DLPS194A November 2020 – June 2022 DLP670S
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 Storage Conditions
- 6.3 ESD Ratings
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 Capacitance at Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.8 Timing Requirements
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics
- 6.10 System Mounting Interface Loads
- 6.11 Micromirror Array Physical Characteristics
- 6.12 Micromirror Array Optical Characteristics
- 6.13 Window Characteristics
- 6.14 Chipset Component Usage Specification
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- FYR|350
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
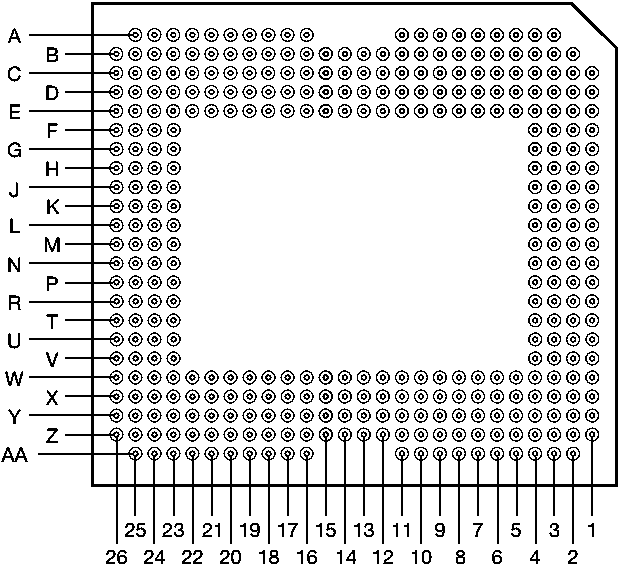 Figure 5-1 FYR Package350-Pin CPGABottom View
Figure 5-1 FYR Package350-Pin CPGABottom ViewCAUTION: To ensure reliable, long-term operation of the DLP670S DMD, it is critical to properly manage the layout and operation of the signals identified in the table below. For specific details and guidelines, refer to Section 10.1 before designing the board. |
Table 5-1 Pin Functions(1)
| PIN(2) | TYPE (I/O/P) | SIGNAL | DATA RATE(4) | INTERNAL TERM(5) | DESCRIPTION | TRACE (mils)(6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||||
| DATA INPUTS | |||||||
| D_AN(0) | C7 | Input | 2xLVDS | DDR | Differential | LVDS pair for Data Bus A (15:0) | 563 |
| D_AP(0) | C8 | ||||||
| D_AN(1) | D4 | ||||||
| D_AP(1) | E4 | ||||||
| D_AN(2) | C5 | ||||||
| D_AP(2) | C4 | ||||||
| D_AN(3) | D6 | ||||||
| D_AP(3) | C6 | ||||||
| D_AN(4) | D8 | ||||||
| D_AP(4) | D7 | ||||||
| D_AN(5) | D3 | ||||||
| D_AP(5) | E3 | ||||||
| D_AN(6) | B3 | ||||||
| D_AP(6) | C3 | ||||||
| D_AN(7) | E11 | ||||||
| D_AP(7) | E10 | ||||||
| D_AN(8) | E6 | ||||||
| D_AP(8) | E5 | ||||||
| D_AN(9) | B10 | ||||||
| D_AP(9) | C10 | ||||||
| D_AN(10) | B8 | ||||||
| D_AP(10) | B9 | ||||||
| D_AN(11) | C13 | ||||||
| D_AP(11) | C14 | ||||||
| D_AN(12) | D15 | ||||||
| D_AP(12) | E15 | ||||||
| D_AN(13) | B12 | ||||||
| D_AP(13) | B13 | ||||||
| D_AN(14) | B15 | ||||||
| D_AP(14) | B16 | ||||||
| D_AN(15) | C16 | ||||||
| D_AP(15) | C17 | ||||||
| D_BN(0) | Y8 | Input | 2xLVDS | DDR | Differential | LVDS pair for Data Bus B (15:0) | 563 |
| D_BP(0) | Y7 | ||||||
| D_BN(1) | X4 | ||||||
| D_BP(1) | W4 | ||||||
| D_BN(2) | Z3 | ||||||
| D_BP(2) | Y3 | ||||||
| D_BN(3) | X6 | ||||||
| D_BP(3) | Y6 | ||||||
| D_BN(4) | X8 | ||||||
| D_BP(4) | X7 | ||||||
| D_BN(5) | X3 | ||||||
| D_BP(5) | W3 | ||||||
| D_BN(6) | W15 | ||||||
| D_BP(6) | X15 | ||||||
| D_BN(7) | W11 | ||||||
| D_BP(7) | W10 | ||||||
| D_BN(8) | W6 | ||||||
| D_BP(8) | W5 | ||||||
| D_BN(9) | AA9 | ||||||
| D_BP(9) | AA10 | ||||||
| D_BN(10) | Z8 | ||||||
| D_BP(10) | Z9 | ||||||
| D_BN(11) | Y13 | ||||||
| D_BP(11) | Y14 | ||||||
| D_BN(12) | Z10 | ||||||
| D_BP(12) | Y10 | ||||||
| D_BN(13) | Z12 | ||||||
| D_BP(13) | Z13 | ||||||
| D_BN(14) | Z15 | ||||||
| D_BP(14) | Z16 | ||||||
| D_BN(15) | Y16 | ||||||
| D_BP(15) | Y17 | ||||||
| D_CN(0) | C18 | Input | 2xLVDS | DDR | Differential | LVDS pair for Data Bus C (15:0) | 563 |
