DLPS243B October 2022 – September 2023 DLP801XE
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 Storage Conditions
- 6.3 ESD Ratings
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 12
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 Timing Requirements
- 16
- 6.8 System Mounting Interface Loads
- 18
- 6.9 Micromirror Array Physical Characteristics
- 20
- 6.10 Micromirror Array Optical Characteristics
- 22
- 6.11 Window Characteristics
- 6.12 Chipset Component Usage Specification
-
7 Detailed
Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Optical Interface and System Image Quality Considerations
- 7.6 Micromirror Array Temperature Calculation
- 7.7 Micromirror Power Density Calculation
- 7.8 Window Aperture Illumination Overfill Calculation
- 7.9 Micromirror Landed-On/Landed-Off Duty Cycle
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- FYV|350
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
8.2.3 Application Curve
In a typical projector application, the luminous flux on the screen from the DMD depends on the optical design of the projector. The efficiency and total power of the illumination optical system and the projection optical system determines the overall light output of the projector. The DMD is inherently a linear spatial light modulator, so its efficiency just scales the light output. Figure 8-3 describes the relationship of laser input optical power to light output for a laser-phosphor illumination system, where the phosphor is not at its thermal quenching limit.
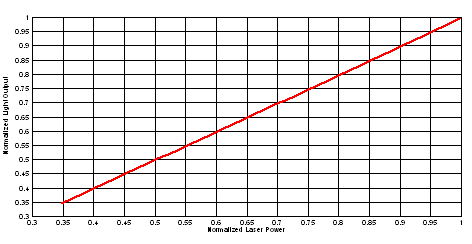 Figure 8-3 Normalized Light Output vs. Normalized Laser Power for Laser Phosphor Illumination
Figure 8-3 Normalized Light Output vs. Normalized Laser Power for Laser Phosphor Illumination