SLOSE60B May 2020 – May 2022 DRV8424E , DRV8425E
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Orderable Information
7.3.4.4 Smart tune Ripple Control
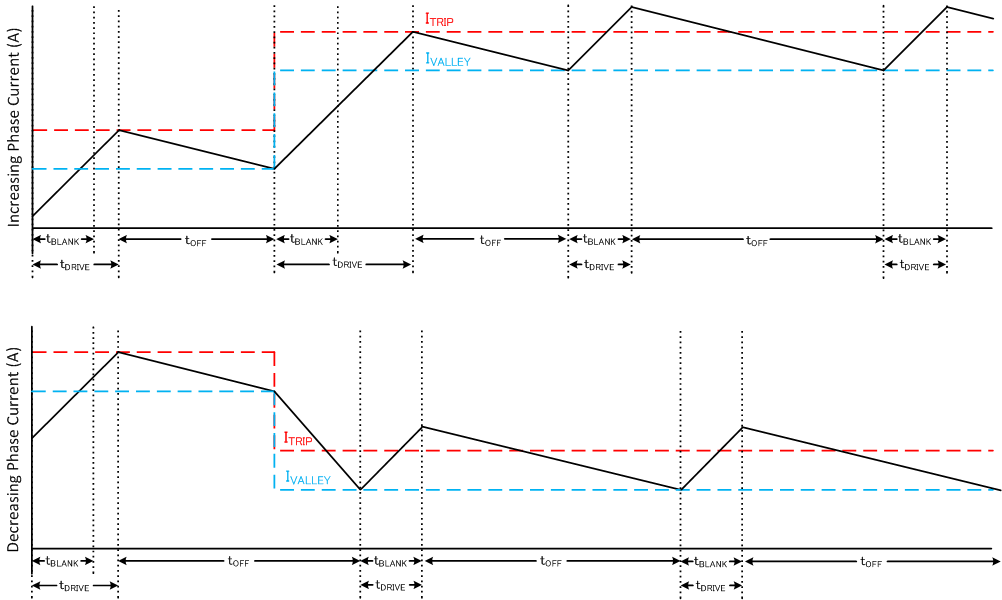 Figure 7-9 Smart tune Ripple Control Decay Mode
Figure 7-9 Smart tune Ripple Control Decay ModeSmart tune Ripple Control operates by setting an IVALLEY level alongside the ITRIP level. When the current level reaches ITRIP, instead of entering slow decay until the tOFF time expires, the driver enters slow decay until IVALLEY is reached. Slow decay operates similar to mode 1 in which both low-side MOSFETs are turned on allowing the current to recirculate. In this mode, tOFF varies depending on the current level and operating conditions.
This method allows much tighter regulation of the current level increasing motor efficiency and system performance. Smart tune Ripple Control can be used in systems that can tolerate a variable off-time regulation scheme to achieve small current ripple in the current regulation.
The ripple current in this decay mode is 19mA + 1% of the ITRIP at a specific microstep level.