SLVSBA4F June 2012 – April 2021 DRV8837 , DRV8838
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DSG|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DSG|8
Orderable Information
9.3 Power Dissipation
Power dissipation in the DRV883x family of devices is dominated by the power dissipated in the output FET resistance, or rDS(on). Use Equation 1 to estimate the average power dissipation when running a stepper motor.
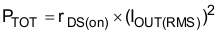
where
- PTOT is the total power dissipation
- rDS(on) is the resistance of the HS plus LS FETs
- IOUT(RMS) is the rms or dc output current being supplied to the load
The maximum amount of power that can be dissipated in the device is dependent on ambient temperature and heatsinking.
The value of rDS(on) increases with temperature, so as the device heats, the power dissipation increases.
The DRV883x family of devices has thermal shutdown protection. If the die temperature exceeds approximately 150°C, the device is disabled until the temperature drops to a safe level.
Any tendency of the device to enter thermal shutdown is an indication of either excessive power dissipation, insufficient heatsinking, or too high an ambient temperature.