SLASEE9B September 2017 – December 2017 TPA3221
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Audio Characteristics (BTL)
- 7.7 Audio Characteristics (PBTL)
- 7.8 Typical Characteristics, BTL Configuration, AD-mode
- 7.9 Typical Characteristics, PBTL Configuration, AD-mode
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4
Device Functional Modes
- 9.4.1 Powering Up
- 9.4.2 Powering Down
- 9.4.3 Device Reset
- 9.4.4 Device Soft Mute
- 9.4.5
Device Protection System
- 9.4.5.1 Overload and Short Circuit Current Protection
- 9.4.5.2 Signal Clipping and Pulse Injector
- 9.4.5.3 DC Speaker Protection
- 9.4.5.4 Pin-to-Pin Short Circuit Protection (PPSC)
- 9.4.5.5 Overtemperature Protection OTW and OTE
- 9.4.5.6 Undervoltage Protection (UVP), Overvoltage Protection (OVP) and Power-on Reset (POR)
- 9.4.5.7 Fault Handling
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDV|44
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DDV|44
Orderable Information
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted) (1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage | PVDD to GND(2) | –0.3 | 37 | V |
| BST_X to GVDD(2) | –0.3 | 37 | V | |
| BST1_M, BST1_P, BST2_M, BST2_P to GND(2) | –0.3 | 47.8 | V | |
| VDD to GND | –0.3 | 43 | V | |
| GVDD to GND(2) | –0.3 | 5.5 | V | |
| AVDD to GND | –0.3 | 5.5 | V | |
| Interface pins | OUT1_M, OUT1_P, OUT2_M, OUT2_P to GND(2) | –0.3 | 43 | V |
| IN1_M, IN1_P, IN2_M, IN2_P to GND | –0.3 | 5.5 | V | |
| HEAD, FREQ_ADJ, GAIN/SLV, CMUTE, RESET, OSCP, OSCM to GND | –0.3 | 5.5 | V | |
| FAULT, OTW_CLIP to GND | –0.3 | 5.5 | V | |
| Continuous sink current, FAULT, OTW_CLIP to GND | 9 | mA | ||
| TJ | Operating junction temperature range | –40 | 150 | °C |
| Tstg | Storage temperature range | –40 | 150 | °C |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) These voltages represents the DC voltage + peak AC waveform measured at the terminal of the device in all conditions.
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VESD | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001, all pins (1) | ±1000 | V |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101, all pins(2) | ±250 | V | ||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDD | Power-stage supply | DC supply voltage | 7 | 30 | 32 | V |
| VDD(1) | Supply voltage for internal LDO regulator to supply GVDD and AVDD | DC supply voltage | 7 | 32 | V | |
| External supply for VDD, GVDD and AVDD. Internal LDO bypassed | DC supply voltage | 4.5 | 5 | 5.5 | V | |
| AVDD | Supply voltage for analog circuits | DC supply voltage | 4.5 | 5 | 5.5 | V |
| GVDD | Supply voltage for gate-drive circuitry | DC supply voltage | 4.5 | 5 | 5.5 | V |
| LOUT(BTL) | Output filter inductance | Minimum output inductance at IOC | 5 | 10 | μH | |
| LOUT(PBTL) | Output filter inductance, PBTL before the LC filter | Minimum output inductance at IOC | 5 | 10 | ||
| Output filter inductance, PBTL after the LC filter | Minimum output inductance at half IOC , each inductor | 5 | 10 | |||
| FPWM | PWM frame rate selectable for AM interference avoidance; 1% Resistor tolerance | Nominal | 575 | 600 | 625 | kHz |
| AM1 | 510 | 533 | 555 | |||
| AM2 | 460 | 480 | 500 | |||
| R(FREQ_ADJ) | PWM frame rate programming resistor | Nominal; Master mode | 49.5 | 50 | 50.5 | kΩ |
| AM1; Master mode | 29.7 | 30 | 30.3 | |||
| AM2; Master mode | 9.9 | 10 | 10.1 | |||
| CPVDD | PVDD close decoupling capacitors | 1.0 | μF | |||
| V(FREQ_ADJ) | Voltage on FREQ_ADJ pin for slave mode operation | Slave Mode (Connect to AVDD) | 5 | V | ||
(1) VDD must be connected to a supply of 5V in LDO bypass mode; OR 7V to 30V with LDO active. VDD can be connected directly to PVDD in LDO bypass mode, but must not exceed PVDD voltage.
