 2 CAL bridge (CSI2)
- 4.4.5 External Memory Interface (EMIF SDRAM)
- 4.4.6 General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 4.4.7 Timers
- 4.4.8 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface (I2C)
- 4.4.9 Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART)
- 4.4.10 Multichannel Serial Peripheral Interface (McSPI)
- 4.4.11 Quad Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI)
- 4.4.12 Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP)
- 4.4.13 Universal Serial Bus (USB)
- 4.4.14 SATA
- 4.4.15 Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe)
- 4.4.16 Controller Area Network Interface (DCAN)
- 4.4.17 Ethernet Interface (GMAC_SW)
- 4.4.18 eMMC/SD/SDIO
- 4.4.19 General-Purpose Interface (GPIO)
- 4.4.20 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Interface
- 4.4.21 Test Interfaces
- 4.4.22 System and Miscellaneous
- 4.4.23 Power Supplies
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Power-On-Hour (POH) Limits
- 5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.5 Operating Performance Points
- 5.6 Power Consumption Summary
- 5.7
Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.1 LVCMOS DDR DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.2 HDMIPHY DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.3 Dual Voltage LVCMOS I2C DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.4 IQ1833 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.5 IHHV1833 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.6 LVCMOS OSC Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.7 LVCMOS CSI2 DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.8 BC1833IHHV Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.9 USBPHY DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.10 Dual Voltage SDIO1833 DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.11 Dual Voltage LVCMOS DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.12 SATAPHY DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.13 PCIEPHY DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.8 VPP Specifications for One-Time Programmable (OTP) eFuses
- 5.9 Thermal Characteristics
- 5.10 Power Supply Sequences
- 6 Clock Specifications
-
7 Timing Requirements and Switching Characteristics
- 7.1 Timing Test Conditions
- 7.2 Interface Clock Specifications
- 7.3 Timing Parameters and Information
- 7.4 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 7.5 Virtual and Manual I/O Timing Modes
- 7.6 Video Input Ports (VIP)
- 7.7 Display Subsystem - Video Output Ports
- 7.8 Display Subsystem - High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI)
- 7.9 Camera Serial Interface 2 CAL bridge (CSI2)
- 7.10 External Memory Interface (EMIF)
- 7.11 General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 7.12 Timers
- 7.13 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface (I2C)
- 7.14 Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART)
- 7.15 Multichannel Serial Peripheral Interface (McSPI)
- 7.16 Quad Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI)
- 7.17 Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP)
- 7.18 Universal Serial Bus (USB)
- 7.19 Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA)
- 7.20 Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe)
- 7.21 Controller Area Network Interface (DCAN)
- 7.22
Ethernet Interface (GMAC_SW)
- 7.22.1
GMAC MII Timings
- Table 7-66 Timing Requirements for miin_rxclk - MII Operation
- Table 7-67 Timing Requirements for miin_txclk - MII Operation
- Table 7-68 Timing Requirements for GMAC MIIn Receive 10/100 Mbit/s
- Table 7-69 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for GMAC MIIn Transmit 10/100 Mbits/s
- 7.22.2 GMAC MDIO Interface Timings
- 7.22.3
GMAC RMII Timings
- Table 7-74 Timing Requirements for GMAC REF_CLK - RMII Operation
- Table 7-75 Timing Requirements for GMAC RMIIn Receive
- Table 7-76 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for GMAC REF_CLK - RMII Operation
- Table 7-77 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for GMAC RMIIn Transmit 10/100 Mbits/s
- 7.22.4
GMAC RGMII Timings
- Table 7-81 Timing Requirements for rgmiin_rxc - RGMIIn Operation
- Table 7-82 Timing Requirements for GMAC RGMIIn Input Receive for 10/100/1000 Mbps
- Table 7-83 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for rgmiin_txctl - RGMIIn Operation for 10/100/1000 Mbit/s
- Table 7-84 Switching Characteristics for GMAC RGMIIn Output Transmit for 10/100/1000 Mbps
- 7.22.1
GMAC MII Timings
- 7.23
eMMC/SD/SDIO
- 7.23.1
MMC1-SD Card Interface
- 7.23.1.1 Default speed, 4-bit data, SDR, half-cycle
- 7.23.1.2 High speed, 4-bit data, SDR, half-cycle
- 7.23.1.3 SDR12, 4-bit data, half-cycle
- 7.23.1.4 SDR25, 4-bit data, half-cycle
- 7.23.1.5 UHS-I SDR50, 4-bit data, half-cycle
- 7.23.1.6 UHS-I SDR104, 4-bit data, half-cycle
- 7.23.1.7 UHS-I DDR50, 4-bit data
- 7.23.2 MMC2 - eMMC
- 7.23.3 MMC3 and MMC4-SDIO/SD
- 7.23.1
MMC1-SD Card Interface
- 7.24 General-Purpose Interface (GPIO)
- 7.25 System and Miscellaneous interfaces
- 7.26
Test Interfaces
- 7.26.1
IEEE 1149.1 Standard-Test-Access Port (JTAG)
- 7.26.1.1
JTAG Electrical Data/Timing
- Table 7-131 Timing Requirements for IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
- Table 7-132 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
- Table 7-133 Timing Requirements for IEEE 1149.1 JTAG With RTCK
- Table 7-134 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for IEEE 1149.1 JTAG With RTCK
- 7.26.1.1
JTAG Electrical Data/Timing
- 7.26.2 Trace Port Interface Unit (TPIU)
- 7.26.1
IEEE 1149.1 Standard-Test-Access Port (JTAG)
-
8 Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8.1 Introduction
- 8.2 Power Optimizations
- 8.3 Core Power Domains
- 8.4 Single-Ended Interfaces
- 8.5
Differential Interfaces
- 8.5.1 General Routing Guidelines
- 8.5.2
USB 2.0 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.5.2.1 Background
- 8.5.2.2
USB PHY Layout Guide
- 8.5.2.2.1 General Routing and Placement
- 8.5.2.2.2
Specific Guidelines for USB PHY Layout
- 8.5.2.2.2.1 Analog, PLL, and Digital Power Supply Filtering
- 8.5.2.2.2.2 Analog, Digital, and PLL Partitioning
- 8.5.2.2.2.3 Board Stackup
- 8.5.2.2.2.4 Cable Connector Socket
- 8.5.2.2.2.5 Clock Routings
- 8.5.2.2.2.6 Crystals/Oscillator
- 8.5.2.2.2.7 DP/DM Trace
- 8.5.2.2.2.8 DP/DM Vias
- 8.5.2.2.2.9 Image Planes
- 8.5.2.2.2.10 Power Regulators
- 8.5.2.3 References
- 8.5.3 USB 3.0 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.5.4 HDMI Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.5.5 SATA Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.5.6 PCIe Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.5.7 CSI2 Board Design and Routing Guidelines
- 8.6 Clock Routing Guidelines
- 8.7
DDR3 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.7.1 DDR3 General Board Layout Guidelines
- 8.7.2
DDR3 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.7.2.1 Board Designs
- 8.7.2.2 DDR3 EMIF
- 8.7.2.3 DDR3 Device Combinations
- 8.7.2.4 DDR3 Interface Schematic
- 8.7.2.5 Compatible JEDEC DDR3 Devices
- 8.7.2.6 PCB Stackup
- 8.7.2.7 Placement
- 8.7.2.8 DDR3 Keepout Region
- 8.7.2.9 Bulk Bypass Capacitors
- 8.7.2.10 High Speed Bypass Capacitors
- 8.7.2.11 Net Classes
- 8.7.2.12 DDR3 Signal Termination
- 8.7.2.13 VREF_DDR Routing
- 8.7.2.14 VTT
- 8.7.2.15 CK and ADDR_CTRL Topologies and Routing Definition
- 8.7.2.16 Data Topologies and Routing Definition
- 8.7.2.17 Routing Specification
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ABC|760
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.7 Display Subsystem - Video Output Ports
Three Display Parallel Interfaces (DPI) channels are available in DSS named DPI Video Output 1, DPI Video Output 2 and DPI Video Output 3.
