SLRS073A May 2017 – May 2018 TPL7407LA
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- D|16
Orderable Information
8.1.1 Unipolar Stepper Motor Driver
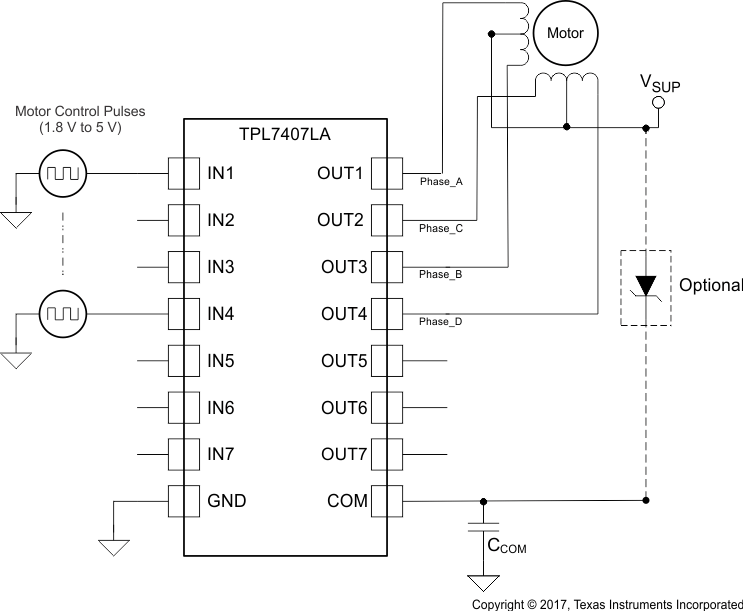 Figure 7. Stepper Motor Driver Schematic
Figure 7. Stepper Motor Driver Schematic
Figure 7 shows an implementation of the TPL7407LA for driving a uniploar stepper motor. The unconnected input channels can be used for other functions. When an input pin is left open the internal 1-MΩ pull down resistor pulls the respective input pin to GND potential. For higher noise immunity use an external short across an unconnected input and GND pins. The COM pin must be tied to the supply of whichever inductive load is being driven for the driver to be protected by the free-wheeling diode.
For more information on this application, see the Stepper Motor Driving With Peripheral Drivers (Driver ICs) application report.