| D_CP(0) | C19 | ||||||
| D_CN(1) | A20 | ||||||
| D_CP(1) | A19 | ||||||
| D_CN(2) | L23 | ||||||
| D_CP(2) | K23 | ||||||
| D_CN(3) | C23 | ||||||
| D_CP(3) | B23 | ||||||
| D_CN(4) | G23 | ||||||
| D_CP(4) | H23 | ||||||
| D_CN(5) | H24 | ||||||
| D_CP(5) | G24 | ||||||
| D_CN(6) | B18 | ||||||
| D_CP(6) | B19 | ||||||
| D_CN(7) | C21 | ||||||
| D_CP(7) | B21 | ||||||
| D_CN(8) | D23 | ||||||
| D_CP(8) | E23 | ||||||
| D_CN(9) | D25 | ||||||
| D_CP(9) | C25 | ||||||
| D_CN(10) | L24 | ||||||
| D_CP(10) | K24 | ||||||
| D_CN(11) | K25 | ||||||
| D_CP(11) | J25 | ||||||
| D_CN(12) | B24 | ||||||
| D_CP(12) | A24 | ||||||
| D_CN(13) | D26 | ||||||
| D_CP(13) | C26 | ||||||
| D_CN(14) | G25 | ||||||
| D_CP(14) | F25 | ||||||
| D_CN(15) | K26 | ||||||
| D_CP(15) | J26 | ||||||
| D_DN(0) | Y18 | Input | 2xLVDS | DDR | Differential | LVDS pair for Data Bus D (15:0) | 563 |
| D_DP(0) | Y19 | ||||||
| D_DN(1) | AA20 | ||||||
| D_DP(1) | AA19 | ||||||
| D_DN(2) | N23 | ||||||
| D_DP(2) | P23 | ||||||
| D_DN(3) | Y23 | ||||||
| D_DP(3) | Z23 | ||||||
| D_DN(4) | U23 | ||||||
| D_DP(4) | T23 | ||||||
| D_DN(5) | T24 | ||||||
| D_DP(5) | U24 | ||||||
| D_DN(6) | Z18 | ||||||
| D_DP(6) | Z19 | ||||||
| D_DN(7) | Y21 | ||||||
| D_DP(7) | Z21 | ||||||
| D_DN(8) | X23 | ||||||
| D_DP(8) | W23 | ||||||
| D_DN(9) | X25 | ||||||
| D_DP(9) | Y25 | ||||||
| D_DN(10) | N24 | ||||||
| D_DP(10) | P24 | ||||||
| D_DN(11) | P25 | ||||||
| D_DP(11) | R25 | ||||||
| D_DN(12) | Z24 | ||||||
| D_DP(12) | AA24 | ||||||
| D_DN(13) | X26 | ||||||
| D_DP(13) | Y26 | ||||||
| D_DN(14) | U25 | ||||||
| D_DP(14) | V25 | ||||||
| D_DN(15) | P26 | ||||||
| D_DP(15) | R26 | ||||||
| DCLK_AN | B6 | Input | LVDS | Differential | LVDS pair for Data Clock A (7) | 563 | |
| DCLK_AP | B5 | ||||||
| DCLK_BN | Z6 | Input | LVDS | Differential | LVDS pair for Data Clock B (7) | 563 | |
| DCLK_BP | Z5 | ||||||
| DCLK_CN | G26 | Input | LVDS | Differential | LVDS pair for Data Clock C (7) | 563 | |
| DCLK_CP | F26 | ||||||
| DCLK_DN | U26 | Input | LVDS | Differential | LVDS pair for Data Clock D (7) | 563 | |
| DCLK_DP | V26 | ||||||
| DATA CONTROL INPUTS | |||||||
| SCTRL_AN | A10 | Input | LVDS | DDR | Differential | LVDS pair for Serial Control (Sync) A(7) | 563 |
| SCTRL_AP | A9 | ||||||
| SCTRL_BN | Y4 | Input | LVDS | DDR | Differential | LVDS pair for Serial Control (Sync) B(7) | 563 |
| SCTRL_BP | Y5 | ||||||
| SCTRL_CN | E24 | Input | LVDS | DDR | Differential | LVDS pair for Serial Control (Sync) C(7) | 563 |
| SCTRL_CP | D24 | ||||||
| SCTRL_DN | W24 | Input | LVDS | DDR | Differential | LVDS pair for Serial Control (Sync) D(7) | 563 |
| SCTRL_DP | X24 | ||||||
| DAD CONTROL INPUTS | |||||||
| RESET_ADDR(0) | R3 | Input | LVCMOS | Pulldown | Reset Driver Address Select. Bond pad connects to an internal pulldown circuit.(7) | ||
| RESET_ADDR(1) | R4 | ||||||
| RESET_ADDR(2) | T3 | ||||||
| RESET_ADDR(3) | U2 | ||||||
| RESET_MODE(0) | P4 | Input | LVCMOS | Pulldown | Reset Driver Mode Select. Bond pad connects to an internal pulldown circuit.(7) | ||
