DLPS132 May 2018 DLPA4000
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Description
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Supply and Monitoring
- 7.3.2 Illumination
- 7.3.3 External Power MOSFET Selection
- 7.3.4 DMD Supplies
- 7.3.5 Buck Converters
- 7.3.6 Auxiliary LDOs
- 7.3.7 Measurement System
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PFD|100
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PFD|100
Orderable Information
10.1.1.3 Return Current from LEDs and RSense
The RSENSE resistor (R72) senses the LED current. Connect the RLIM_K_1 and RLIM_K_2 lines close to the top side of the measurement resistor to accurately measure the LED current. Connect the RLIM_BOT_K_1 and RLIM_BOT_K_2 lines close to the bottom side of the measurement resistor to accurately measure the LED current.
The switched LED current flows through the RLIM resistor and the RSENSE resistor. Design a low-ohmic ground connection from the RSENSE resistor that retuns to the input voltage connector. Make sure the PGND return has a dedicated plane on the top layer that returns to the connector. However, the PGND top layer must have vias placed from inside the top layer to the internal PGND plane. Make sure the PGND vias underneath the power block are compliant with the power block layout thermal guidelines. See CSD87350Q5D data sheet for guidelines..
Make sure the designer considers the entire return path for current from the LED connector through the RLIM resistor plane and the RSENSE resistor (R72) during layout. Any obstacles between the LED connectors and the PGND on the input power connector can cause power reduction. Similar obstacles can cause possible image artifacts due to slow LED turn-on times. See the reference design for a suggested placement and plane sizes.
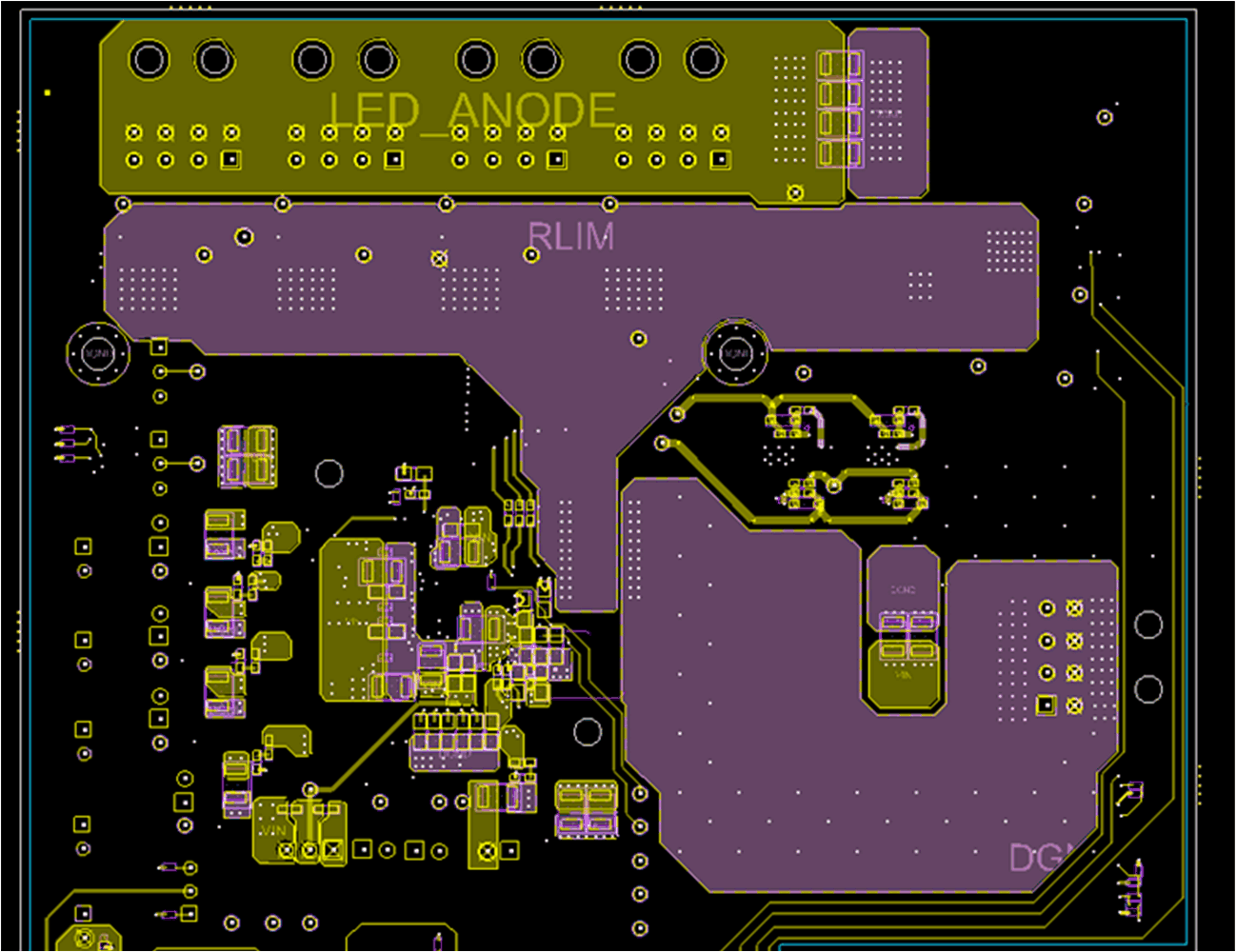 Figure 28. Current Return Path
Figure 28. Current Return Path