SLUSBH2G March 2013 – March 2019
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Maximum Power Point Tracking
- 7.3.2 Battery Undervoltage Protection
- 7.3.3 Battery Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.4 Battery Voltage within Operating Range (VBAT_OK Output)
- 7.3.5 Storage Element / Battery Management
- 7.3.6 Programming OUT Regulation Voltage
- 7.3.7 Step Down (Buck) Converter
- 7.3.8 Nano-Power Management and Efficiency
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGR|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGR|20
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
The recommended L1 = 22 µH with ISAT ≥ I-CHG(CBC_LIM)MAX, L2 = 10 µH with ISAT ≥ I-BUCK(CBC_LIM)MAX, CBYP = 0.01 µF and low leakage CREF = 10 nF are selected. In order to ensure the fastest recovery of the harvester output voltage to the MPPT level following power extraction, the minimum recommended CIN = 4.7 µF is selected. Because no large system load transients are expected and to ensure fast charge time during cold start, the minimum recommended CSTOR = 4.7 µF.
No MPPT resistors are required because VOC_SAMP can be tied to VSTOR to give 80% MPPT.
- Keeing in mind VBAT_UV < VBAT_OV ≤ 5.5 V, to size the VBAT_OV resistors, first choose RSUMOV = ROV1 + ROV2 = 13 MΩ then solve Equation 2 for
- ROV2 = RSUMOV - ROV1 = 13 MΩ - 5.62 MΩ = 7.38 MΩ → 7.32 MΩ resulting in VBAT_OV = 4.18V due to rounding to the nearest 1% resistor.
- Keeping in mind VBAT_OV ≥ VBAT_OK_HYST > VBAT_OK ≥ VBAT_UV, to size the VBAT_OK and VBAT_OK_HYST resistors, first choose RSUMOK = ROK1 + ROK2 + ROK3 = 13 MΩ then solve Equation 3 and Equation 4 for
- ROK3 = RSUMOK - ROK1 - ROK2 = 13 MΩ - 5.62 MΩ - 5.479 MΩ = 1.904 MΩ → 1.87 MΩ to give VBAT_OK = 2.39 V and VBAT_OK_HYST = 2.80 V.
- For VOUT, first choose ROUT1 + ROUT2 = RSUMOUT = 13 MΩ, then solve Equation 5 for ROUT1 = VBIAS / VOUT x RSUMOUT = 1.21 V / 1.8 V x 13 MΩ = 8.74 MΩ → 8.66 MΩ after rounding to nearest 1% value.
- ROUT2 = RSUM - ROUT1 = 13 MΩ - 8.66 MΩ = 4.34 MΩ → 4.22 MΩ after rounding.
Equation 12. 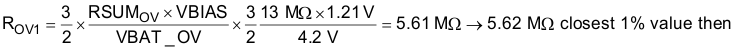
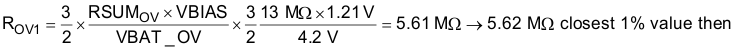
Equation 13. 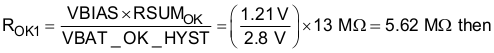
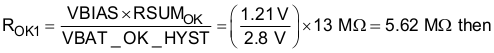
Equation 14. 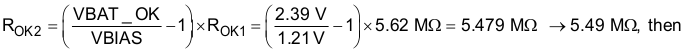
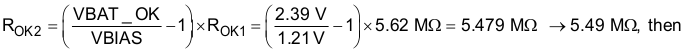
SLUC484 provides help on sizing and selecting the resistors.