SLVS515D December 2004 – November 2015 TLC5940
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
9.1 Application Information
The device is a 16-channel, constant sink current, LED driver. This device can be connected in series to drive many LED lamps with only a few controller ports. Output current control data, dot correction data and PWM control data can be written from the SIN input terminal.
9.2 Typical Application
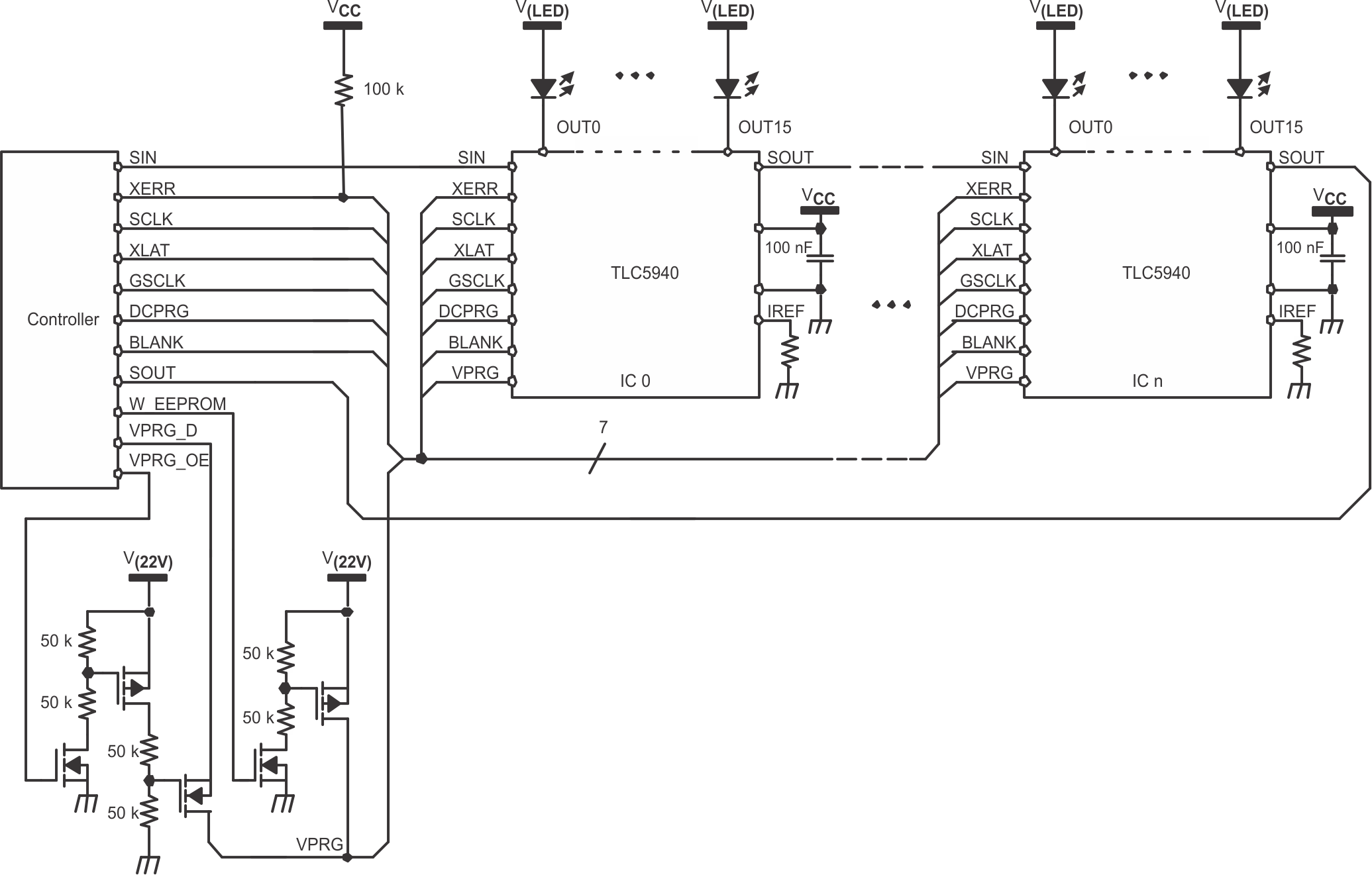 Figure 22. Cascading Devices
Figure 22. Cascading Devices
9.2.1 Design Requirements
For this design example, use the input parameters shown in Table 4.