NOTE
The DPI Video Output i (i = 1 to 3) interface is also referred to as VOUTi.
Every VOUT interface consists of:
- 24-bit data bus (data[23:0])
- Horizontal synchronization signal (HSYNC)
- Vertical synchronization signal (VSYNC)
- Data enable (DE)
- Field ID (FID)
- Pixel clock (CLK)
NOTE
For more information, see Display Subsystem chapter in the device TRM.
CAUTION
The I/O Timings provided in this section are valid only if signals within a single IOSET are used. The IOSETs are defined in Table 7-18 .
CAUTION
The I/O Timings provided in this section are valid only for some DSS usage modes when the corresponding Virtual I/O Timings or Manual I/O Timings are configured as described in the tables found in this section.
CAUTION
All pads/balls configured as vouti_* signals must be programmed to use slow slew rate by setting the corresponding CTRL_CORE_PAD_*[SLEWCONTROL] register field to SLOW (0b1).
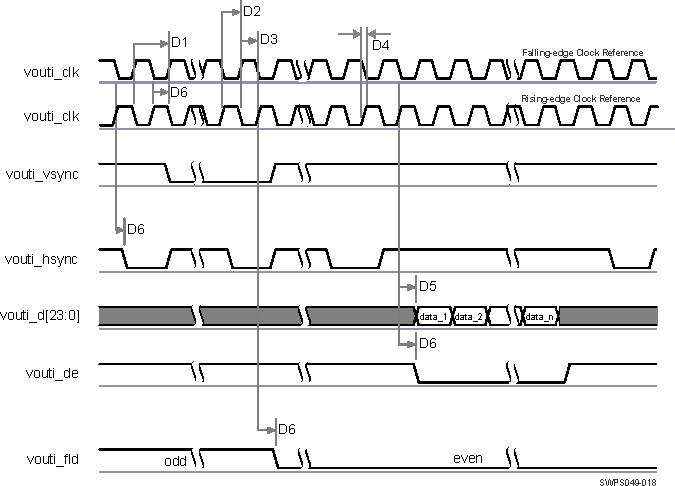
Table 7-14 through Table 7-17, and Figure 7-6 assume testing over the recommended operating conditions and electrical characteristic conditions.
Table 7-14 DPI Video Output i (i = 1..3) Default Switching Characteristics
| NO. | PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION | MODE | MIN | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | tc(clk) | Cycle time, output pixel clock vouti_clk | DPI1/2/3 in 1.8V mode
DPI2 in 3.3V mode |
11.76(3) | ns | |
| DPI1/3 in 3.3V mode | 13.33(3) | ns | ||||
| D2 | tw(clkL) | Pulse duration, output pixel clock vouti_clk low | P*0.5-1 (1) | ns | ||
| D3 | tw(clkH) | Pulse duration, output pixel clock vouti_clk high | P*0.5-1 (1) | ns | ||
| D5 | td(clk-ctlV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output data vouti_d[23:0] valid | DPI1 | -2.5 | 2.5 | ns |
| D6 | td(clk-dV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output control signals vouti_vsync, vouti_hsync, vouti_de, and vouti_fld valid | DPI1 | -2.5 | 2.5 | ns |
| D5 | td(clk-ctlV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output data vouti_d[23:0] valid | DPI2 (vin2a_fld0 clock reference) | -2.5 | 2.5 | ns |
| D6 | td(clk-dV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output control signals vouti_vsync, vouti_hsync, vouti_de, and vouti_fld valid | DPI2 (vin2a_fld0 clock reference) | -2.5 | 2.5 | ns |
| D5 | td(clk-ctlV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output data vouti_d[23:0] valid | DPI2 (xref_clk2 clock reference) | -2.5 | 2.5 | ns |
| D6 | td(clk-dV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output control signals vouti_vsync, vouti_hsync, vouti_de, and vouti_fld valid | DPI2 (xref_clk2 clock reference) | -2.5 | 2.5 | ns |
| D5 | td(clk-ctlV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output data vouti_d[23:0] valid | DPI3 | -2.5 | 2.5 | ns |
| D6 | td(clk-dV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output control signals vouti_vsync, vouti_hsync, vouti_de, and vouti_fld valid | DPI3 | -2.5 | 2.5 | ns |
- P = output vouti_clk period in ns.
- All pads/balls configured as vouti_* signals must be programmed to use slow slew rate by setting the corresponding CTRL_CORE_PAD_*[SLEWCONTROL] register field to SLOW (0b1).
- SERDES transceivers may be sensitive to the jitter profile of vouti_clk. See Application Note SPRAC62 for additional guidance.
