SLUSBH2G March 2013 – March 2019
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Maximum Power Point Tracking
- 7.3.2 Battery Undervoltage Protection
- 7.3.3 Battery Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.4 Battery Voltage within Operating Range (VBAT_OK Output)
- 7.3.5 Storage Element / Battery Management
- 7.3.6 Programming OUT Regulation Voltage
- 7.3.7 Step Down (Buck) Converter
- 7.3.8 Nano-Power Management and Efficiency
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGR|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGR|20
Orderable Information
8.2.1.3 Application Curves
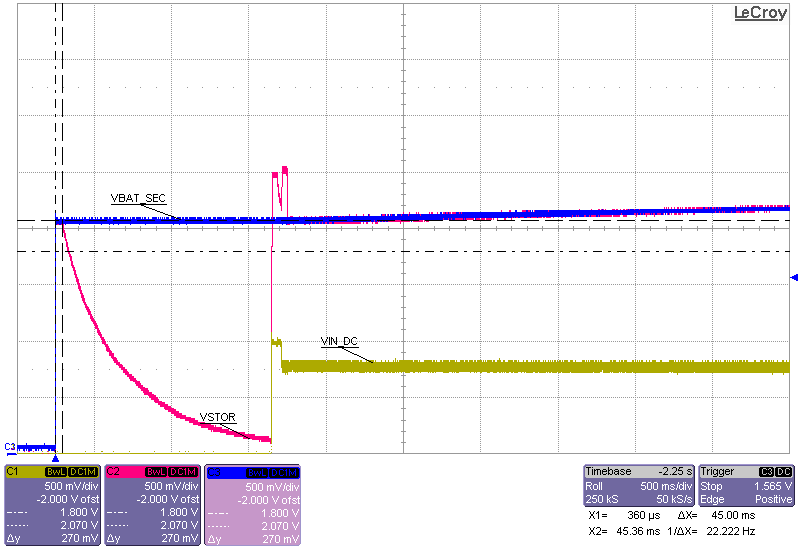
| Sourcemeter with VSOURCE = 1.0 V and compliance of 8.5 mA subsequently applied to VIN_DC |
