SLLSF68 September 2019 THVD1505
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.1.5 Stub Length
When connecting a node to the bus, the distance between the transceiver inputs and the cable trunk, known as the stub, should be as short as possible. The reason for the short distance is because a stub presents a non-terminated piece of bus line which can introduce reflections if the distance is too long. As a general guideline, the electrical length or round-trip delay of a stub should be less than one-tenth of the rise time of the driver, thus leading to a maximum physical stub length of as shown in Equation 2.
Equation 2. LS ≤ 0.1 × tr × v × c
where
- tr is the 10/90 rise time of the driver
- c is the speed of light (3 × 108 m/s or 9.8 × 108 ft/s)
- v is the signal velocity of the cable (v = 78%) or trace (v = 45%) as a factor of c
Based on Equation 2, with a minimum rise time of 400 ns, Equation 3 shows the maximum cable-stub length of the THVD1505.
Equation 3. LS ≤ 0.1 × 400 × 10-9 × 3 108 × 0.78 = 9.4 m (or 30.6 ft)
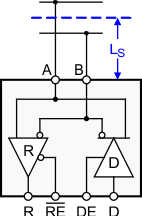 Figure 24. Stub Length
Figure 24. Stub Length