Table 7-15 DPI Video Output i (i = 1..3) Alternate Switching Characteristics(2)
| NO. | PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION | MODE | MIN | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | tc(clk) | Cycle time, output pixel clock vouti_clk | DPI1/2/3 in 1.8V mode
DPI2 in 3.3V mode |
6.06(3) | ns | |
| DPI1/3 in 3.3V mode | 13.33(3) | ns | ||||
| D2 | tw(clkL) | Pulse duration, output pixel clock vouti_clk low | P*0.5-1 (1) | ns | ||
| D3 | tw(clkH) | Pulse duration, output pixel clock vouti_clk high | P*0.5-1 (1) | ns | ||
| D5 | td(clk-ctlV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output data vouti_d[23:0] valid | DPI1 | 1.51 | 4.55 | ns |
| D6 | td(clk-dV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output control signals vouti_vsync, vouti_hsync, vouti_de, and vouti_fld valid | DPI1 | 1.51 | 4.55 | ns |
| D5 | td(clk-ctlV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output data vouti_d[23:0] valid | DPI2 (vin2a_fld0 clock reference) | 1.51 | 4.55 | ns |
| D6 | td(clk-dV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output control signals vouti_vsync, vouti_hsync, vouti_de, and vouti_fld valid | DPI2 (vin2a_fld0 clock reference) | 1.51 | 4.55 | ns |
| D5 | td(clk-ctlV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output data vouti_d[23:0] valid | DPI2 (xref_clk2 clock reference) | 1.51 | 4.55 | ns |
| D6 | td(clk-dV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output control signals vouti_vsync, vouti_hsync, vouti_de, and vouti_fld valid | DPI2 (xref_clk2 clock reference) | 1.51 | 4.55 | ns |
| D5 | td(clk-ctlV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output data vouti_d[23:0] valid | DPI3 | 1.51 | 4.55 | ns |
| D6 | td(clk-dV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output control signals vouti_vsync, vouti_hsync, vouti_de, and vouti_fld valid | DPI3 | 1.51 | 4.55 | ns |
- P = output vouti_clk period in ns.
- All pads/balls configured as vouti_* signals must be programmed to use slow slew rate by setting the corresponding CTRL_CORE_PAD_*[SLEWCONTROL] register field to SLOW (0b1).
- SERDES transceivers may be sensitive to the jitter profile of vouti_clk. See Application Note SPRAC62 for additional guidance.
Table 7-16 DPI Video Output i (i = 1..3) MANUAL4 Switching Characteristics (2)
| NO. | PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION | MODE | MIN | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | tc(clk) | Cycle time, output pixel clock vouti_clk | DPI1/2/3 in 1.8V mode DPI2 in 3.3V mode | 6.06 (3) | ns | |
| DPI1/3 in 3.3V mode | 13.33 (3) | ns | ||||
| D2 | tw(clkL) | Pulse duration, output pixel clock vouti_clk low | P*0.5-1 (1) | ns | ||
| D3 | tw(clkH) | Pulse duration, output pixel clock vouti_clk high | P*0.5-1 (1) | ns | ||
| D5 | td(clk-ctlV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output data vouti_d[23:0] valid | DPI1 | 2.85 | 5.56 | ns |
| D6 | td(clk-dV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output control signals vouti_vsync, vouti_hsync, vouti_de, and vouti_fld valid | DPI1 | 2.85 | 5.56 | ns |
| D5 | td(clk-ctlV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output data vouti_d[23:0] valid | DPI2 (vin2a_fld0 clock reference) | 2.85 | 5.56 | ns |
| D6 | td(clk-dV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output control signals vouti_vsync, vouti_hsync, vouti_de, and vouti_fld valid | DPI2 (vin2a_fld0 clock reference) | 2.85 | 5.56 | ns |
| D5 | td(clk-ctlV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output data vouti_d[23:0] valid | DPI2 (xref_clk2 clock reference) | 2.85 | 5.56 | ns |
| D6 | td(clk-dV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output control signals vouti_vsync, vouti_hsync, vouti_de, and vouti_fld valid | DPI2 (xref_clk2 clock reference) | 2.85 | 5.56 | ns |
| D5 | td(clk-ctlV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output data vouti_d[23:0] valid | DPI3 | 2.85 | 5.56 | ns |
| D6 | td(clk-dV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output control signals vouti_vsync, vouti_hsync, vouti_de, and vouti_fld valid | DPI3 | 2.85 | 5.56 | ns |
- P = output vouti_clk period in ns.
- All pads/balls configured as vouti_* signals must be programmed to use slow slew rate by setting the corresponding CTRL_CORE_PAD_*[SLEWCONTROL] register field to SLOW (0b1).
- SERDES transceivers may be sensitive to the jitter profile of vouti_clk. See Application Note SPRAC62 for additional guidance.
Table 7-17 DPI Video Output i (i = 1..3) MANUAL5 Switching Characteristics (2)
| NO. | PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION | MODE | MIN | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | tc(clk) | Cycle time, output pixel clock vouti_clk | DPI1/2/3 in 1.8V mode DPI2 in 3.3V mode | 6.06 (3) | ns | |
| DPI1/3 in 3.3V mode | 13.33 (3) | ns | ||||
| D2 | tw(clkL) | Pulse duration, output pixel clock vouti_clk low | P*0.5-1 (1) | ns | ||
| D3 | tw(clkH) | Pulse duration, output pixel clock vouti_clk high | P*0.5-1 (1) | ns | ||
| D5 | td(clk-ctlV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output data vouti_d[23:0] valid | DPI1 | 3.55 | 6.61 | ns |
| D6 | td(clk-dV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output control signals vouti_vsync, vouti_hsync, vouti_de, and vouti_fld valid | DPI1 | 3.55 | 6.61 | ns |
| D5 | td(clk-ctlV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output data vouti_d[23:0] valid | DPI2 (vin2a_fld0 clock reference) | 3.55 | 6.61 | ns |
| D6 | td(clk-dV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output control signals vouti_vsync, vouti_hsync, vouti_de, and vouti_fld valid | DPI2 (vin2a_fld0 clock reference) | 3.55 | 6.61 | ns |
| D5 | td(clk-ctlV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output data vouti_d[23:0] valid | DPI2 (xref_clk2 clock reference) | 3.55 | 6.61 | ns |
| D6 | td(clk-dV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output control signals vouti_vsync, vouti_hsync, vouti_de, and vouti_fld valid | DPI2 (xref_clk2 clock reference) | 3.55 | 6.61 | ns |
| D5 | td(clk-ctlV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output data vouti_d[23:0] valid | DPI3 | 3.55 | 6.61 | ns |
| D6 | td(clk-dV) | Delay time, output pixel clock vouti_clk transition to output control signals vouti_vsync, vouti_hsync, vouti_de, and vouti_fld valid | DPI3 | 3.55 | 6.61 | ns |
- P = output vouti_clk period in ns.