| VBAT = 0.1 F capacitor charged to 2.0 V |
| Resistance on VSTOR = 100 kΩ |
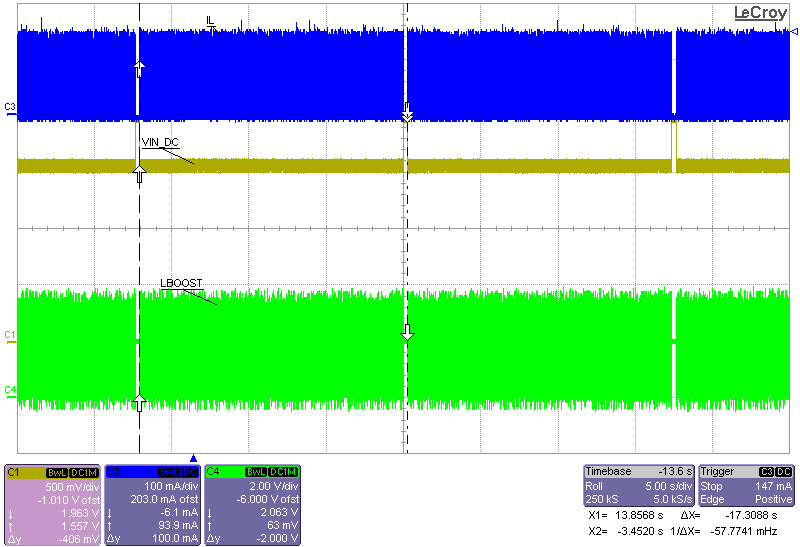
| VIN_DC = sourcemeter with VSOURCE = 2.0 V and compliance
of 43 mA |
| VBAT = sourcemeter with VSOURCE = 3.0 V and compliance
of 1 A |
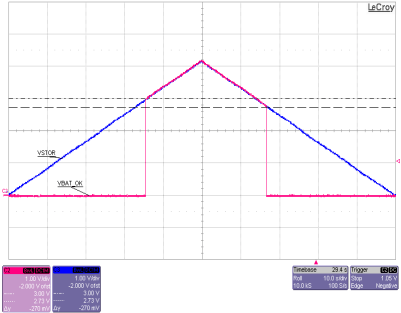
| VIN_DC = 1.5 V with 75 Ω series resistance |
| No storage element on VBAT or VBAT_PRI |
| VSTOR artifically ramped from 0 V to 4.2 V to 0 V using a power amp driven by a function generator |
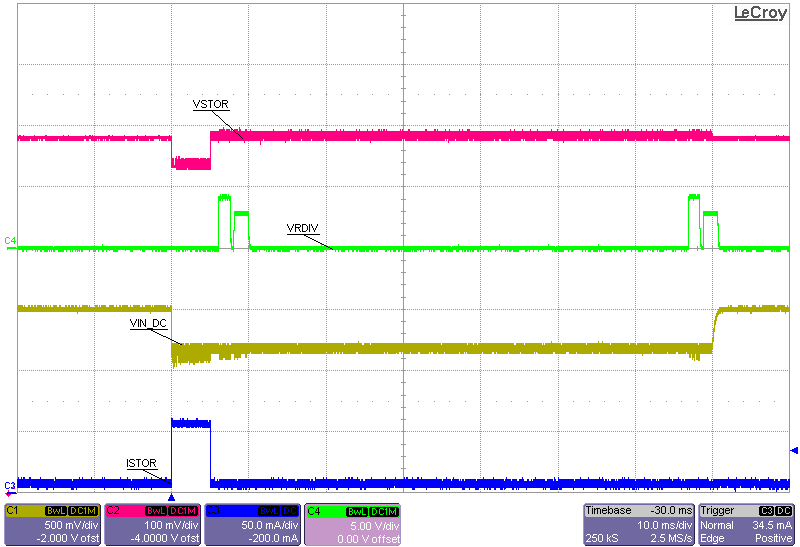
| VIN_DC = 1.5 V with 75 Ω series resistance |
| VBAT = 4.2 V charged 0.5 F capacitor |
| R(VSTOR) = open to 84 Ω to open |
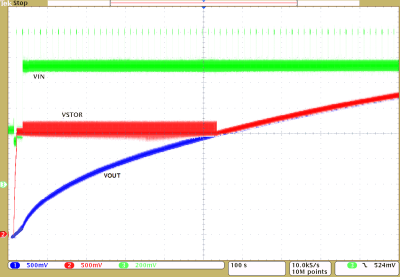
| VIN_DC = source meter with 1.2 V compliance and ISC = 1.0 mA |