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TPA3221 | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DDV 44-PINS HTSSOP | ||||
| JEDEC STANDARD 4 LAYER PCB | FIXED 85°C HEATSINK TEMPERATURE(2) | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 44.8 | 5.5 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 1.1 | 2.0 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 14.9 | n/a | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.6 | n/a | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 14.7 | n/a | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | n/a | n/a | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report.
(2) Thermal data are obtained with 85°C heat sink temperature using thermal compound with 0.7W/mK thermal conductivity and 2mil thickness. In this model heat sink temperature is considered to be the ambient temperature and only path for dissipation is to the heatsink.
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
PVDD_X = 30 V, VDD = 5 V, GVDD = 5 V, TC (Case temperature) = 75 °C, fS = 600 kHz, unless otherwise specified.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
INTERNAL VOLTAGE REGULATOR AND CURRENT CONSUMPTION |
||||||
| AVDD | Voltage regulator. Only used as reference node when supplied by internal LDO. Voltage regulator bypassed for VDD = 5 V. | VDD = 30 V | 5 | V | ||
| IVDD | VDD supply current. LDO mode (VDD > 7 V) | Operating, no audio signal | 25 | mA | ||
| Reset mode | 118 | µA | ||||
| VDD supply current. LDO bypass mode (VDD = 5 V) | Operating, no audio signal | 150 | ||||
| Reset mode | 50 | |||||
| IAVDD | Gate-supply current. LDO bypass mode (VDD = 5 V) | Operating, no audio signal | 10 | mA | ||
| Reset mode | 1 | |||||
| IGVDD | Gate-supply current. LDO bypass mode (VDD = 5 V), AD-mode modulation | 50% duty cycle | 16 | |||
| Reset mode | 50 | µA | ||||
| Gate-supply current. LDO bypass mode (VDD = 5 V), HEAD-mode modulation | HEAD-mode modulation | 16 | mA | |||
| Reset mode | 50 | µA | ||||
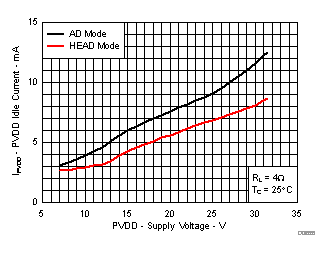
| IPVDD | Total PVDD idle current, AD-mode modulation, BTL | 50% duty cycle with recommended output filter | 15 | mA | ||
| 50% duty cycle with recommended output filter, TC = 25 ºC | 13 | |||||
| Reset mode, No switching | 1 | |||||
| Total PVDD idle current, HEAD-mode modulation, BTL | HEAD-mode modulation with recommended output filter | 10 | ||||
| HEAD-mode with recommended output filter, TC = 25 ºC | 9 | |||||
| Reset mode, No switching | 1 | |||||
| ANALOG INPUTS | ||||||
| VIN | Maximum input voltage swing | ±2.8 | V | |||
| IIN | Maximum input current | -1 | 1 | mA | ||
| G | Inverting voltage Gain, VOUT/VIN(Master Mode) | R1 = 5.6 kΩ, R2 = OPEN | 18 | dB | ||
| R1 = 20 kΩ, R2 = 100 kΩ | 24 | |||||
| R1 = 39 kΩ, R2 = 100 kΩ | 30 | |||||
| R1 = 47 kΩ, R2 = 75 kΩ | 34 | |||||
| Inverting voltage Gain, VOUT/VIN(Slave Mode) | R1 = 51 kΩ, R2 = 51 kΩ | 18 | ||||
| R1 = 75 kΩ, R2 = 47 kΩ | 24 | |||||
| R1 = 100 kΩ, R2 = 39 kΩ | 30 | |||||
