SBOS877A April 2018 – September 2018 THS6301
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RSA|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RSA|16
Orderable Information
7.3 Feature Description
The THS6301 is a line driver that has a high current drive and a differential input and output. Figure 41 shows an example circuit of the THS6301 configured to drive the G.Fast 212-MHz DSL profile. The bias control pins B1 and B2 are set to 3.3 V and ground, respectively, to put the device in the G.Fast 212-MHz bias mode. This bias mode optimizes the internal power consumption of the device to meet performance specifications of the G.Fast 212-MHz profile and can be changed to meet several different DSL profiles and other modes listed in Table 1. The IADJ pin is biased with a 75-kΩ (RIADJ) resistor that adjusts the device quiescent current to a nominal state. RIADJ can be increased to lower the quiescent current or decreased to raise the quiescent current of the device for fine-tuning. CIADJ provides decoupling for the IADJ pin and is typically 100 pF.
The THS6301 has a 10-kΩ, internally-set differential input impedance and low output impedance. In Figure 41 the input impedance is matched to 100 Ω by using a 100-Ω resistor connected differentially across the inputs. This value can easily be changed by using a different resistor to create the desired impedance at the input. Remember that the impedance in the device is actually the parallel combination of 10 kΩ and the external input resistor. For low impedances, this effect is minimal, but must be considered if the matched input impedance is increased. The output impedance of the THS6301 in Figure 41 is set by the two RSERIES resistors to match 100 Ω. The internal output resistance is very low (< 2 Ω per output), so the output impedance is primarily set by the RSERIES resistors. These resistors can be adjusted to match various output impedance values.
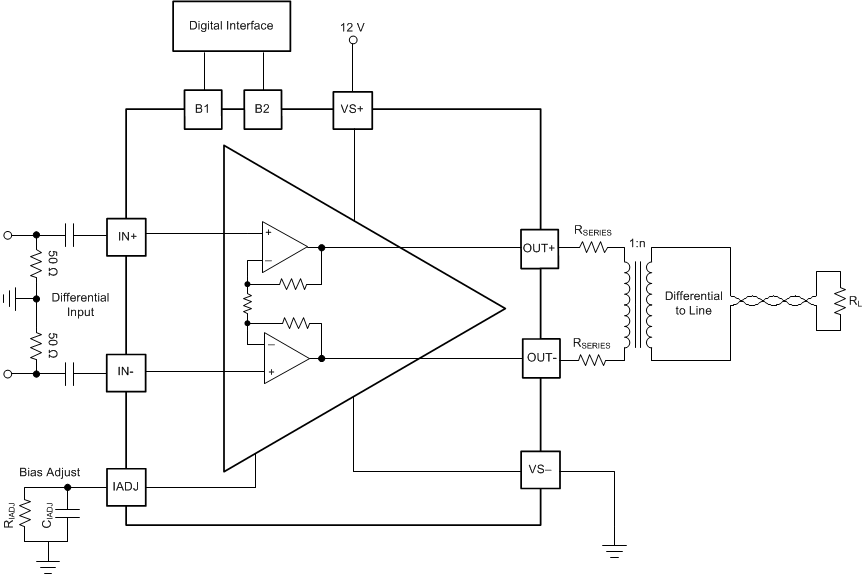 Figure 41. G.Fast, 212-MHz Driving Mode Example Circuit
Figure 41. G.Fast, 212-MHz Driving Mode Example Circuit