SLLSE39E June 2010 – May 2015 ISO7520C , ISO7521C
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: VCC1 and VCC2 at 5 V ± 5%
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: VCC1 at 5 V ± 5%, VCC2 at 3.3 V ± 5%
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: VCC1 at 3.3 V ± 5%, VCC2 at 5 V ± 5%
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics: VCC1 and VCC2 at 3.3 V ± 5%
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics: VCC1 and VCC2 at 5 V ± 5%
- 6.10 Switching Characteristics: VCC1 at 5 V ± 5%, VCC2 at 3.3 V ± 5%
- 6.11 Switching Characteristics: VCC1 at 3.3 V ± 5%, VCC2 at 5 V ± 5%
- 6.12 Switching Characteristics: VCC1 and VCC2 at 3.3 V ± 5%
- 6.13 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- DW|16
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- DW|16
発注情報
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
The isolator in Figure 7 is based on a capacitive isolation barrier technique. The I/O channel of the device consists of two internal data channels, a high-frequency channel (HF) with a bandwidth from 100 kbps up to 1 Mbps, and a low-frequency channel (LF) covering the range from 100 kbps down to DC. In principle, a single- ended input signal entering the HF-channel is split into a differential signal through the inverter gate at the input. The following capacitor-resistor networks differentiate the signal into transients, which then are converted into differential pulses by two comparators. The comparator outputs drive a NOR-gate flip-flop whose output feeds an output multiplexer. A decision logic (DCL) at the driving output of the flip-flop measures the durations between signal transients. If the duration between two consecutive transients exceeds a certain time limit, (as in the case of a low-frequency signal), the DCL forces the output-multiplexer to switch from the high- to the low frequency channel. Because low-frequency input signals require the internal capacitors to assume prohibitively large values, these signals are pulse-width modulated (PWM) with the carrier frequency of an internal oscillator, thus creating a sufficiently high frequency signal, capable of passing the capacitive barrier. As the input is modulated, a low-pass filter (LPF) is needed to remove the high-frequency carrier from the actual data before passing it on to the output multiplexer.
8.2 Functional Block Diagram
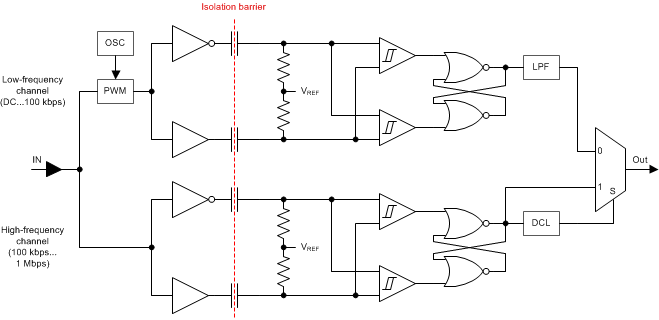 Figure 7. Conceptual Block Diagram of a Digital Capacitive Isolator
Figure 7. Conceptual Block Diagram of a Digital Capacitive Isolator
8.3 Feature Description
8.3.1 Insulation Characteristics
over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted)8.3.3 Package Insulation and Safety-Related Specifications
over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L(I01) | Minimum air gap (Clearance) | Shortest terminal-to-terminal distance through air | 8.34 | mm | ||
| L(I02) | Minimum external tracking (Creepage) | Shortest terminal-to-terminal distance across the package surface | 8.1 | mm | ||
| CTI | Tracking resistance (Comparative Tracking Index) | DIN EN 60112 (VDE 0303-11); IEC 60112 | >400 | V | ||
| Minimum internal gap (Internal Clearance) | Distance through the insulation | 0.014 | mm | |||
| RIO | Isolation resistance, input to output(1) | VIO = 500 V, TA = 25ºC | >1012 | Ω | ||
| VIO = 500 V, 100ºC ≤ TA ≤ TA max | >1011 | |||||
| CIO | Barrier capacitance input to output(1) | VIO = 0.4 sin(2πft), f = 1 MHz | 2 | pF | ||
| CI | Input capacitance to ground(2) | VI = VCC/2 + 0.4 sin(2πft), f = 1 MHz, VCC = 5 V | 2 | pF | ||
NOTE
Creepage and clearance requirements should be applied according to the specific equipment isolation standards of an application. Care should be taken to maintain the creepage and clearance distance of a board design to ensure that the mounting pads of the isolator on the printed-circuit-board (PCB) do not reduce this distance.
Creepage and clearance on a PCB become equal according to the measurement techniques shown in the Isolation Glossary. Techniques such as inserting grooves and/or ribs on a printed circuit board are used to help increase these specifications.
8.3.4 Safety Limiting Values
Safety limiting intends to prevent potential damage to the isolation barrier upon failure of input or output circuitry. A failure of the I/O can allow low resistance to ground or the supply and, without current-limiting, dissipate sufficient power to overheat the die and damage the isolation barrier potentially leading to secondary system failures.
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Is | Safety input, output, or supply current | θJA =79.9°C/W, VI = 5.25 V, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C | 298 | mA | ||
| θJA =79.9°C/W, VI = 3.45 V, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C | 453 | |||||
| Ts | Maximum Case Temperature | 150 | °C | |||
The safety-limiting constraint is the absolute maximum junction temperature specified in the absolute maximum ratings table. The power dissipation and junction-to-air thermal impedance of the device installed in the application hardware determines the junction temperature. The assumed junction-to-air thermal resistance in the Thermal Information table is that of a device installed on a High-K Test Board for Leaded Surface-Mount Packages. The power is the recommended maximum input voltage times the current. The junction temperature is then the ambient temperature plus the power times the junction-to-air thermal resistance.
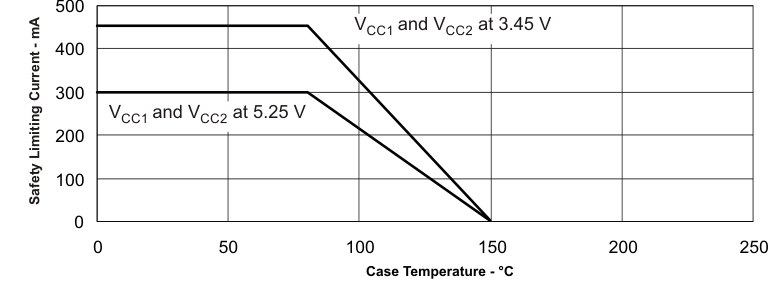 Figure 8. DW-16 RΘJC Thermal Derating Curve for VDE
Figure 8. DW-16 RΘJC Thermal Derating Curve for VDE
8.3.5 Regulatory Information
8.4 Device Functional Modes
Table 1. Device Function Table
| VCCI(1) | VCCO(1) | INPUT (INA, INB)(1) | OUTPUT (OUTA, OUTB)(1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PU | PU | H | H |
| L | L | ||
| Open | H | ||
| PD | PU | X | H |
| X | PD | X | Undetermined |
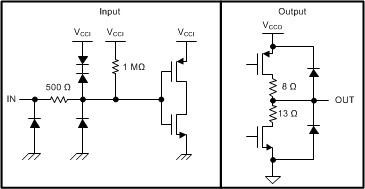 Figure 9. Equivalent Input and Output Schematic Diagrams
Figure 9. Equivalent Input and Output Schematic Diagrams