- All pads/balls configured as vouti_* signals must be programmed to use slow slew rate by setting the corresponding CTRL_CORE_PAD_*[SLEWCONTROL] register field to SLOW (0b1).
- SERDES transceivers may be sensitive to the jitter profile of vouti_clk. See Application Note SPRAC62 for additional guidance.
- The configuration of assertion of the data can be programmed on the falling or rising edge of the pixel clock.
- The polarity and the pulse width of vouti_hsync and vouti_vsync are programmable, refer to the DSS section of the device TRM.
- The vouti_clk frequency can be configured, refer to the DSS section of the device TRM.
In Table 7-18 are presented the specific groupings of signals (IOSET) for use with VOUT2.
Table 7-18 VOUT2 IOSETs
| SIGNALS | IOSET1 | IOSET2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BALL | MUX | BALL | MUX | |
| vout2_d23 | F2 | 4 | AA4 | 6 |
| vout2_d22 | F3 | 4 | AB3 | 6 |
| vout2_d21 | D1 | 4 | AB9 | 6 |
| vout2_d20 | E2 | 4 | AA3 | 6 |
| vout2_d19 | D2 | 4 | D17 | 6 |
| vout2_d18 | F4 | 4 | G16 | 6 |
| vout2_d17 | C1 | 4 | A21 | 6 |
| vout2_d16 | E4 | 4 | C18 | 6 |
| vout2_d15 | F5 | 4 | A17 | 6 |
| vout2_d14 | E6 | 4 | B17 | 6 |
| vout2_d13 | D3 | 4 | B16 | 6 |
| vout2_d12 | F6 | 4 | D15 | 6 |
| vout2_d11 | D5 | 4 | A15 | 6 |
| vout2_d10 | C2 | 4 | B15 | 6 |
| vout2_d9 | C3 | 4 | A20 | 6 |
| vout2_d8 | C4 | 4 | E15 | 6 |
| vout2_d7 | B2 | 4 | D12 | 6 |
| vout2_d6 | D6 | 4 | C12 | 6 |
| vout2_d5 | C5 | 4 | F13 | 6 |
| vout2_d4 | A3 | 4 | E12 | 6 |
| vout2_d3 | B3 | 4 | J11 | 6 |
| vout2_d2 | B4 | 4 | G13 | 6 |
| vout2_d1 | B5 | 4 | J14 | 6 |
| vout2_d0 | A4 | 4 | B14 | 6 |
| vout2_vsync | G6 | 4 | F20 | 6 |
| vout2_hsync | G1 | 4 | E21 | 6 |
| vout2_clk | H7 | 4 | B26 | 6 |
| vout2_fld | E1 | 4 | F21 | 6 |
| vout2_de | G2 | 4 | C23 | 6 |
NOTE
To configure the desired virtual mode the user must set MODESELECT bit and DELAYMODE bit field for each corresponding pad control register.
The pad control registers are presented in Table 4-3 and described in Device TRM, Control Module Chapter.
Virtual IO Timings Modes must be used to ensure some IO timings for VOUT1. See Table 7-2Modes Summary for a list of IO timings requiring the use of Virtual IO Timings Modes. See Table 7-19Virtual Functions Mapping for VOUT1 for a definition of the Virtual modes.
Table 7-19 presents the values for DELAYMODE bit field.
Table 7-19 Virtual Functions Mapping for DSS VOUT1
| BALL | BALL NAME | Delay Mode Value | MUXMODE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSS_VIRTUAL1 | 0 | 3 | ||
| H3 | gpmc_ad15 | 14 | vout3_d15 | |
| D9 | vout1_d9 | 15 | vout1_d9 | |
| N7 | gpmc_a8 | 15 | vout3_hsync | |
| L6 | gpmc_ad4 | 14 | vout3_d4 | |
| E8 | vout1_d8 | 15 | vout1_d8 | |
| M6 | gpmc_ad0 | 14 | vout3_d0 | |
| F9 | vout1_d5 | 15 | vout1_d5 | |
| J3 | gpmc_ad13 | 14 | vout3_d13 | |
| T6 | gpmc_a2 | 15 | vout3_d18 | |
| M2 | gpmc_ad1 | 14 | vout3_d1 | |
| P6 | gpmc_a4 | 15 | vout3_d20 | |
| B10 | vout1_de | 15 | vout1_de | |
| B7 | vout1_d16 | 15 | vout1_d16 | |
| R5 | gpmc_a6 | 15 | vout3_d22 | |
| A9 | vout1_d21 | 15 | vout1_d21 | |
| H2 | gpmc_ad14 | 14 | vout3_d14 | |
| T9 | gpmc_a1 | 15 | vout3_d17 | |
| E7 | vout1_d7 | 15 | vout1_d7 | |
| C11 | vout1_hsync | 15 | vout1_hsync | |
| D11 | vout1_clk | 15 | vout1_clk | |
| P1 | gpmc_cs3 | 15 | vout3_clk | |
| B9 | vout1_d22 | 15 | vout1_d22 | |
| G11 | vout1_d3 | 15 | vout1_d3 | |
| R4 | gpmc_a9 | 15 | vout3_vsync | |
| D8 | vout1_d11 | 15 | vout1_d11 | |
| J2 | gpmc_ad11 | 14 | vout3_d11 | |
| L3 | gpmc_ad6 | 14 | vout3_d6 | |
| D7 | vout1_d10 | 15 | vout1_d10 | |
| L5 | gpmc_ad2 | 14 | vout3_d2 | |
| F10 | vout1_d2 | 15 | vout1_d2 | |
| M1 | gpmc_ad3 | 14 | vout3_d3 | |
| P5 | gpmc_a7 | 15 | vout3_d23 | |
| T7 | gpmc_a3 | 15 | vout3_d19 | |
| A7 | vout1_d18 | 15 | vout1_d18 | |
| C7 | vout1_d15 | 15 | vout1_d15 | |
| J1 | gpmc_ad10 | 14 | vout3_d10 | |
| L2 | gpmc_ad7 | 14 | vout3_d7 | |
| N9 | gpmc_a10 | 15 | vout3_de | |
| F11 | vout1_d0 | 15 | vout1_d0 | |
| G10 | vout1_d1 | 15 | vout1_d1 | |
| R9 | gpmc_a5 | 15 | vout3_d21 | |
| L1 | gpmc_ad8 | 14 | vout3_d8 | |
| F8 | vout1_d6 | 15 | vout1_d6 | |
| L4 | gpmc_ad5 | 14 | vout3_d5 | |
| A10 | vout1_d23 | 15 | vout1_d23 | |
| E11 | vout1_vsync | 15 | vout1_vsync | |
| C9 | vout1_d20 | 15 | vout1_d20 | |
| R6 | gpmc_a0 | 15 | vout3_d16 | |
| A8 | vout1_d19 | 15 | vout1_d19 | |
| E9 | vout1_d4 | 15 | vout1_d4 | |
| H1 | gpmc_ad12 | 14 | vout3_d12 | |
| B11 | vout1_fld | 15 | vout1_fld | |
| P9 | gpmc_a11 | 15 | vout3_fld | |
| K2 | gpmc_ad9 | 14 | vout3_d9 | |
| C6 | vout1_d13 | 15 | vout1_d13 | |
| B8 | vout1_d17 | 15 | vout1_d17 | |
| A5 | vout1_d12 | 15 | vout1_d12 | |
| C8 | vout1_d14 | 15 | vout1_d14 | |
NOTE
To configure the desired Manual IO Timing Mode the user must follow the steps described in section "Manual IO Timing Modes" in the device TRM.