| R1 = 100 kΩ, R2 = 16 kΩ | 34 | |||||
| RIN | Input resistance | G = 18 dB | 48 | kΩ | ||
| G = 24 dB | 24 | |||||
| G = 30 dB | 12 | |||||
| G = 34 dB | 7.7 | |||||
| OSCILLATOR | ||||||
| fOSC(IO) (1) | Nominal, Master Mode | FPWM × 6 | 3.45 | 3.6 | 3.75 | MHz |
| AM1, Master Mode | 3.06 | 3.198 | 3.33 | |||
| AM2, Master Mode | 2.76 | 2.88 | 3 | |||
| VIH | High level input voltage | 1.88 | V | |||
| VIL | Low level input voltage | 1.65 | V | |||
| EXTERNAL OSCILLATOR (Slave Mode) | ||||||
| fOSC(IO) | CLK input on OSCM/OSCP (Slave Mode) | 2.3 | 3.78 | MHz | ||
|
OUTPUT-STAGE MOSFETs |
||||||
| RDS(on) | Drain-to-source resistance, low side (LS) | TJ = 25 °C, Excludes metallization resistance, GVDD = 5 V |
70 | mΩ | ||
| Drain-to-source resistance, high side (HS) | 70 | mΩ | ||||
| I/O PROTECTION | ||||||
| Vuvp,AVDD | Undervoltage protection limit, AVDD | 4 | V | |||
| Vuvp,AVDD,hyst (2) | Undervoltage protection hysteresis, AVDD | 0.1 | V | |||
| Vuvp,PVDD | Undervoltage protection limit, PVDD_x | 6.4 | V | |||
| Vuvp,PVDD,hyst (2) | Undervoltage protection hysteresis, PVDD_x | 0.45 | V | |||
| Vovp,PVDD | Overvoltage protection limit, PVDD_x | 34 | V | |||
| Vovp,PVDD,hyst (2) | Overvoltage protection hysteresis, PVDD_x | 0.45 | V | |||
| OTW | Overtemperature warning, OTW_CLIP (2) | 115 | 125 | 135 | °C | |
| OTWhyst (2) | Temperature drop needed below OTW temperature for OTW_CLIP to be inactive after OTW event. | 20 | °C | |||
| OTE(2) | Overtemperature error | 145 | 155 | 165 | °C | |
| OTEhyst (2) | A reset needs to occur for FAULT to be released following an OTE event | 20 | °C | |||
| OTE-OTW(differential) (2) | OTE-OTW differential | 25 | °C | |||
| OLPC | Overload protection counter | fPWM = 600 kHz (1024 PWM cycles) | 1.7 | ms | ||
| IOC, BTL | Overcurrent limit protection, speaker output current | Nominal peak current in 1Ω load | 10 | A | ||
| IOC, PBTL | 20 | A | ||||
| IDCspkr, BTL | DC Speaker Protection Current Threshold | BTL current imbalance threshold | 1.8 | A | ||
| IDCspkr, PBTL | PBTL current imbalance threshold | 3.6 | A | |||
| IOCT | Overcurrent response time | Time from switching transition to flip-state induced by overcurrent. | 150 | ns | ||
| IPD | Output pulldown current of each half | Connected when RESET is active to provide bootstrap charge. Not used in SE mode. | 3 | mA | ||
| STATIC DIGITAL SPECIFICATIONS | ||||||
| VIH | High level input voltage | HEAD, OSCM, OSCP,CMUTE, RESET | 1.9 | V | ||
| VIL | Low level input voltage | 0.8 | V | |||
| Ilkg | Input leakage current | 100 | μA | |||
| OTW/SHUTDOWN (FAULT) | ||||||
| RINT_PU | Internal pullup resistance, OTW_CLIP to AVDD, FAULT to AVDD | 20 | 26 | 32 | kΩ | |
| VOH | High level output voltage | Internal pullup resistor | 3 | 3.3 | 3.6 | V |
| VOL | Low level output voltage | IO = 4 mA | 200 | 500 | mV | |
| Device fanout | OTW_CLIP, FAULT | No external pullup | 30 | devices | ||
(1) Nominal, AM1 and AM2 use same internal oscillator with fixed ratio 4 : 4.5 : 5
(2) Specified by design.
