SLVSD12D May 2015 – July 2019 DRV8305-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Integrated Three-Phase Gate Driver
- 7.3.2 INHx/INLx: Gate Driver Input Modes
- 7.3.3 VCPH Charge Pump: High-Side Gate Supply
- 7.3.4 VCP_LSD LDO: Low-Side Gate Supply
- 7.3.5 GHx/GLx: Half-Bridge Gate Drivers
- 7.3.6 DVDD and AVDD: Internal Voltage Regulators
- 7.3.7 VREG: Voltage Regulator Output
- 7.3.8 Protection Features
- 7.3.9 Undervoltage Warning (UVFL), Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO), and Overvoltage (OV) Protection
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 Status Registers
- 7.6.2
Control Registers
- 7.6.2.1 HS Gate Drive Control (Address = 0x5)
- 7.6.2.2 LS Gate Drive Control (Address = 0x6)
- 7.6.2.3 Gate Drive Control (Address = 0x7)
- 7.6.2.4 IC Operation (Address = 0x9)
- 7.6.2.5 Shunt Amplifier Control (Address = 0xA)
- 7.6.2.6 Voltage Regulator Control (Address = 0xB)
- 7.6.2.7 VDS Sense Control (Address = 0xC)
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PHP|48
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PHP|48
Orderable Information
9.1 Power Supply Consideration in Generator Mode
When the motor shaft of BLDC or PMSM motor is turned by an external force, the motor windings will generate a voltage on the motor inputs. This condition is known as generator mode or motor back-drive. In the generator mode, a positive voltage can be observed on SHx pins of the device. If there is a switch between VDRAIN and PVDD (SWVDRAIN in Figure 24 ), and the following conditions exist in the system, the absolute maximum voltage of VCPH with respect to PVDD must be reviewed:
- Generator mode
- SWVDRAIN is off
- PVDD and VCPH are low voltage (for example, PVDD = 0 V)
If SHx voltage (VSHx) exceeds the VCPH voltage, the VCPH voltage starts following VSHx because of the device internal diodes D1 and D2 (or D3). If the VCPH-PVDD voltage exceeds the absolute maximum voltage of DRV8305-Q1, the ESD diode D4 starts conducting, and results in a big current from SHx to PVDD through the diodes D2, D1, and D4. To avoid this condition, TI recommends to add an external diode DVDRAIN_PVDD between VDRAIN and PVDD.
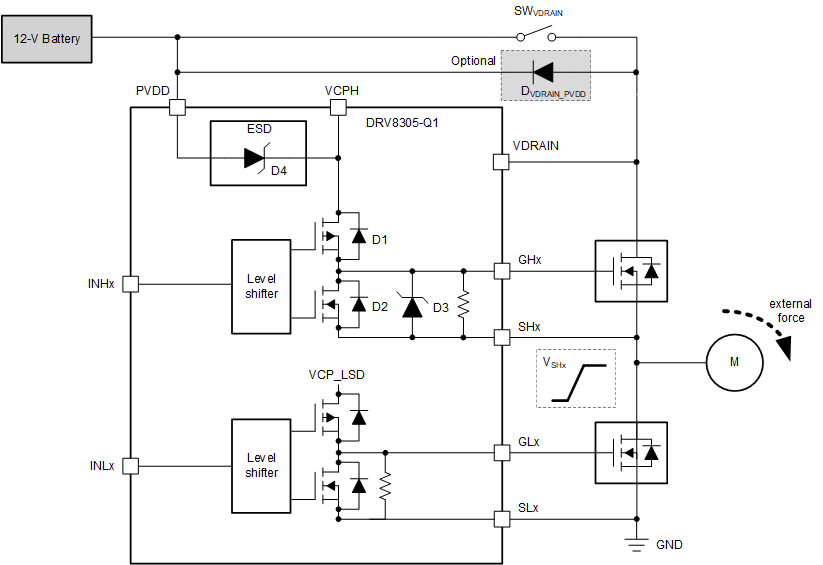 Figure 24. Power Supply Consideration in Generator Mode
Figure 24. Power Supply Consideration in Generator Mode