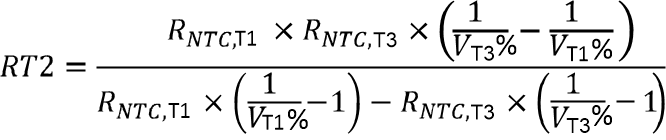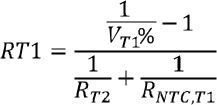SLUSDC7A March 2020 – November 2020 BQ25306
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Orderable Information
9.3.2.6 Thermistor Temperature Monitoring
The charger device provides a single thermistor input TS pin for battery temperature monitor. RT1 and RT2 programs the cold temperature T1 and hot temperature T3. In the equations, RNTC,T1 is NTC thermistor resistance value at temperature T1 and RNTC,T3 is NTC thermistor resistance values at temperature T3. Assuming RHOT = 0, select 0°C to 45°C for battery charge temperature range, then NTC thermistor 103AT-2 resistance RNTC,T1 = 27.28 kΩ ( at 0°C) and RNTC,T3 = 4.91 kΩ (at 45°C), from the Equation 1 and Equation 2, RT1 and RT2 are derived as:
• RT1 = 4.527 kΩ
• RT2 = 23.26 kΩ
On top of the calculation results, adding RHOT resisitor can shift HOT temperature T3 up and only slightly shift up COLD temperature T1. The actual temperature T3 can be looked up in a NTC resistance table based on (RNTC,T3 - RHOT) and T1 can be looked up in a NTC resistance table based on (RNTC,T1 - RHOT). Because RNTC,T1 is much higher than RNTC,T3, RHOT can adjust HOT temperature significantly with mimimal affect on COLD temperature. RHOT is optional.
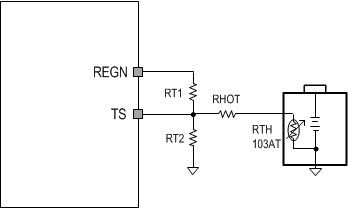 Figure 9-2 Battery Temperature Sensing Circuit
Figure 9-2 Battery Temperature Sensing Circuit