SLUSCU6C August 2017 – January 2020 UCC256301
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Hybrid Hysteretic Control
- 7.3.2 Regulated 12-V Supply
- 7.3.3 Feedback Chain
- 7.3.4 Optocoupler Feedback Signal Input and Bias
- 7.3.5 System External Shut Down
- 7.3.6 Pick Lower Block and Soft Start Multiplexer
- 7.3.7 Pick Higher Block and Burst Mode Multiplexer
- 7.3.8 VCR Comparators
- 7.3.9 Resonant Capacitor Voltage Sensing
- 7.3.10 Resonant Current Sensing
- 7.3.11 Bulk Voltage Sensing
- 7.3.12 Output Voltage Sensing
- 7.3.13 High Voltage Gate Driver
- 7.3.14 Protections
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 LLC Power Stage Requirements
- 8.2.2.2 LLC Gain Range
- 8.2.2.3 Select Ln and Qe
- 8.2.2.4 Determine Equivalent Load Resistance
- 8.2.2.5 Determine Component Parameters for LLC Resonant Circuit
- 8.2.2.6 LLC Primary-Side Currents
- 8.2.2.7 LLC Secondary-Side Currents
- 8.2.2.8 LLC Transformer
- 8.2.2.9 LLC Resonant Inductor
- 8.2.2.10 LLC Resonant Capacitor
- 8.2.2.11 LLC Primary-Side MOSFETs
- 8.2.2.12 Design Considerations for Adaptive Dead-Time
- 8.2.2.13 LLC Rectifier Diodes
- 8.2.2.14 LLC Output Capacitors
- 8.2.2.15 HV Pin Series Resistors
- 8.2.2.16 BLK Pin Voltage Divider
- 8.2.2.17 BW Pin Voltage Divider
- 8.2.2.18 ISNS Pin Differentiator
- 8.2.2.19 VCR Pin Capacitor Divider
- 8.2.2.20 Burst Mode Programming
- 8.2.2.21 Soft-Start Capacitor
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDB|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.2.19 VCR Pin Capacitor Divider
The capacitor divider on the VCR pin sets two parameters: (1) the divider ratio of the resonant capacitor voltage; (2) the amount of frequency compensation to be added. The first criteria the capacitor divider needs to meet is that under over load condition, the peak-to-peak voltage on VCR pin is with in 6 V.
As derived earlier, the following relationship between VCOMP voltage, ΔVCR, switching period, input average current, and the VCR capacitor divider is shown in Equation 66
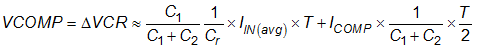
In this equation, C1 is the upper capacitor on the capacitor divider; C2 is the lower capacitor on the capacitor divider. VCOMP is contributed by two parts – the divided resonant capacitor voltage, and the voltage generated by the VCR pin internal current sources. Define the contribution of the internal current source to be KVCRRamp.
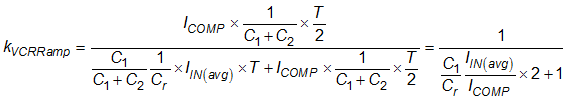
Select C1 and C2 so that KVCRRamp is within 0.1 ~ 0.6 range, and at over load condition, VCOMP is less than 6 V. In this example C1 = 150 pF and C2 = 15 nF is select.