7.6 Audio Characteristics (BTL)
PCB and system configuration are in accordance with recommended guidelines. Audio frequency = 1 kHz, PVDD_X = 30 V, VDD = 5 V, GVDD = 5 V, RL = 4 Ω, fS = 600 kHz, TC = 75°C, Output Filter: LDEM = 10 μH, CDEM = 1 µF, AD-Modulation, AES17 + AUX-0025 measurement filters, unless otherwise noted.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
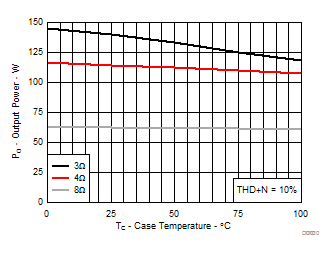
| PO | Power output per channel | RL = 3 Ω, 10% THD+N | 112 | W | ||
| RL = 4 Ω, 10% THD+N | 105 | |||||
| RL = 3 Ω, 1% THD+N | 100 | |||||
| RL = 4 Ω, 1% THD+N | 88 | |||||
| THD+N | Total harmonic distortion + noise | 1 W | 0.02 | % | ||
| Vn | Output integrated noise | A-weighted, AES17 filter, Input Capacitor Grounded, Gain = 18 dB | 75 | μV | ||
| |VOS| | Output offset voltage | Inputs AC coupled to GND | 20 | 60 | mV | |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio(1) | A-weighted, Gain = 18 dB | 108 | dB | ||
| DNR | Dynamic range | A-weighted, Gain = 18 dB | 109 | dB | ||
| Pidle | Power dissipation due to idle losses (IPVDD_X) | PO = 0, all outputs switching, AD-modulation, TC = 25°C(2) | 0.37 | W | ||
| PO = 0, all outputs switching, HEAD-modulation, TC = 25°C(2) | 0.25 | W | ||||
(1) SNR is calculated relative to 1% THD+N output level.
(2) Actual system idle losses also are affected by core losses of output inductors.
7.7 Audio Characteristics (PBTL)
PCB and system configuration are in accordance with recommended guidelines. Audio frequency = 1 kHz, PVDD_X = 30 V, VDD = 5 V, GVDD = 5 V, RL = 2 Ω, fS = 600 kHz, TC = 75°C, Output Filter: LDEM = 10 μH, CDEM = 1 µF, Pre-Filter PBTL, AD-Modulation, AES17 + AUX-0025 measurement filters, unless otherwise noted.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PO | Power output per channel | RL = 2 Ω, 10% THD+N | 208 | W | ||
| RL = 3 Ω, 10% THD+N | 155 | |||||
| RL = 4 Ω, 10% THD+N | 120 | |||||
| RL = 2 Ω, 1% THD+N | 170 | |||||
| RL = 3 Ω, 1% THD+N | 125 | |||||
| RL = 4 Ω, 1% THD+N | 98 | |||||
| THD+N | Total harmonic distortion + noise | 1 W | 0.02 | % | ||
| Vn | Output integrated noise | A-weighted, AES17 filter, Input Capacitor Grounded, Gain = 18 dB | 75 | μV | ||
| |VOS| | Output offset voltage | Inputs AC coupled to GND | 20 | 60 | mV | |
| SNR | Signal to noise ratio(1) | A-weighted, Gain = 18 dB | 108 | dB | ||
| DNR | Dynamic range | A-weighted, Gain = 18 dB | 110 | dB | ||
| Pidle | Power dissipation due to idle losses (IPVDD_X) | PO = 0, all outputs switching, AD-modulation, TC = 25°C(2) | 0.20 | W | ||
| PO = 0, all outputs switching, HEAD-modulation, TC = 25°C(2) | 0.17 | W | ||||
(1) SNR is calculated relative to 1% THD+N output level.
(2) Actual system idle losses are affected by core losses of output inductors.
