SLAS536D September 2007 – November 2021 DAC5662A
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configurations and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics, AC
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics, DC
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PFB|48
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.2 Analog Outputs
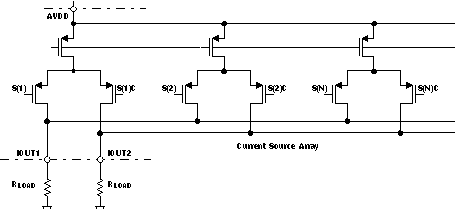 Figure 8-1 Analog Outputs
Figure 8-1 Analog OutputsThe DAC5662A provides two complementary current outputs, IOUT1 and IOUT2. The simplified circuit of the analog output stage representing the differential topology is shown in Figure 8-1. The output impedance of IOUT1 and IOUT2 results from the parallel combination of the differential switches, along with the current sources and associated parasitic capacitances.
The signal voltage swing that may develop at the two outputs, IOUT1 and IOUT2, is limited by a negative and positive compliance. The negative limit of –1 V is given by the breakdown voltage of the CMOS process and exceeding it compromises the reliability of the DAC5662A or even causes permanent damage. With the full-scale output set to 20 mA, the positive compliance equals 1.2 V. Note that the compliance range decreases to about 1 V for a selected output current of I(OUTFS) = 2 mA. Care should be taken that the configuration of DAC5662A does not exceed the compliance range to avoid degradation of the distortion performance and integral linearity.
Best distortion performance is typically achieved with the maximum full-scale output signal limited to approximately 0.5 VPP. This is the case for a 50-Ω doubly terminated load and a 20-mA full-scale output current. A variety of loads can be adapted to the output of the DAC5662A by selecting a suitable transformer while maintaining optimum voltage levels at IOUT1 and IOUT2. Furthermore, using the differential output configuration in combination with a transformer will be instrumental for achieving excellent distortion performance. Common-mode errors, such as even-order harmonics or noise, can be substantially reduced. This is particularly the case with high output frequencies.
For those applications requiring the optimum distortion and noise performance, it is recommended to select a full-scale output of 20 mA. A lower full-scale range of 2 mA may be considered for applications that require low power consumption, but can tolerate a slight reduction in performance level.