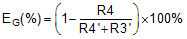SBAS771C June 2017 – February 2020 AMC1303E0510 , AMC1303E0520 , AMC1303E2510 , AMC1303E2520 , AMC1303M0510 , AMC1303M0520 , AMC1303M2510 , AMC1303M2520
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Power Ratings
- 7.6 Insulation Specifications
- 7.7 Safety-Related Certifications
- 7.8 Safety Limiting Values
- 7.9 Electrical Characteristics: AMC1303x05x
- 7.10 Electrical Characteristics: AMC1303x25x
- 7.11 Switching Characteristics
- 7.12 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 7.13 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DWV|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.2.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
As indicated in Figure 55, the output of the integrated differential amplifier is internally biased to a common-mode voltage of 1.9 V. This voltage results in a bias current IIB through the resistive network R4 and R5 (or R4' and R5') used for setting the gain of the amplifier. The value range of this current is specified in the Electrical Characteristics table. This bias current generates additional offset error that depends on the value of the resistor R3. Because the value of this bias current depends on the actual common-mode amplitude of the input signal (as illustrated in Figure 56), the initial system offset calibration does not minimize its effect. Therefore, in systems with high accuracy requirements, TI recommends using a series resistor at the negative input (AINN) of the AMC1303 with a value equal to the shunt resistor R3 (that is, R3' = R3 in Figure 55) to eliminate the effect of the bias current.
This additional series resistor (R3') influences the gain error of the circuit. The effect is calculated using Equation 5 with R5 = R5' = 50 kΩ and R4 = R4' = 12.5 kΩ for the AMC1303x25x.