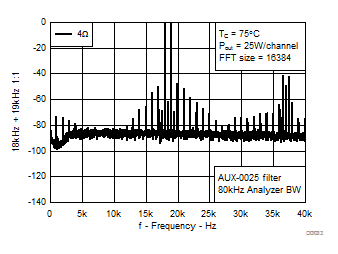
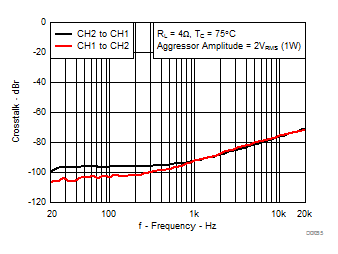
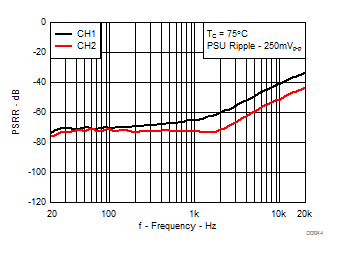
7.8 Typical Characteristics, BTL Configuration, AD-mode
All Measurements taken at audio frequency = 1 kHz, PVDD_X = 30 V, VDD = 5 V, GVDD = 5 V, RL = 4 Ω, fS = 600 kHz, 18 dB, TC = 75°C, Output Filter: LDEM = 10 μH, CDEM = 1 µF, AD-Modulation, AES17 + AUX-0025 measurement filters, unless otherwise noted.
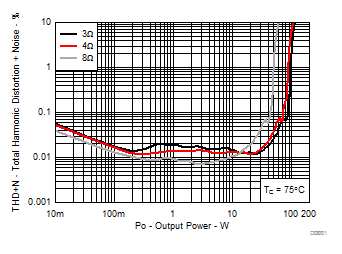
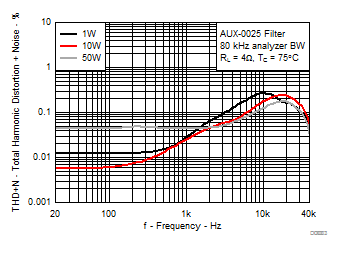
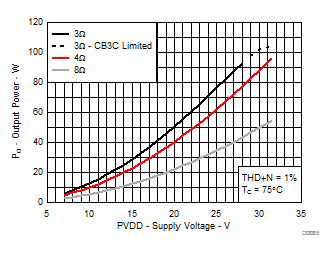
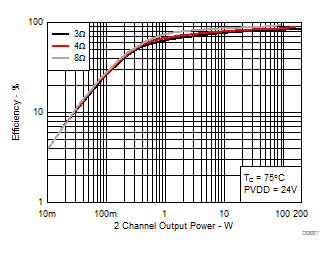
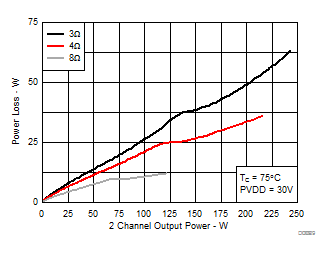
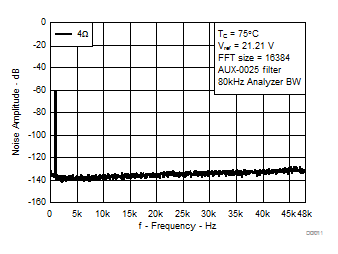
| 18 kHz + 19 kHz | Ratio 1 : 1 |
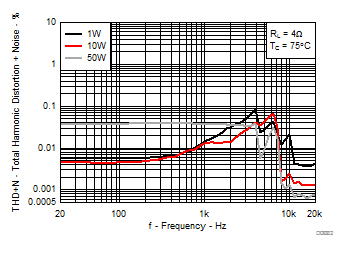
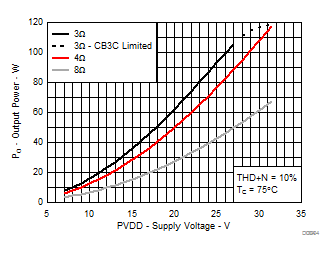
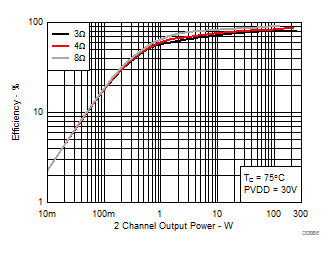
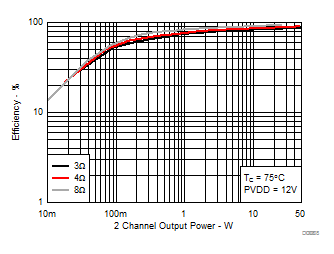
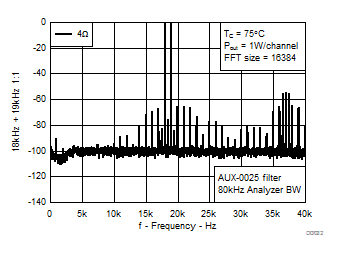
| 18 kHz + 19 kHz | Ratio 1 : 1 |
7.9 Typical Characteristics, PBTL Configuration, AD-mode
All Measurements taken at audio frequency = 1 kHz, PVDD_X = 30 V, VDD = 5 V, GVDD = 5 V, RL = 2 Ω, fS = 600 kHz, 18 dB, TC = 75°C, Output Filter: LDEM = 10 μH, CDEM = 1 µF, Pre-Filter PBTL, AD Modulation, AES17 + AUX-0025 measurement filters, unless otherwise noted.
