SLVSBK0D October 2012 – March 2017 TPS54340
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation Output Current
- 7.3.3 Pulse Skip Eco-mode
- 7.3.4 Low Dropout Operation and Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.8 Internal Soft-Start
- 7.3.9 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK) Terminal)
- 7.3.10 Accurate Current Limit Operation and Maximum Switching Frequency
- 7.3.11 Synchronization to RT/CLKTerminal
- 7.3.12 Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.14 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.15 Simple Small Signal Model for Peak Current Mode Control
- 7.3.16 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Buck Converter
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedures
- 8.2.1.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH Tools
- 8.2.1.2.2 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.1.2.3 Output Inductor Selection (LO)
- 8.2.1.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.5 Catch Diode
- 8.2.1.2.6 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.8 Undervoltage Lockout Set Point
- 8.2.1.2.9 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors Selection
- 8.2.1.2.10 Minimum VIN
- 8.2.1.2.11 Compensation
- 8.2.1.2.12 Discontinuous Conduction Mode and Eco-mode Boundary
- 8.2.1.2.13 Power Dissipation
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 Inverting Power
- 8.2.3 Split Rail Power Supply
- 8.2.1
Buck Converter
- 8.3 WEBENCH Power Designer
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Orderable Information
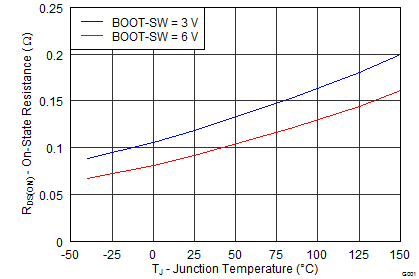
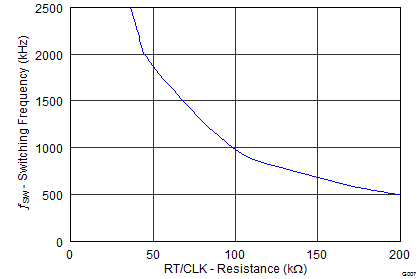
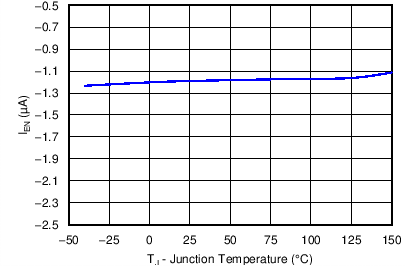
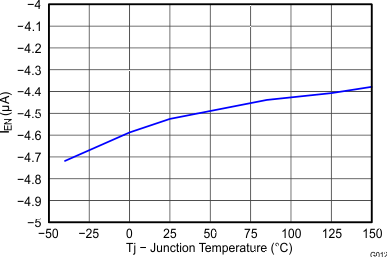
6.7 Typical Characteristics
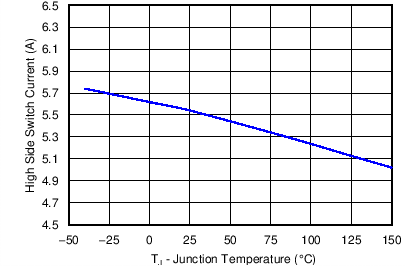
| VIN = 12 V |
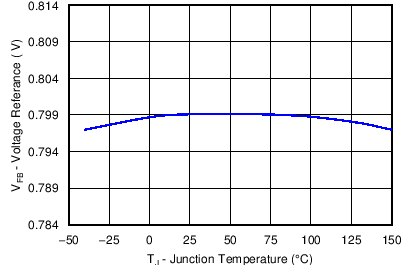
| VIN = 12 V |
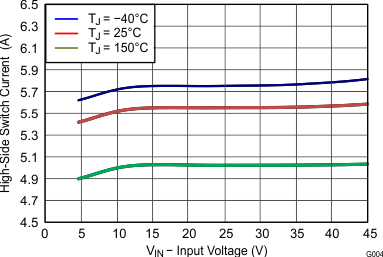
| VIN = 12V |
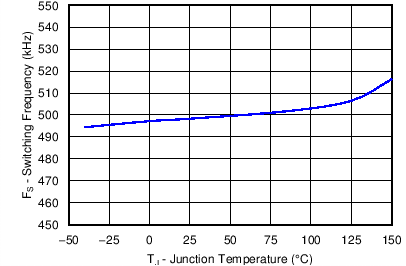
| VIN = 12 V | RT = 200 kΩ | |
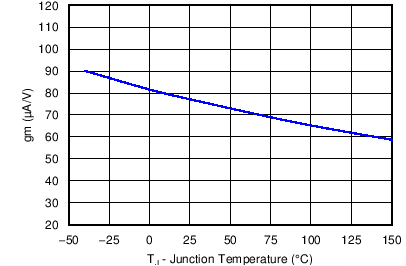
| VIN = 12 V |
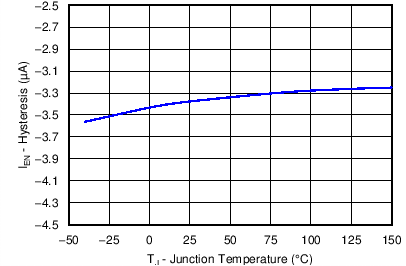
| VIN = 12 V |
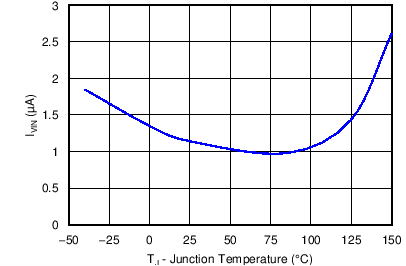
| VIN = 12 V |
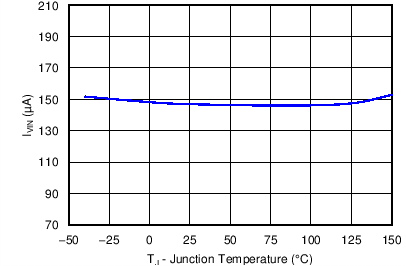
| VIN = 12 V |
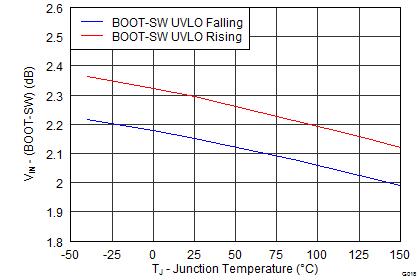 Figure 19. BOOT-SW UVLO vs Junction Temperature
Figure 19. BOOT-SW UVLO vs Junction Temperature 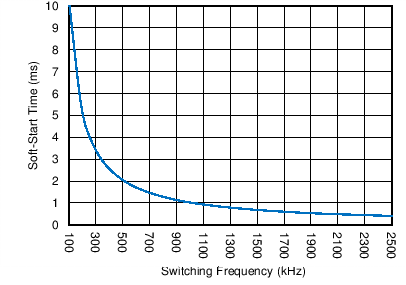
| VIN = 12 V | TJ = 25°C |
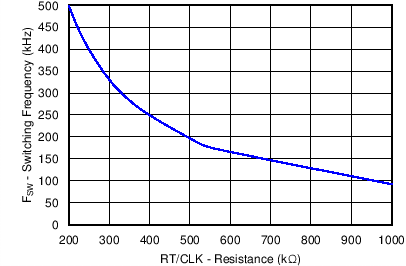
| ƒsw (kHz) = 92417 x RT (kΩ) -0.991 | ||
| RT (kΩ) = 101756 x ƒsw (kHz) -1.008 |
Low Frequency Range
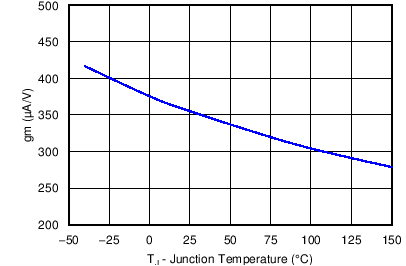
| VIN = 12 V |
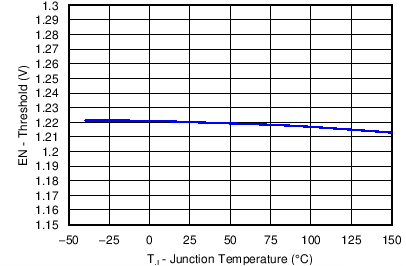
| VIN = 12 V |
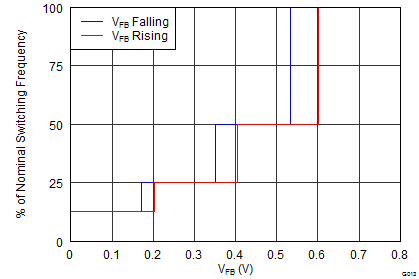
| VIN = 12V |
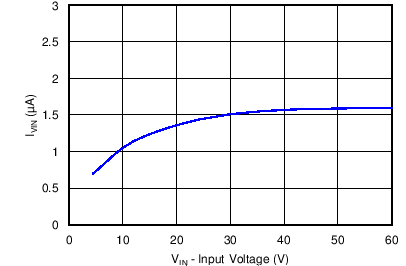
| TJ = 25°C |
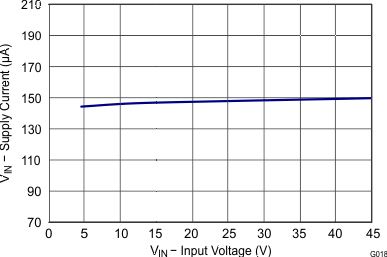
| TJ = 25°C |
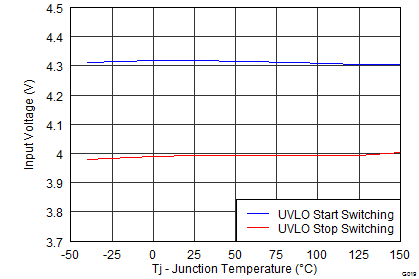 Figure 20. Input Voltage UVLO vs Junction Temperature
Figure 20. Input Voltage UVLO vs Junction Temperature