SBAS661C February 2015 – May 2021 ADS1262 , ADS1263
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8.1 Offset Temperature Drift Measurement
- 8.2 Gain Temperature Drift Measurement
- 8.3 Common-Mode Rejection Ratio Measurement
- 8.4 Power-Supply Rejection Ratio Measurement
- 8.5 Crosstalk Measurement (ADS1263)
- 8.6 Reference-Voltage Temperature-Drift Measurement
- 8.7 Reference-Voltage Thermal-Hysteresis Measurement
- 8.8 Noise Performance
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Multifunction Analog Inputs
- 9.3.2 Analog Input Description
- 9.3.3 Sensor Bias
- 9.3.4 Temperature Sensor
- 9.3.5 Power-Supply Monitor
- 9.3.6 PGA
- 9.3.7 PGA Voltage Overrange Monitors
- 9.3.8 ADC Reference Voltage
- 9.3.9 ADC1 Modulator
- 9.3.10 Digital Filter
- 9.3.11 Sensor-Excitation Current Sources (IDAC1 and IDAC2)
- 9.3.12 Level-Shift Voltage
- 9.3.13 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 9.3.14 Test DAC (TDAC)
- 9.3.15 ADC2 (ADS1263)
- 9.4
Device Functional Modes
- 9.4.1 Conversion Control
- 9.4.2 Conversion Latency
- 9.4.3 Programmable Time Delay
- 9.4.4 Serial Interface
- 9.4.5 Data Ready Pin (DRDY)
- 9.4.6 Conversion Data Software Polling
- 9.4.7 Read Conversion Data
- 9.4.8 ADC Clock Modes
- 9.4.9
Calibration
- 9.4.9.1 Offset and Full-Scale Calibration
- 9.4.9.2 ADC1 Offset Self-Calibration (SFOCAL1)
- 9.4.9.3 ADC1 Offset System Calibration (SYOCAL1)
- 9.4.9.4 ADC2 Offset Self-Calibration ADC2 (SFOCAL2)
- 9.4.9.5 ADC2 Offset System Calibration ADC2 (SYOCAL2)
- 9.4.9.6 ADC1 Full-Scale System Calibration (SYGCAL1)
- 9.4.9.7 ADC2 Full-Scale System Calibration ADC2 (SYGCAL2)
- 9.4.9.8 Calibration Command Procedure
- 9.4.9.9 User Calibration Procedure
- 9.4.10 Reset
- 9.4.11 Power-Down Mode
- 9.4.12 Chop Mode
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6
Register Maps
- 9.6.1 Device Identification Register (address = 00h) [reset = x]
- 9.6.2 Power Register (address = 01h) [reset = 11h]
- 9.6.3 Interface Register (address = 02h) [reset = 05h]
- 9.6.4 Mode0 Register (address = 03h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.5 Mode1 Register (address = 04h) [reset = 80h]
- 9.6.6 Mode2 Register (address = 05h) [reset = 04h]
- 9.6.7 Input Multiplexer Register (address = 06h) [reset = 01h]
- 9.6.8 Offset Calibration Registers (address = 07h, 08h, 09h) [reset = 00h, 00h, 00h]
- 9.6.9 Full-Scale Calibration Registers (address = 0Ah, 0Bh, 0Ch) [reset = 40h, 00h, 00h]
- 9.6.10 IDACMUX Register (address = 0Dh) [reset = BBh]
- 9.6.11 IDACMAG Register (address = 0Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.12 REFMUX Register (address = 0Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.13 TDACP Control Register (address = 10h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.14 TDACN Control Register (address = 11h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.15 GPIO Connection Register (address = 12h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.16 GPIO Direction Register (address = 13h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.17 GPIO Data Register (address = 14h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.18 ADC2 Configuration Register (address = 15h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.19 ADC2 Input Multiplexer Register (address = 16h) [reset = 01h]
- 9.6.20 ADC2 Offset Calibration Registers (address = 17h, 18h) [reset = 00h, 00h]
- 9.6.21 ADC2 Full-Scale Calibration Registers (address = 19h, 1Ah) [reset = 00h, 40h]
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PW|28
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PW|28
Orderable Information
9.5.7 WREG Command
Use the WREG command to write the device register data. The register data are written one register at a time or as a block of register data. The starting register address is any register in the map.
The WREG opcode consists of two bytes. The first byte specifies the starting register address: 010r rrrr, where r rrrr is the starting register address The second opcode byte is the number of registers to write (minus one): 000n nnnn, where n nnnn is the number of registers to write minus one. The following byte (or bytes) is the register data, most significant bit first. If the byte count exceeds the last register address, the ADC ignores the data (the address pointer does not wrap). Writing new data to certain registers results in a reset of ADC1 or ADC2 conversions, as specified in the ADC restart column in the Section 9.6. The previous conversion data are cleared at restart; therefore, read the data before the register write operation. After the register write command has been started, further commands are disabled until one of these conditions occur:
1) The write operation is completed.
2) The write operation is terminated by taking CS high.
3) The write operation is terminated by a serial interface auto-reset
4) The ADC is reset by toggling the RESET/PWDN pin.
Figure 9-57 depicts a two-register write operation example. As shown, the required opcodes to write data to two registers starting at register MODE2 (address = 05h) are: OPCODE 1 = 45h and OPCODE 2 = 01h.
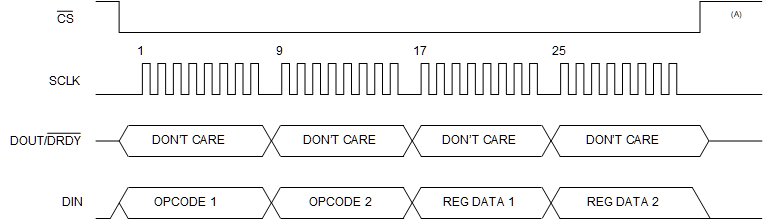
The MODE2 and INPMUX registers are modified. Typically, register changes take effect immediately after the data are written. However, if the registers are part of a group, then the data are written only after all data for the grouped registers in the write block have been sent. In this example, data for MODE2 and INPMUX are written only after the data for INPMUX are sent. See the Section 9.6 section for those registers that are grouped when writing register data.