SWRS215D April 2019 – May 2021 CC3235S , CC3235SF
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Functional Block Diagrams
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Device Comparison
- 7 Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 ESD Ratings
- 8.3 Power-On Hours (POH)
- 8.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.5 Current Consumption Summary (CC3235S)
- 8.6 Current Consumption Summary (CC3235SF)
- 8.7 TX Power Control for 2.4 GHz Band
- 8.8 TX Power Control for 5 GHz
- 8.9 Brownout and Blackout Conditions
- 8.10 Electrical Characteristics for GPIO Pins
- 8.11 Electrical Characteristics for Pin Internal Pullup and Pulldown
- 8.12 WLAN Receiver Characteristics
- 8.13 WLAN Transmitter Characteristics
- 8.14 WLAN Transmitter Out-of-Band Emissions
- 8.15 BLE/2.4 GHz Radio Coexistence and WLAN Coexistence Requirements
- 8.16 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for RGK Package
- 8.17
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 8.17.1 Power Supply Sequencing
- 8.17.2 Device Reset
- 8.17.3 Reset Timing
- 8.17.4 Wakeup From HIBERNATE Mode
- 8.17.5 Clock Specifications
- 8.17.6 Peripherals Timing
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGK|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGK|64
Orderable Information
10.1.2 Antenna Selection
The CC3235x device is designed to also support antenna selection and is controlled from Image Creator. When enabled, there are 3 options possible options:
- ANT 1: When selected, the GPIOs that are defined for antenna selection with set the RF path for antenna 1.
- ANT 2: When selected, the GPIOs that are defined for antenna selection will set the RF path for antenna 2.
- Autoselect: When selected, during a scan and prior to connecting to an AP, CC3235x device will determine the best RF path and select the appropriate antenna (13)(14). The result is the saved as port of the profile.
Figure 10-5 shows the implementation of a complete Bluetooth® low energy and WLAN coexistence network with the WLAN operating on either a 2.4- or a 5 GHz band with antenna selection. The SOP lines control the 5 GHz switch. The Coex switch is controlled by a GPIO signal from the BLE device and a GPIO signal from the CC3235x device. The Antenna switch is controlled by 2 GPIO lines from the CC3235x device.
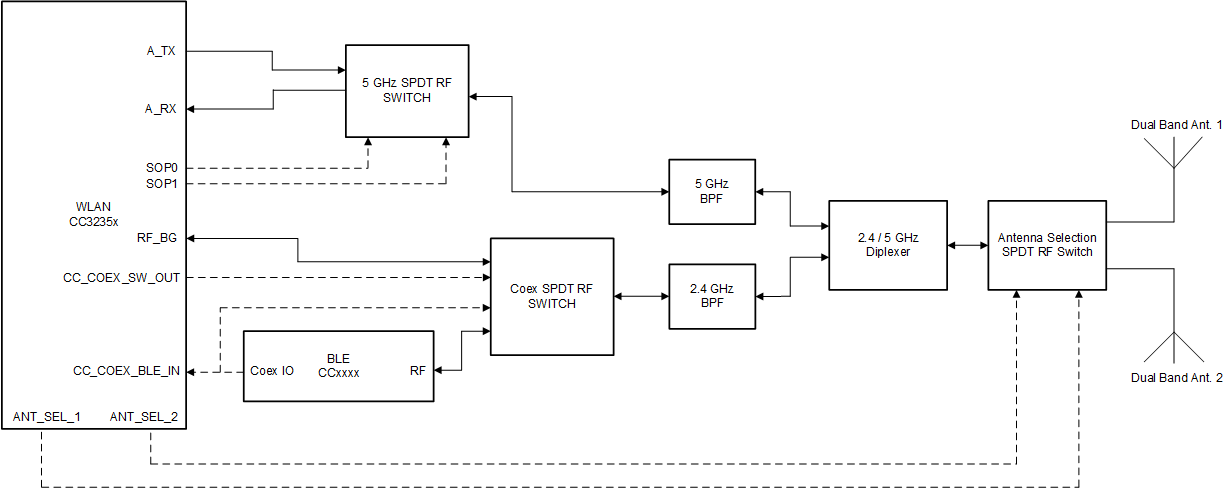 Figure 10-5 Antenna Selection Solution with Coexistence Solution and 5 GHz Wi-Fi
Figure 10-5 Antenna Selection Solution with Coexistence Solution and 5 GHz Wi-FiFigure 10-6 shows the antenna selection implementation for Wi-Fi, with BLE operating on it's own antenna. The SOP lines control the 5 GHz switch. Note in this implementation no Coex switch is required and only a single GPIO from the BLE device to the CC3235x device is required. The Antenna switch is controlled by 2 GPIO lines from the CC3235x device.
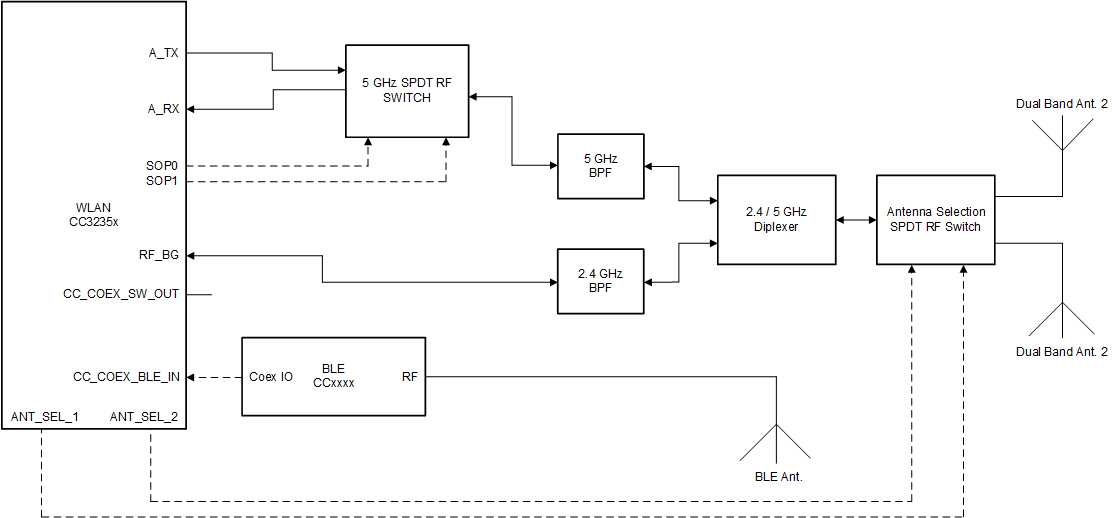 Figure 10-6 Coexistence Solution with Wi-Fi Antenna Selection and dedicated BLE antenna
Figure 10-6 Coexistence Solution with Wi-Fi Antenna Selection and dedicated BLE antenna