The associated registers to configure are listed in the CFG REGISTER column. For more information, see Control Module chapter in the device TRM.
Manual IO Timings Modes must be used to ensure some IO timings for VOUT1. See Table 7-2Modes Summary for a list of IO timings requiring the use of Manual IO Timings Modes. See Table 7-20Manual Functions Mapping for DSS VOUT1 for a definition of the Manual modes.
Table 7-20 lists the A_DELAY and G_DELAY values needed to calculate the correct values to be set in the CFG_x registers.
Table 7-20 Manual Functions Mapping for DSS VOUT1
| BALL | BALL NAME | VOUT1_MANUAL1 | VOUT1_MANUAL4 | VOUT1_MANUAL5 | CFG REGISTER | MUXMODE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A_DELAY (ps) | G_DELAY (ps) | A_DELAY (ps) | G_DELAY (ps) | A_DELAY (ps) | G_DELAY (ps) | 0 | |||
| D11 | vout1_clk | 0 | 212 | 0 | 249 | 0 | 249 | CFG_VOUT1_CLK_OUT | vout1_clk |
| F11 | vout1_d0 | 2502 | 0 | 3778 | 0 | 4648 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D0_OUT | vout1_d0 |
| G10 | vout1_d1 | 2402 | 0 | 3650 | 0 | 4520 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D1_OUT | vout1_d1 |
| D7 | vout1_d10 | 2147 | 0 | 3353 | 0 | 4223 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D10_OUT | vout1_d10 |
| D8 | vout1_d11 | 2249 | 0 | 3588 | 0 | 4458 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D11_OUT | vout1_d11 |
| A5 | vout1_d12 | 2410 | 0 | 3733 | 0 | 4603 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D12_OUT | vout1_d12 |
| C6 | vout1_d13 | 2129 | 0 | 3427 | 0 | 4297 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D13_OUT | vout1_d13 |
| C8 | vout1_d14 | 2279 | 0 | 3485 | 0 | 4355 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D14_OUT | vout1_d14 |
| C7 | vout1_d15 | 2266 | 23 | 3573 | 0 | 4443 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D15_OUT | vout1_d15 |
| B7 | vout1_d16 | 1798 | 0 | 3069 | 0 | 3939 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D16_OUT | vout1_d16 |
| B8 | vout1_d17 | 2243 | 0 | 3492 | 0 | 4362 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D17_OUT | vout1_d17 |
| A7 | vout1_d18 | 2127 | 0 | 3319 | 0 | 4189 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D18_OUT | vout1_d18 |
| A8 | vout1_d19 | 2096 | 0 | 3455 | 0 | 4225 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D19_OUT | vout1_d19 |
| F10 | vout1_d2 | 2375 | 0 | 3788 | 0 | 4658 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D2_OUT | vout1_d2 |
| C9 | vout1_d20 | 2105 | 0 | 3402 | 0 | 4272 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D20_OUT | vout1_d20 |
| A9 | vout1_d21 | 2120 | 0 | 3477 | 0 | 4347 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D21_OUT | vout1_d21 |
| B9 | vout1_d22 | 2013 | 65 | 3395 | 0 | 4265 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D22_OUT | vout1_d22 |
| A10 | vout1_d23 | 1887 | 0 | 3213 | 0 | 3983 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D23_OUT | vout1_d23 |
| G11 | vout1_d3 | 2429 | 0 | 3753 | 0 | 4623 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D3_OUT | vout1_d3 |
| E9 | vout1_d4 | 2639 | 0 | 3728 | 0 | 4598 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D4_OUT | vout1_d4 |
| F9 | vout1_d5 | 2319 | 0 | 3643 | 0 | 4363 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D5_OUT | vout1_d5 |
| F8 | vout1_d6 | 2227 | 0 | 3544 | 0 | 4264 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D6_OUT | vout1_d6 |
| E7 | vout1_d7 | 2309 | 0 | 3707 | 0 | 4427 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D7_OUT | vout1_d7 |
| E8 | vout1_d8 | 1999 | 0 | 3315 | 0 | 4185 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D8_OUT | vout1_d8 |
| D9 | vout1_d9 | 2276 | 0 | 3539 | 0 | 4409 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_D9_OUT | vout1_d9 |
| B10 | vout1_de | 1933 | 0 | 3507 | 0 | 4177 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_DE_OUT | vout1_de |
| B11 | vout1_fld | 1825 | 0 | 3382 | 0 | 4052 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_FLD_OUT | vout1_fld |
| C11 | vout1_hsync | 1741 | 13 | 3408 | 0 | 4278 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_HSYNC_OUT | vout1_hsync |
| E11 | vout1_vsync | 2338 | 0 | 3718 | 0 | 4588 | 0 | CFG_VOUT1_VSYNC_OUT | vout1_vsync |
Manual IO Timings Modes must be used to ensure some IO timings for VOUT2. See Table 7-2Modes Summary for a list of IO timings requiring the use of Manual IO Timings Modes. See Table 7-21Manual Functions Mapping for DSS VOUT2 IOSET1 for a definition of the Manual modes.
