DLPS132 May 2018 DLPA4000
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Description
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Supply and Monitoring
- 7.3.2 Illumination
- 7.3.3 External Power MOSFET Selection
- 7.3.4 DMD Supplies
- 7.3.5 Buck Converters
- 7.3.6 Auxiliary LDOs
- 7.3.7 Measurement System
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PFD|100
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PFD|100
Orderable Information
7.3.3.3 On-resistance RDS(on)
Consider two issues relative to the drain-to-source on-resistance (RDS(on)) to select a MOSFET. The first consideration is for the high-side MOSFET of the illumination buck-converter the RDS(ON) is a factor in the over-current detection. Secondly, for the other four MOSFETs the power dissipation drives the choice of the MOSFETs RDS(on).
The DLPA4000 measures the drain-to-source voltage drop of the high-side MOSFET when energized to detect an overcurrent situation. When the device detection circuit triggers, and de-energizes the high-side FET, the high-side drive over current threshold (VDC-Th ) is 185 mV . Use Equation 8 to calculate the actual current level, (IOC) that trigger the overcurrent detection.
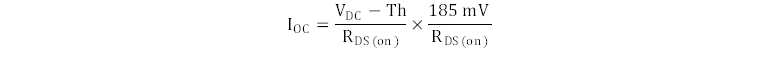
Use the on-resistance specification listed in the MOSFET datasheet for a high-temperature condition.For example, the CSD87350Q5D NexFET specifies the on-resistance of 5 mΩ at 125 °C. The overcurrent level for a design that uses this MOSFET is 37 A. This MOSFET is a good choice for a 32-A application.
Power dissipation due to conduction losses determines the on-resistance selection for the low-side MOSFET and the three LED selection MOSFETs. Use Equation 9 to calculate the power dissipated in these MOSFETs.
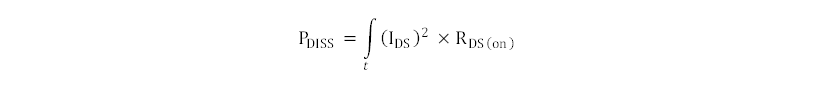
where
- IDS is the FET current
The lower the on-resistance the lower the power dissipation. For example, the on-resistance specified for the CSD17556Q5B MOSFET is 1.2 mΩ. For a drain-to-source current of 32 A with a duty cycle of 25% (when the MOSFET is used as LED selection switch) the dissipation is approximately 0.3 W.