| RESET_MODE(1) | V3 | ||||||
| RESET_OEZ | R2 | Input | LVCMOS | Pullup | Active Low. Output Enable signal for internal Reset Driver circuitry. Bond Pad connects to an internal pullup circuit.(7) | ||
| RESET_SEL(0) | P3 | Input | LVCMOS | Pulldown | Reset Driver Level Select. Bond pad connects to an internal pulldown circuit.(7) | ||
| RESET_SEL(1) | V2 | ||||||
| RESET_STROBE | W8 | Input | LVCMOS | Pulldown | Rising edge on RESET_STROBE latches in the control signals. Bond pad connects to an internal pulldown circuit.(7) | ||
| RESETZ | U4 | Input | LVCMOS | Pullup | Active Low. Places reset circuitry in known VOFFSET state. Bond pad connects to an internal pulldown circuit.(7) | ||
| SCP CONTROL | |||||||
| SCPCLK | W17 | Input | LVCMOS | Pulldown | Serial Communications Port Clock. SCPCLK is only active when SCPENZ goes low. Bond pad connects to an internal pulldown circuit.(7) | ||
| SCPDI | W18 | Input | LVCMOS | SDR | Pulldown | Serial Communications Port Data. Synchronous to the Rising Edge of SCPCLK. Bond pad connects to an internal pulldown circuit.(7) | |
| SCPENZ | X18 | Input | LVCMOS | Pulldown | Active Low Serial Communications Port Enable. Bond pad connects to an internal pulldown circuit.(7) | ||
| SCPDO | W16 | Output | LVCMOS | SDR | Serial Communications Port output | ||
| EXTERNAL REGULATOR SIGNALS | |||||||
| EN_BIAS | J4 | Output | LVCMOS | Active High. Enable signal for external VBIAS regulator | |||
| EN_OFFSET | H3 | Output | LVCMOS | Active High. Enable signal for external VOFFSET regulator | |||
| EN_RESET | J3 | Output | LVCMOS | Active High. Enable signal for external VRESET regulator | |||
| PG_BIAS | K3 | Input | LVCMOS | Active low fault from external VBIAS regulator(7) | |||
| PG_OFFSET | F2 | Input | LVCMOS | Active low fault from external VOFFSET regulator(7) | |||
| PG_RESET | F3 | Input | LVCMOS | Active low fault from external VRESET regulator(7) | |||
| OTHER SIGNALS | |||||||
| RESET_IRQZ | U3 | Output | LVCMOS | Active Low. Output Interrupt to DLP controller (ASIC) | |||
| TEMP_PLUS | E16 | Input | Analog | Temperature Sensor Diode Anode(3) | |||
| TEMP_MINUS | E17 | Input | Analog | Temperature Sensor Diode Cathode (3) | |||
| POWER | |||||||
| VBIAS | A5, A6, A7, AA5, AA6, AA7 | Power | Analog | Power supply for Positive Bias level of micromirror reset signal | |||
| VCC | A8, B2, C1, D1, D10, D12, D19, E1, E19, E20, E21, F1, K1, L1, M1, N1, P1,V1, W1, W19, W20, W21, X1, X10, X12, X19, Y1, Z1, Z2, AA2, AA8, | Power | Analog | Power supply for low voltage CMOS logic. Power supply for normal high voltage at micromirror address electrodes. Power supply for Offset level during the power-down sequence | |||
| VCCI | A11, A16, A17, A18, A21, A22, A23, AA11, AA16, AA17, AA18, AA21, AA22, AA23, | Power | Analog | Power supply for low voltage CMOS LVDS interface | |||
| VOFFSET | A3, A4, A25, B26, L26, M26, N26, Z26, AA3, AA4, AA25 | Power | Analog | Power supply for high voltage CMOS logic. Power supply for stepped high voltage at micromirror address electrodes. Power supply for Offset level of MBRST(15:0) | |||
