SNOSCY5B August 2014 – April 2015 FDC1004
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Typical Application
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Applications and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DSC|10
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
The FDC1004 measures the capacitances connected between the CINn (n=1..4) pins and GND. To get the best result, locate the FDC1004 as close as possible to the capacitive sensor. Minimize the connection length between the sensor and FDC1004 CINn pins and between the sensor ground and the FDC1004 GND pin. If a shielded cable is used for remote sensor connection, the shield should be connected to the SHLDm (m=1...2) pin according to the configured measurement.
11.2 Layout Example
Figure 17 below is optimized for applications where the sensor is not too far from the FDC1004. Each channel trace runs between 2 shield traces. This layout allows the measurements of 4 single ended capacitance or 2 differential capacitance. The ground plane needs to be far from the channel traces, it is mandatory around or below the I2C pin.
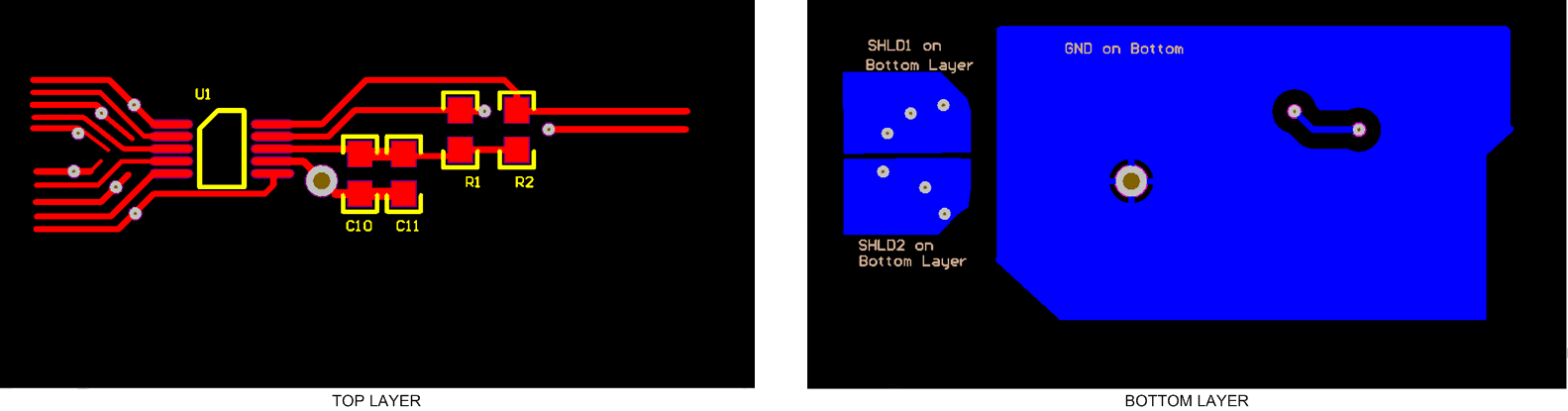 Figure 17. Layout
Figure 17. Layout