SBAS649B June 2021 – June 2022 DAC12DL3200
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics - DC Specifications
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics - Power Consumption
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics - AC Specifications
- 6.8 Timing Requirements
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 DAC Output Modes
- 7.3.2 DAC Output Interface
- 7.3.3 LVDS Interface
- 7.3.4 Multi-Device Synchronization (SYSREF+/-)
- 7.3.5 Alarms
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.2.1 DAC Output Structure
DAC12DL3200 analog output structure is shown in Figure 7-9 for one DAC channel. The outputs VOUTx+/- must have a DC path to an external supply voltage, and the DAC sink current from the external supply. A differential termination resistance sits between the two current output pins, VOUTx+/-. The current steering switch array connects to the outputs and steers current between the output pins based on the digital code. A constant DC current bias, IBIAS, draws current from both outputs regardless of the digital code.
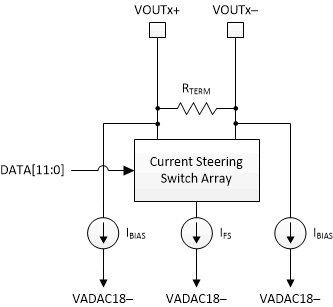 Figure 7-9 DAC12DL3200 Analog Output
Structure
Figure 7-9 DAC12DL3200 Analog Output
StructureExamples of conversions from digital codes to currents on the VOUTx+/- outputs are given in Table 7-2. The currents provided include both the current steered portion and the bias currents on each leg.
| 2's COMPLEMENT | IOUTx+ CURRENT | IOUTx- CURRENT |
|---|---|---|
| 0111 1111 1111 | IFS + IBIAS | IBIAS |
| 0011 1111 1111 | ¾ IFS + IBIAS | ¼ IFS + IBIAS |
| 0000 0000 0000 | ½ IFS + IBIAS | ½ IFS + IBIAS |
| 1100 0000 0001 | ¼ IFS + IBIAS | ¾ IFS + IBIAS |
| 1000 0000 0000 | IBIAS | IFS + IBIAS |