SNOSC16D March 2000 – January 2015 LM124-N , LM224-N , LM2902-N , LM324-N
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- D|14
Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
The V + pin should be bypassed to ground with a low-ESR capacitor. The optimum placement is closest to the V + and ground pins.
Take care to minimize the loop area formed by the bypass capacitor connection between V + and ground.
The ground pin should be connected to the PCB ground plane at the pin of the device.
The feedback components should be placed as close to the device as possible minimizing strays.
10.2 Layout Example
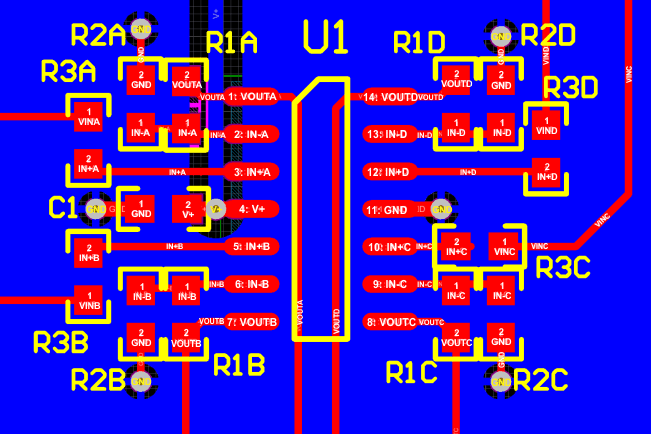 Figure 43. Layout Example
Figure 43. Layout Example