| VRESET | G1, H1, J1, R1, T1, U1 | Power | Analog | Power supply for Negative Reset level of micromirror reset signal | |||
| VSS (Ground) | B4, B7, B11, B14, B17, B20, B22, B25, C2, C9, C20, C22, C24, D2, D5, D9, D11, D14, D18, D20, D21, D22, E2, E7, E9, E22, E25, E26, F4, F23, F24, H2, H4, H25, H26, J23, J24, K2, L2, L3, L4, L25, M2, M3, M4, M23, M24, M25, N2, N3, N25, P2,R23, R24, T2, T4, T25, T26, V4, V23, V24, W2, W7, W9, W22, W25, W26, X2, X5, X9, X11, X14, X20, X21, X22, Y2, Y9, Y20, Y22, Y24, Z4, Z7, Z11, Z14, Z17, Z20, Z22, Z25 | Ground | Common Return for all power | ||||
| RESERVED SIGNALS | |||||||
| RESERVED_PFE | E18 | Ground | LVCMOS | Do Not Connect on the printed circuit board (PCB) | |||
| RESERVED_TM | G4 | Ground | LVCMOS | Do Not Connect on the printed circuit board (PCB) | |||
| RESERVED_TP0 | E8 | Input | Analog | Do Not Connect on the printed circuit board (PCB) | |||
| RESERVED_TP1 | J2 | Input | Analog | Do Not Connect on the printed circuit board (PCB) | |||
| RESERVED_TP2 | G2 | Input | Analog | Do Not Connect on the printed circuit board (PCB) | |||
| RESERVED_BA | N4 | Output | LVCMOS | Do Not Connect on the printed circuit board (PCB) | |||
| RESERVED_BB | K4 | Output | LVCMOS | Do Not Connect on the printed circuit board (PCB) | |||
| RESERVED_BC | X17 | Output | LVCMOS | Do Not Connect on the printed circuit board (PCB) | |||
| RESERVED_BD | D17 | Output | LVCMOS | Do Not Connect on the printed circuit board (PCB) | |||
| NO CONNECT | C11, C12, C15, D13, D16, E12, E13, E14, W13, W12, W14, X13, X16, Y11, Y12, Y15, | NC | For TI Test Purposes only, Do Not Connect on the printed circuit board (PCB) | ||||
(1) The DLP670S DMD is a component of a DLP® chipset. Reliable
function and operation of the DLP670S DMD requires that it be used in
conjunction with the other components of the applicable DLP® chipset, including
those components that contain or implement TI DMD control technology. TI DMD
control technology is the TI technology and devices for operating or controlling
a DLP® DMD.
(2) The following power supplies are required for all DMD operating
modes: VSS, VBIAS, VCC, VCCI, VOFFSET, and VRESET.
(3) VSS must be connected for proper DMD operation.
(4) DDR = Double Data Rate, SDR = Single Data Rate, Refer to the
Timing
Requirements for specifications and relationships.
(5) Internal term = CMOS level internal termination. Refer to Recommended
Operating Conditions for differential termination specification.
(6) Dielectric Constant for the DMD FYR (S610) ceramic package is
approximately 9.6. For the package trace lengths shown: Propagation Speed = 11.8
/ sqrt(9.6) = 3.808 in/ns. Propagation Delay = 0.262 ns/in = 10.315 ps/mm.
(7) These signals are very sensitive to noise or intermittent power
connections, which can cause irreversible DMD micromirror array damage or, to a
lesser extent, image disruption. Consider this precaution during DMD board
design and manufacturer handling of the DMD sub-assemblies.