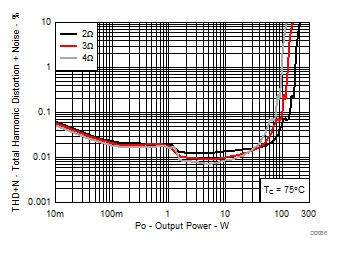
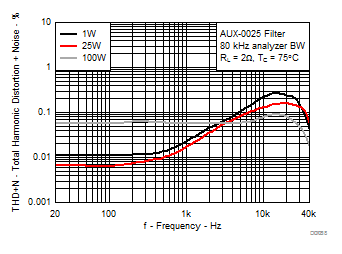
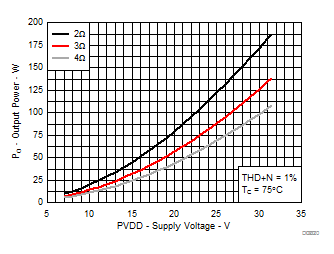
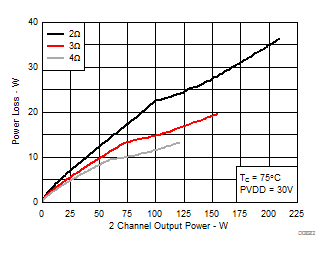
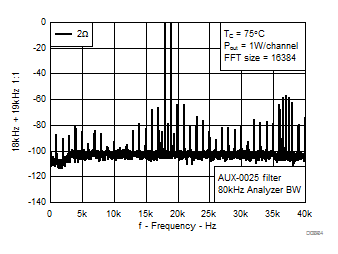
| 18 kHz + 19 kHz | Ratio 1 : 1 |
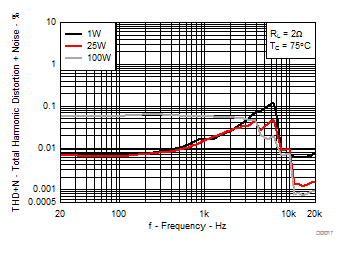
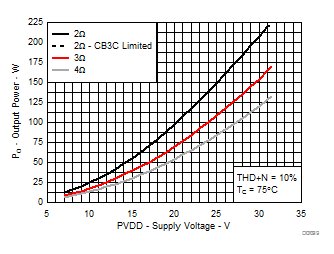
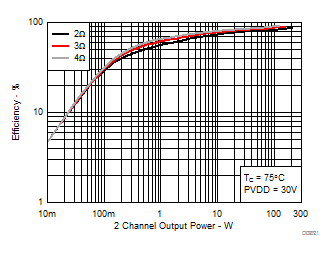
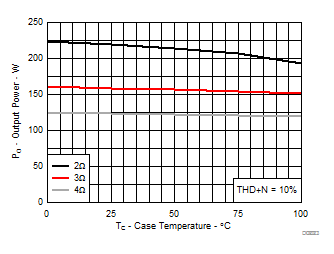
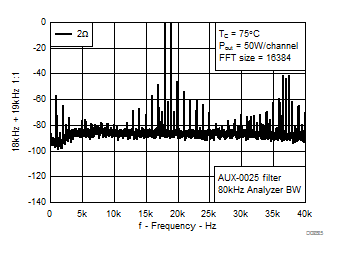
| 18 kHz + 19 kHz | Ratio 1 : 1 |