Table 7-21 lists the A_DELAY and G_DELAY values needed to calculate the correct values to be set in the CFG_x registers.
Table 7-21 Manual Functions Mapping for DSS VOUT2 IOSET1
| BALL | BALL NAME | VOUT2_IOSET1_
MANUAL1 |
VOUT2_IOSET1_
MANUAL2 |
VOUT2_IOSET1_
MANUAL3 |
VOUT2_IOSET1_
MANUAL4 |
VOUT2_IOSET1_
MANUAL5 |
CFG REGISTER | MUXMODE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A_DELAY (ps) | G_DELAY (ps) | A_DELAY (ps) | G_DELAY (ps) | A_DELAY (ps) | G_DELAY (ps) | A_DELAY (ps) | G_DELAY (ps) | A_DELAY (ps) | G_DELAY (ps) | 4 | |||
| E1 | vin2a_clk0 | 2571 | 0 | 1059 | 0 | 1025 | 0 | 4110 | 0 | 4980 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_CLK0_OUT | vout2_fld |
| F2 | vin2a_d0 | 2124 | 0 | 589 | 0 | 577 | 0 | 3613 | 0 | 4483 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D0_OUT | vout2_d23 |
| F3 | vin2a_d1 | 2103 | 0 | 568 | 0 | 557 | 0 | 3442 | 0 | 4312 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D1_OUT | vout2_d22 |
| D3 | vin2a_d10 | 2091 | 0 | 557 | 0 | 545 | 0 | 3430 | 0 | 4200 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D10_OUT | vout2_d13 |
| F6 | vin2a_d11 | 2142 | 0 | 608 | 0 | 596 | 0 | 3481 | 0 | 4251 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D11_OUT | vout2_d12 |
| D5 | vin2a_d12 | 2920 | 385 | 1816 | 255 | 1783 | 276 | 3943 | 601 | 4713 | 601 | CFG_VIN2A_D12_OUT | vout2_d11 |
| C2 | vin2a_d13 | 2776 | 322 | 1872 | 192 | 1838 | 213 | 3799 | 538 | 4669 | 538 | CFG_VIN2A_D13_OUT | vout2_d10 |
| C3 | vin2a_d14 | 2904 | 0 | 1769 | 0 | 1757 | 0 | 3869 | 174 | 4739 | 174 | CFG_VIN2A_D14_OUT | vout2_d9 |
| C4 | vin2a_d15 | 2670 | 257 | 1665 | 127 | 1632 | 148 | 3792 | 473 | 4662 | 473 | CFG_VIN2A_D15_OUT | vout2_d8 |
| B2 | vin2a_d16 | 2814 | 155 | 1908 | 31 | 1878 | 43 | 3837 | 371 | 4707 | 371 | CFG_VIN2A_D16_OUT | vout2_d7 |
| D6 | vin2a_d17 | 3002 | 199 | 1897 | 69 | 1865 | 89 | 4024 | 415 | 4894 | 415 | CFG_VIN2A_D17_OUT | vout2_d6 |
| C5 | vin2a_d18 | 1893 | 0 | 358 | 0 | 347 | 0 | 3432 | 0 | 4302 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D18_OUT | vout2_d5 |
| A3 | vin2a_d19 | 1698 | 0 | 163 | 0 | 151 | 0 | 3237 | 0 | 4007 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D19_OUT | vout2_d4 |
| D1 | vin2a_d2 | 2193 | 0 | 658 | 0 | 646 | 0 | 3531 | 0 | 4401 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D2_OUT | vout2_d21 |
| B3 | vin2a_d20 | 1736 | 0 | 202 | 0 | 190 | 0 | 3075 | 0 | 3945 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D20_OUT | vout2_d3 |
| B4 | vin2a_d21 | 1636 | 0 | 101 | 0 | 89 | 0 | 3074 | 0 | 3944 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D21_OUT | vout2_d2 |
| B5 | vin2a_d22 | 1628 | 0 | 93 | 0 | 81 | 0 | 3266 | 0 | 4036 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D22_OUT | vout2_d1 |
| A4 | vin2a_d23 | 1538 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2968 | 0 | 3838 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D23_OUT | vout2_d0 |
| E2 | vin2a_d3 | 1997 | 0 | 462 | 0 | 450 | 0 | 3335 | 0 | 4205 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D3_OUT | vout2_d20 |
| D2 | vin2a_d4 | 2528 | 0 | 993 | 0 | 982 | 0 | 3867 | 0 | 4537 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D4_OUT | vout2_d19 |
| F4 | vin2a_d5 | 2038 | 0 | 503 | 0 | 492 | 0 | 3577 | 0 | 4347 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D5_OUT | vout2_d18 |
| C1 | vin2a_d6 | 1746 | 0 | 211 | 0 | 200 | 0 | 3285 | 0 | 4055 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D6_OUT | vout2_d17 |
| E4 | vin2a_d7 | 2213 | 0 | 678 | 0 | 666 | 0 | 3552 | 0 | 4272 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D7_OUT | vout2_d16 |
| F5 | vin2a_d8 | 2268 | 0 | 733 | 0 | 721 | 0 | 3607 | 0 | 4277 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D8_OUT | vout2_d15 |
| E6 | vin2a_d9 | 2170 | 0 | 635 | 0 | 623 | 0 | 3509 | 0 | 4379 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_D9_OUT | vout2_d14 |
| G2 | vin2a_de0 | 2102 | 0 | 568 | 0 | 556 | 0 | 3841 | 0 | 4611 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_DE0_OUT | vout2_de |
| H7 | vin2a_fld0 | 0 | 983 | 1398 | 1185 | 1385 | 1202 | 0 | 994 | 0 | 994 | CFG_VIN2A_FLD0_OUT | vout2_clk |
| G1 | vin2a_hsync0 | 2482 | 0 | 974 | 0 | 936 | 0 | 4021 | 0 | 4891 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_HSYNC0_OUT | vout2_hsync |
| G6 | vin2a_vsync0 | 2296 | 0 | 784 | 0 | 750 | 0 | 3935 | 0 | 4805 | 0 | CFG_VIN2A_VSYNC0_OUT | vout2_vsync |
Manual IO Timings Modes must be used to ensure some IO timings for VOUT2. See Table 7-2Modes Summary for a list of IO timings requiring the use of Manual IO Timings Modes. See Table 7-22Manual Functions Mapping for DSS VOUT2 IOSET2 for a definition of the Manual modes.