| 120 mF super capacitor on VOUT with VOUT regulation voltage changed to 4.2 V. |
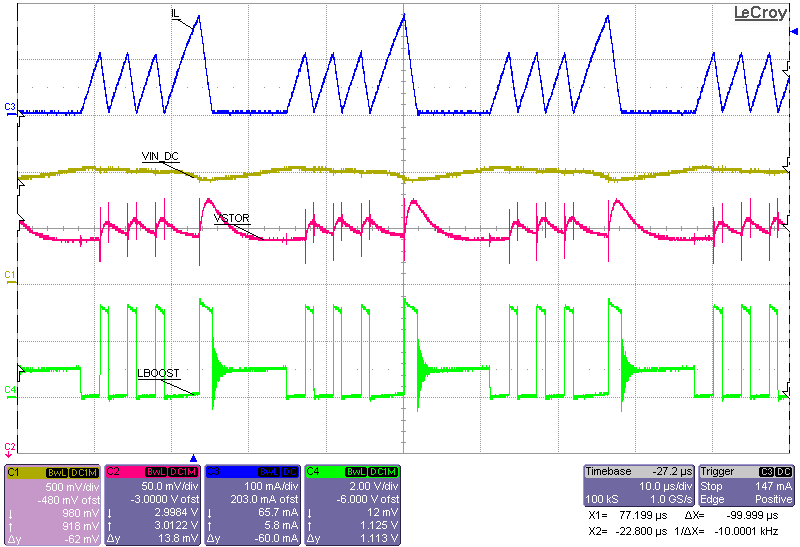
| VIN_DC = sourcemeter with VSOURCE = 2.0 V and compliance of 43 mA |
| VBAT = sourcemeter with VSOURCE = 3.0 V and compliance of |
| 1 A |
| IL = inductor current |
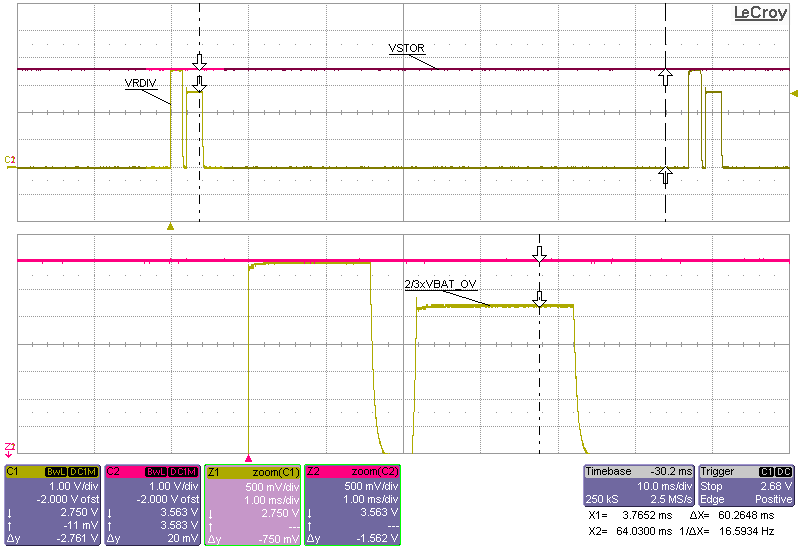
| VIN_DC = sourcemeter with VSOURCE = 2.0 V and compliance of 43 mA |
| VBAT = sourcemeter with VSOURCE = 3.6 V and compliance
of 1 A |
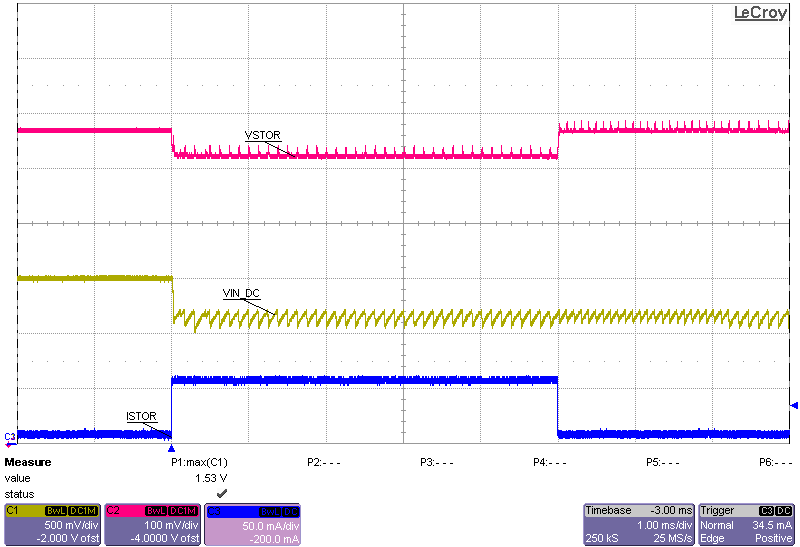
| VIN_DC = 1.5 V with 75 Ω series resistance |
| VBAT = 4.2 V charged 0.5 F capacitor |
| R(VSTOR) = open to 84 Ω to open |
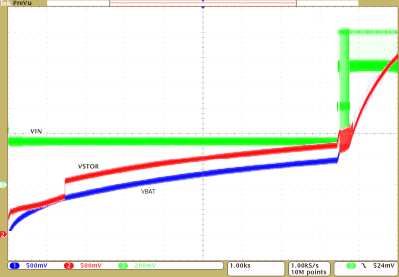
| VIN_DC = source meter with 1.2 V compliance and ISC = 1.0 mA |
| 120 mF super capacitor on VBAT |