SLUSA75B July 2010 – January 2020 BQ24650
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Battery Voltage Regulation
- 8.3.2 Input Voltage Regulation
- 8.3.3 Battery Current Regulation
- 8.3.4 Battery Precharge
- 8.3.5 Charge Termination and Recharge
- 8.3.6 Power Up
- 8.3.7 Enable and Disable Charging
- 8.3.8 Automatic Internal Soft-Start Charger Current
- 8.3.9 Converter Operation
- 8.3.10 Synchronous and Non-Synchronous Operation
- 8.3.11 Cycle-by-Cycle Charge Undercurrent
- 8.3.12 Input Overvoltage Protection (ACOV)
- 8.3.13 Input Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 8.3.14 Battery Overvoltage Protection
- 8.3.15 Cycle-by-Cycle Charge Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.16 Thermal Shutdown Protection
- 8.3.17 Temperature Qualification
- 8.3.18 Charge Enable
- 8.3.19 Inductor, Capacitor, and Sense Resistor Selection Guidelines
- 8.3.20 Charge Status Outputs
- 8.3.21 Battery Detection
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RVA|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RVA|16
Orderable Information
8.3.9 Converter Operation
The synchronous buck PWM converter uses a fixed frequency voltage mode with feed-forward control scheme. A type III compensation network allows using ceramic capacitors at the output of the converter. The compensation input stage is connected internally between the feedback output (FBO) and the error amplifier input (EAI). The feedback compensation stage is connected between the error amplifier input (EAI) and error amplifier output (EAO). The LC output filter must be selected to give a resonant frequency of 12 kHz – 17 kHz for the BQ24650, where resonant frequency, fo, is given by:
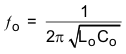
An internal saw-tooth ramp is compared to the internal EAO error control signal to vary the duty-cycle of the converter. The ramp height is 7% of the input adapter voltage making it always directly proportional to the input adapter voltage. This cancels out any loop gain variation due to a change in input voltage and simplifies the loop compensation. The ramp is offset by 300 mV to allow zero percent duty-cycle when the EAO signal is below the ramp. The EAO signal is also allowed to exceed the saw-tooth ramp signal in order to get a 100% duty-cycle PWM request. Internal gate drive logic allows achieving 99.98% duty-cycle while ensuring the N-channel upper device always has enough voltage to stay fully on. If the BTST pin to PH pin voltage falls below 4.2 V for more than 3 cycles, then the high-side N-channel power MOSFET is turned off and the low-side N-channel power MOSFET is turned on to pull the PH node down and recharge the BTST capacitor. Then the high-side driver returns to 100% duty-cycle operation until the (BTST-PH) voltage is detected to fall low again due to leakage current discharging the BTST capacitor below 4.2 V, and the reset pulse is reissued.
The fixed-frequency oscillator keeps tight control of the switching frequency under all conditions of input voltage, battery voltage, charge current, and temperature, simplifying output filter design and keeping it out of the audible noise region.