SLUSCM3K June 2016 – July 2020 BQ77904 , BQ77905
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Protection Summary
- 8.3.2
Fault Operation
- 8.3.2.1 Operation in OV
- 8.3.2.2 Operation in UV
- 8.3.2.3 Operation in OW
- 8.3.2.4 Operation in OCD1
- 8.3.2.5 Operation in OCD2
- 8.3.2.6 Operation in SCD
- 8.3.2.7 Overcurrent Recovery Timer
- 8.3.2.8 Load Removal Detection
- 8.3.2.9 Load Removal Detection in UV
- 8.3.2.10 Operation in OTC
- 8.3.2.11 Operation in OTD
- 8.3.2.12 Operation in UTC
- 8.3.2.13 Operation in UTD
- 8.3.3 Protection Response and Recovery Summary
- 8.3.4 Configuration CRC Check and Comparator Built-In-Self-Test
- 8.3.5 Fault Detection Method
- 8.3.6 State Comparator
- 8.3.7 DSG FET Driver Operation
- 8.3.8 CHG FET Driver Operation
- 8.3.9 External Override of CHG and DSG Drivers
- 8.3.10 Configuring 3-S, 4-S, or 5-S Mode
- 8.3.11 Stacking Implementations
- 8.3.12 Zero-Volt Battery Charging Inhibition
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PW|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PW|20
Orderable Information
9.1.1.2 Protecting CHG and LD
Because both CHG and LD are connected to the PACK– terminal, these pins are specially designed to sustain an absolute max of –30 V. However, the device can be used in a wide variety of applications, and it is possible to expose the pins lower than –30 V absolute max rating.
To protect the pins, TI recommends to put a PMOS FET in series of the CHG pin and a diode in series of the LD pin as shown below.
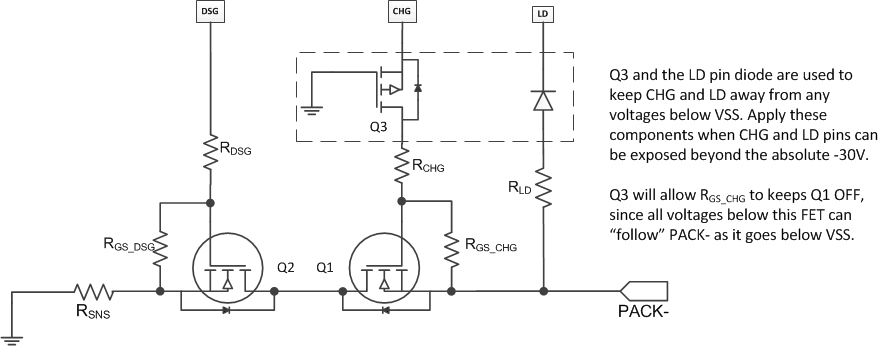 Figure 9-3 Protecting CHG and LD
Figure 9-3 Protecting CHG and LD