SLVSDG2G July 2016 – December 2019 TPS2660
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 9.3.2 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 9.3.3 Reverse Input Supply Protection
- 9.3.4 Hot Plug-In and In-Rush Current Control
- 9.3.5 Overload and Short Circuit Protection
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Application
- 10.2.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.3 Application Curves
- 10.3 System Examples
- 10.4 Do's and Don'ts
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHF|24
- PWP|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Orderable Information
9.3.5.1.1 Active Current Limiting
When the active current limiting mode is selected, during overload events, the device continuously regulates the load current to the overcurrent limit I(OL) programmed by the R(ILIM) resistor as shown in Equation 3.
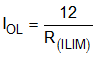
where
- I(OL) is the overload current limit in Ampere
- R(ILIM) is the current limit resistor in kΩ
During an overload condition, the internal current-limit amplifier regulates the output current to I(LIM). The FLT signal assert after a delay of 875 µs.The output voltage droops during the current regulation, resulting in increased power dissipation in the device. If the device junction temperature reaches the thermal shutdown threshold (T(TSD)), the internal FET is turn off. The device configured in latch-off mode stays latched off until it is reset by either of the following conditions:
- Cycling V(IN) below V(PORF)
- Toggling SHDN
Whereas the device configured in auto-retry mode, commences an auto-retry cycle 512 ms after TJ < [T(TSD) – 10°C]. The FLT signal remains asserted until the fault condition is removed and the device resumes normal operation. Figure 39 and Figure 40 illustrates behavior of the system during current limiting with auto-retry functionality.
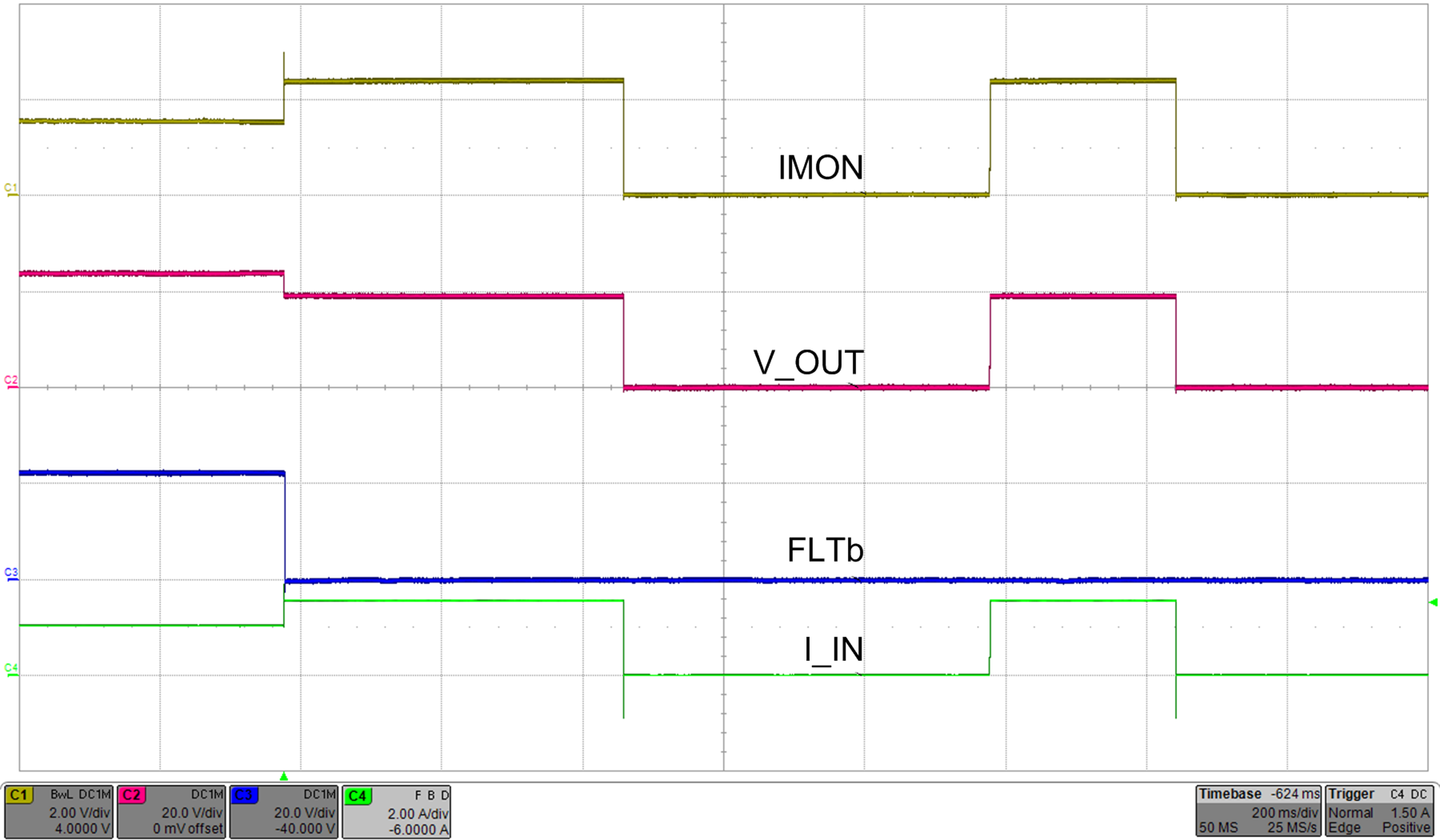
| Load transition from 22 Ω to 12 Ω | MODE pin connected to RTN | |
| RILIM = 8 kΩ | ||
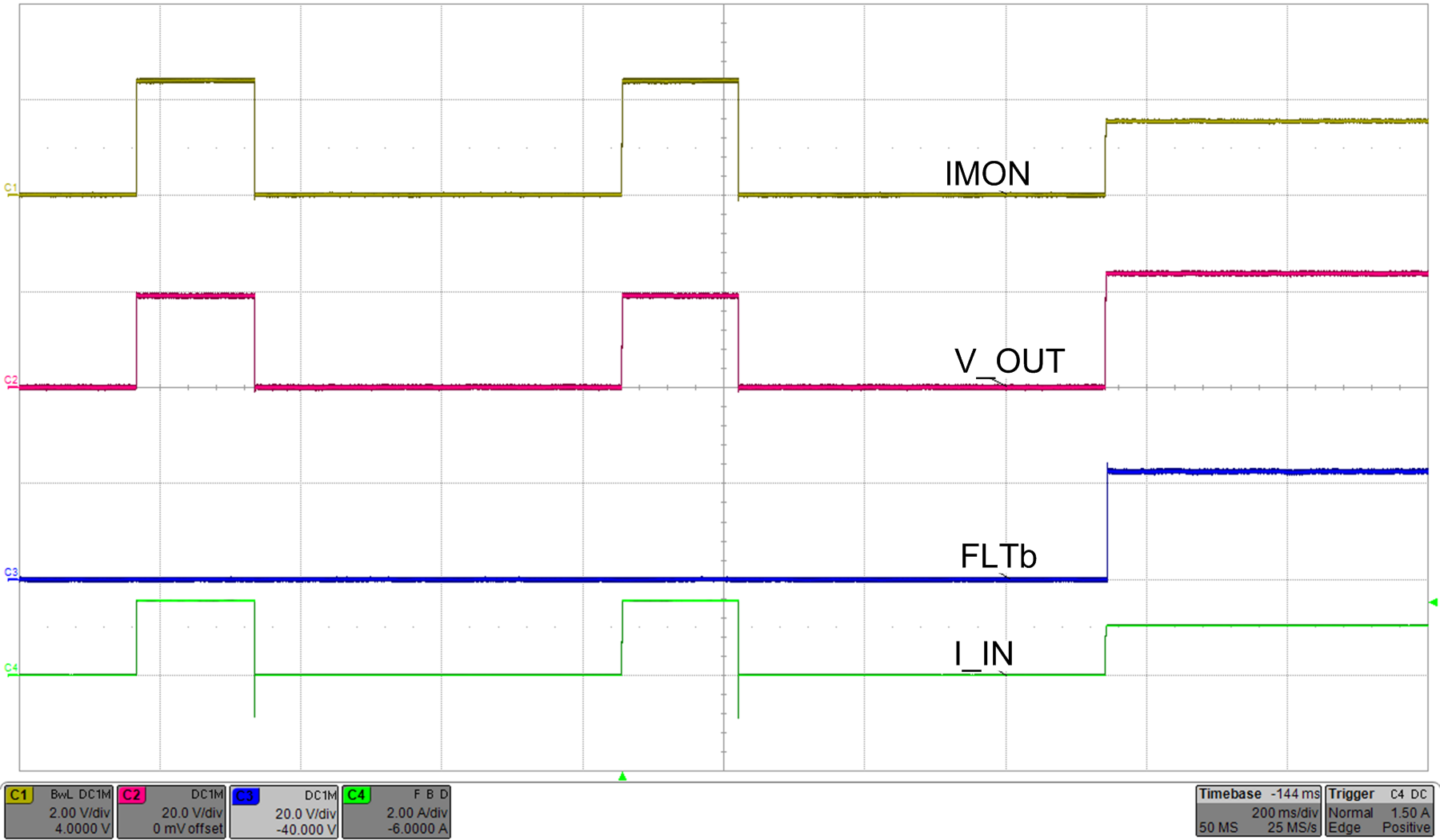
| RILIM = 5.36 kΩ | ||