Table 7-22 lists the A_DELAY and G_DELAY values needed to calculate the correct values to be set in the CFG_x registers.
Table 7-22 Manual Functions Mapping for DSS VOUT2 IOSET2
| BALL | BALL NAME | VOUT2_IOSET2_
MANUAL1 |
VOUT2_IOSET2_
MANUAL2 |
VOUT2_IOSET2_
MANUAL3 |
VOUT2_IOSET2_
MANUAL4 |
VOUT2_IOSET2_
MANUAL5 |
CFG REGISTER | MUXMODE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A_DELAY (ps) | G_DELAY (ps) | A_DELAY (ps) | G_DELAY (ps) | A_DELAY (ps) | G_DELAY (ps) | A_DELAY (ps) | G_DELAY (ps) | A_DELAY (ps) | G_DELAY (ps) | 6 | |||
| E21 | gpio6_14 | 1983 | 0 | 79 | 0 | 68 | 0 | 3513 | 0 | 4383 | 0 | CFG_GPIO6_14_OUT | vout2_hsync |
| F20 | gpio6_15 | 2159 | 0 | 158 | 0 | 148 | 0 | 3689 | 0 | 4559 | 0 | CFG_GPIO6_15_OUT | vout2_vsync |
| F21 | gpio6_16 | 1864 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3394 | 0 | 4264 | 0 | CFG_GPIO6_16_OUT | vout2_fld |
| B14 | mcasp1_aclkr | 2614 | 0 | 1255 | 0 | 1270 | 0 | 4353 | 0 | 5223 | 0 | CFG_MCASP1_ACLKR_OUT | vout2_d0 |
| G13 | mcasp1_axr2 | 2705 | 0 | 1350 | 0 | 1360 | 0 | 4444 | 0 | 5314 | 0 | CFG_MCASP1_AXR2_OUT | vout2_d2 |
| J11 | mcasp1_axr3 | 2865 | 0 | 1210 | 0 | 1219 | 0 | 4504 | 0 | 5374 | 0 | CFG_MCASP1_AXR3_OUT | vout2_d3 |
| E12 | mcasp1_axr4 | 2759 | 0 | 1404 | 0 | 1413 | 0 | 4498 | 0 | 5368 | 0 | CFG_MCASP1_AXR4_OUT | vout2_d4 |
| F13 | mcasp1_axr5 | 2980 | 0 | 1325 | 0 | 1335 | 0 | 4419 | 0 | 5289 | 0 | CFG_MCASP1_AXR5_OUT | vout2_d5 |
| C12 | mcasp1_axr6 | 2634 | 0 | 1275 | 0 | 1289 | 0 | 4373 | 0 | 5243 | 0 | CFG_MCASP1_AXR6_OUT | vout2_d6 |
| D12 | mcasp1_axr7 | 2658 | 0 | 1302 | 0 | 1311 | 0 | 4396 | 0 | 5266 | 0 | CFG_MCASP1_AXR7_OUT | vout2_d7 |
| J14 | mcasp1_fsr | 2818 | 0 | 1163 | 0 | 1172 | 0 | 4456 | 0 | 5326 | 0 | CFG_MCASP1_FSR_OUT | vout2_d1 |
| E15 | mcasp2_aclkr | 2728 | 0 | 1373 | 0 | 1382 | 0 | 4367 | 0 | 5237 | 0 | CFG_MCASP2_ACLKR_OUT | vout2_d8 |
| B15 | mcasp2_axr0 | 2513 | 0 | 319 | 534 | 308 | 560 | 4151 | 0 | 5021 | 0 | CFG_MCASP2_AXR0_OUT | vout2_d10 |
| A15 | mcasp2_axr1 | 2712 | 0 | 1357 | 0 | 1366 | 0 | 4351 | 0 | 5221 | 0 | CFG_MCASP2_AXR1_OUT | vout2_d11 |
| D15 | mcasp2_axr4 | 2529 | 0 | 1169 | 0 | 1184 | 0 | 4267 | 0 | 5137 | 0 | CFG_MCASP2_AXR4_OUT | vout2_d12 |
| B16 | mcasp2_axr5 | 2376 | 0 | 543 | 478 | 1029 | 0 | 4114 | 0 | 4984 | 0 | CFG_MCASP2_AXR5_OUT | vout2_d13 |
| B17 | mcasp2_axr6 | 2620 | 0 | 1265 | 0 | 1274 | 0 | 4359 | 0 | 5229 | 0 | CFG_MCASP2_AXR6_OUT | vout2_d14 |
| A17 | mcasp2_axr7 | 2492 | 0 | 354 | 483 | 845 | 0 | 4130 | 0 | 5000 | 0 | CFG_MCASP2_AXR7_OUT | vout2_d15 |
| A20 | mcasp2_fsr | 2358 | 0 | 12 | 487 | 513 | 0 | 3797 | 0 | 4667 | 0 | CFG_MCASP2_FSR_OUT | vout2_d9 |
| C18 | mcasp4_aclkx | 2524 | 0 | 1165 | 0 | 1179 | 0 | 3863 | 0 | 4733 | 0 | CFG_MCASP4_ACLKX_OUT | vout2_d16 |
| G16 | mcasp4_axr0 | 2578 | 0 | 797 | 0 | 806 | 0 | 4208 | 0 | 5078 | 0 | CFG_MCASP4_AXR0_OUT | vout2_d18 |
| D17 | mcasp4_axr1 | 2253 | 0 | 750 | 0 | 759 | 0 | 3983 | 0 | 4853 | 0 | CFG_MCASP4_AXR1_OUT | vout2_d19 |
| A21 | mcasp4_fsx | 2478 | 0 | 823 | 0 | 832 | 0 | 4117 | 0 | 4987 | 0 | CFG_MCASP4_FSX_OUT | vout2_d17 |
| AA3 | mcasp5_aclkx | 4672 | 1737 | 3256 | 1798 | 3226 | 1837 | 5900 | 1949 | 6770 | 1949 | CFG_MCASP5_ACLKX_OUT | vout2_d20 |
| AB3 | mcasp5_axr0 | 4642 | 1286 | 3226 | 1347 | 3196 | 1386 | 5870 | 1497 | 6740 | 1497 | CFG_MCASP5_AXR0_OUT | vout2_d22 |
| AA4 | mcasp5_axr1 | 4625 | 725 | 3209 | 786 | 3179 | 825 | 6153 | 935 | 7023 | 935 | CFG_MCASP5_AXR1_OUT | vout2_d23 |
| AB9 | mcasp5_fsx | 4565 | 1062 | 3149 | 1123 | 3119 | 1162 | 6093 | 1273 | 6963 | 1273 | CFG_MCASP5_FSX_OUT | vout2_d21 |
| B26 | xref_clk2 | 0 | 49 | 1359 | 466 | 1341 | 512 | 0 | 60 | 0 | 60 | CFG_XREF_CLK2_OUT | vout2_clk |
| C23 | xref_clk3 | 1947 | 0 | 36 | 0 | 45 | 0 | 3378 | 0 | 4248 | 0 | CFG_XREF_CLK3_OUT | vout2_de |
Manual IO Timings Modes must be used to ensure some IO timings for VOUT3. See Table 7-2Modes Summary for a list of IO timings requiring the use of Manual IO Timings Modes. See Table 7-23Manual Functions Mapping for DSS VOUT3 for a definition of the Manual modes.
