SLUSD88A March 2019 – June 2019 BQ25886
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Device Power-On-Reset
- 8.3.2 Device Power Up from Battery without Input Source
- 8.3.3 Device Power Up from Input Source
- 8.3.4 Input Current Optimizer (ICO)
- 8.3.5 Buck Mode Operation from Battery (OTG)
- 8.3.6 PowerPath Management
- 8.3.7 Battery Charging Management
- 8.3.8 Status Outputs
- 8.3.9 Input Current Limit on ILIM Pin
- 8.3.10 Voltage and Current Monitoring
- 8.3.11 Thermal Regulation and Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.12 Battery Protection
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Orderable Information
9.2.2.2 Input (VBUS / PMID) Capacitor
The input capacitor should have enough ripple current rating to absorb input switching ripple current. The worst case RMS ripple current occurs when duty cycle is 0.5. If the converter does not operate at 50% duty cycle, then the worst case capacitor RMS current IPMID occurs where the duty cycle is closest to 50% and can be estimated by
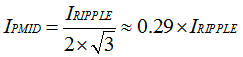
A low ESR ceramic capacitor such as X7R or X5R is preferred for input decoupling capacitor and should be placed close to the PMID and GND pins of the IC. Voltage rating of the capacitor must be higher than normal input voltage level. 25-V rating or higher capacitor is preferred for up to 5-V input voltage. A minimum 10-μF capacitor is suggested for up to 3.3-A input current. Keep in mind, long impedance cable would cause significant voltage drop with higher inrush current. For optimal performance, 44-uF cap on PMID is recommended. In addition, a minimum 1-μF capacitor is suggested at VBUS pin.