Table 4. Design Parameters
| PARAMETERS | VALUES |
|---|---|
| VCC input voltage range | 3.0 V to 5.5 V |
| LED lamp (VLED) input voltage range | >Maximum LED forward voltage (VF) + IC knee voltage |
| SIN, SCLK, XLAT, GSCLK, and BLANK voltage range | Low level = GND, High level = VCC |
9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
9.2.2.1 Serial Data Transfer Rate
Figure 22 shows a cascading connection of n TLC5940 devices connected to a controller, building a basic module of an LED display system. The maximum number of cascading TLC5940 devices depends on the application system and is in the range of 40 devices. Equation 9 calculates the minimum frequency needed:
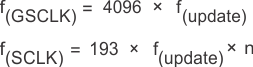
where
- f(GSCLK): minimum frequency needed for GSCLK
- f(SCLK): minimum frequency needed for SCLK and SIN
- f(update): update rate of whole cascading system
- n: number cascaded of TLC5940 device
9.2.2.2 Grayscale (GS) Data
There are a total of 16 sets of 12-bit GS data for the PWM control of each output. Select the GS data of each LED lamp and write the GS data to the register following the signal timing.
9.2.3 Application Curve
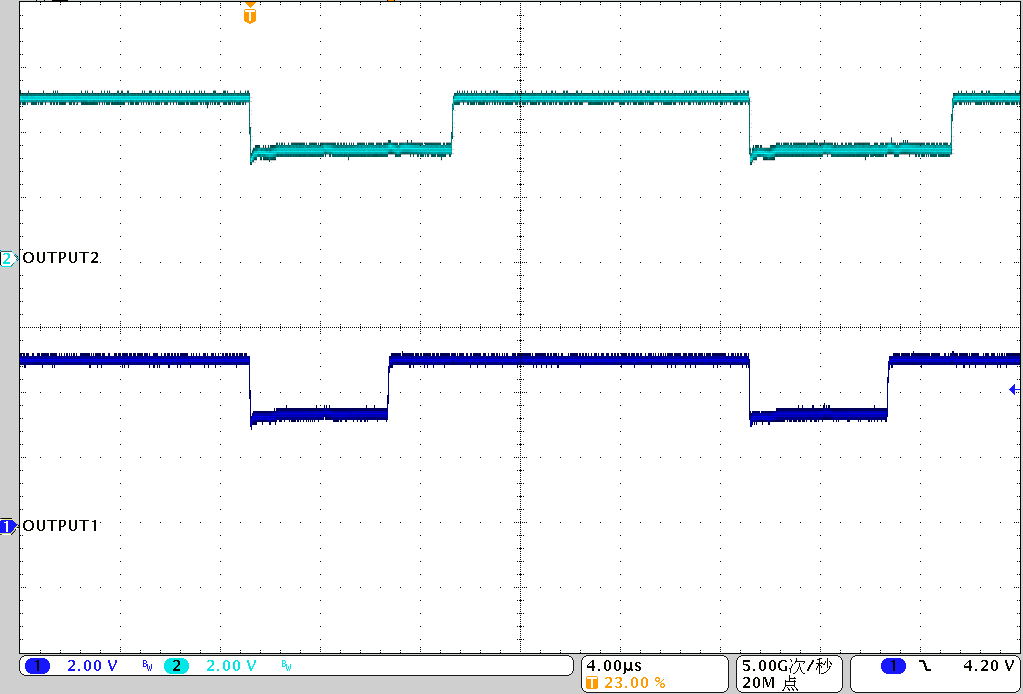 Figure 23. Output Waveform with Different Grayscale PWM Data
Figure 23. Output Waveform with Different Grayscale PWM Data