Table 7-23 lists the A_DELAY and G_DELAY values needed to calculate the correct values to be set in the CFG_x registers.
Table 7-23 Manual Functions Mapping for DSS VOUT3
| BALL | BALL NAME | VOUT3_MANUAL1 | VOUT3_MANUAL4 | VOUT3_MANUAL5 | CFG REGISTER | MUXMODE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A_DELAY (ps) | G_DELAY (ps) | A_DELAY (ps) | G_DELAY (ps) | A_DELAY (ps) | G_DELAY (ps) | 3 | |||
| R6 | gpmc_a0 | 2395 | 0 | 3909 | 0 | 4779 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_A0_OUT | vout3_d16 |
| T9 | gpmc_a1 | 2412 | 0 | 3957 | 0 | 4827 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_A1_OUT | vout3_d17 |
| N9 | gpmc_a10 | 2473 | 0 | 3980 | 0 | 4850 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_A10_OUT | vout3_de |
| P9 | gpmc_a11 | 2906 | 0 | 4253 | 0 | 5123 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_A11_OUT | vout3_fld |
| T6 | gpmc_a2 | 2360 | 0 | 3873 | 0 | 4743 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_A2_OUT | vout3_d18 |
| T7 | gpmc_a3 | 2391 | 0 | 4112 | 0 | 4982 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_A3_OUT | vout3_d19 |
| P6 | gpmc_a4 | 2626 | 0 | 4336 | 0 | 5206 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_A4_OUT | vout3_d20 |
| R9 | gpmc_a5 | 2338 | 0 | 3840 | 0 | 4710 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_A5_OUT | vout3_d21 |
| R5 | gpmc_a6 | 2374 | 0 | 3913 | 0 | 4783 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_A6_OUT | vout3_d22 |
| P5 | gpmc_a7 | 2432 | 0 | 3947 | 0 | 4817 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_A7_OUT | vout3_d23 |
| N7 | gpmc_a8 | 3155 | 0 | 4309 | 105 | 5179 | 105 | CFG_GPMC_A8_OUT | vout3_hsync |
| R4 | gpmc_a9 | 2309 | 0 | 3842 | 0 | 4712 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_A9_OUT | vout3_vsync |
| M6 | gpmc_ad0 | 2360 | 0 | 3652 | 0 | 4522 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_AD0_OUT | vout3_d0 |
| M2 | gpmc_ad1 | 2420 | 0 | 3762 | 0 | 4632 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_AD1_OUT | vout3_d1 |
| J1 | gpmc_ad10 | 2235 | 0 | 3456 | 0 | 4326 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_AD10_OUT | vout3_d10 |
| J2 | gpmc_ad11 | 2253 | 0 | 3584 | 0 | 4454 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_AD11_OUT | vout3_d11 |
| H1 | gpmc_ad12 | 1949 | 427 | 3589 | 0 | 4459 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_AD12_OUT | vout3_d12 |
| J3 | gpmc_ad13 | 2318 | 0 | 3547 | 0 | 4417 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_AD13_OUT | vout3_d13 |
| H2 | gpmc_ad14 | 2123 | 0 | 3302 | 0 | 4172 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_AD14_OUT | vout3_d14 |
| H3 | gpmc_ad15 | 2195 | 29 | 3532 | 0 | 4402 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_AD15_OUT | vout3_d15 |
| L5 | gpmc_ad2 | 2617 | 0 | 3859 | 0 | 4729 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_AD2_OUT | vout3_d2 |
| M1 | gpmc_ad3 | 2350 | 0 | 3590 | 0 | 4460 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_AD3_OUT | vout3_d3 |
| L6 | gpmc_ad4 | 2324 | 0 | 3534 | 0 | 4404 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_AD4_OUT | vout3_d4 |
| L4 | gpmc_ad5 | 2371 | 0 | 3609 | 0 | 4479 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_AD5_OUT | vout3_d5 |
| L3 | gpmc_ad6 | 2231 | 0 | 3416 | 0 | 4286 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_AD6_OUT | vout3_d6 |
| L2 | gpmc_ad7 | 2440 | 0 | 3661 | 0 | 4531 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_AD7_OUT | vout3_d7 |
| L1 | gpmc_ad8 | 2479 | 0 | 3714 | 0 | 4584 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_AD8_OUT | vout3_d8 |
| K2 | gpmc_ad9 | 2355 | 0 | 3593 | 0 | 4463 | 0 | CFG_GPMC_AD9_OUT | vout3_d9 |
| P1 | gpmc_cs3 | 0 | 641 | 0 | 905 | 0 | 905 | CFG_GPMC_CS3_OUT | vout3_clk |