SNOS412Q February 2000 – January 2023 LM1117
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- KTT|3
Orderable Information
8.1 Overview
The LM1117 adjustable version develops a 1.25-V reference voltage, VREF, between the output and the adjust pin. As shown in Figure 8-1, this voltage is applied across resistor R1 to generate a constant current I1. The current IADJ from the adjust pin can introduce error to the output, but because this current is very small (60 μA) compared to the I1 and very constant with line and load changes, the error can be ignored. The constant current I1 then flows through the output set resistor R2 and sets the output voltage to the desired level.
For fixed voltage devices, R1 and R2 are integrated inside the devices.
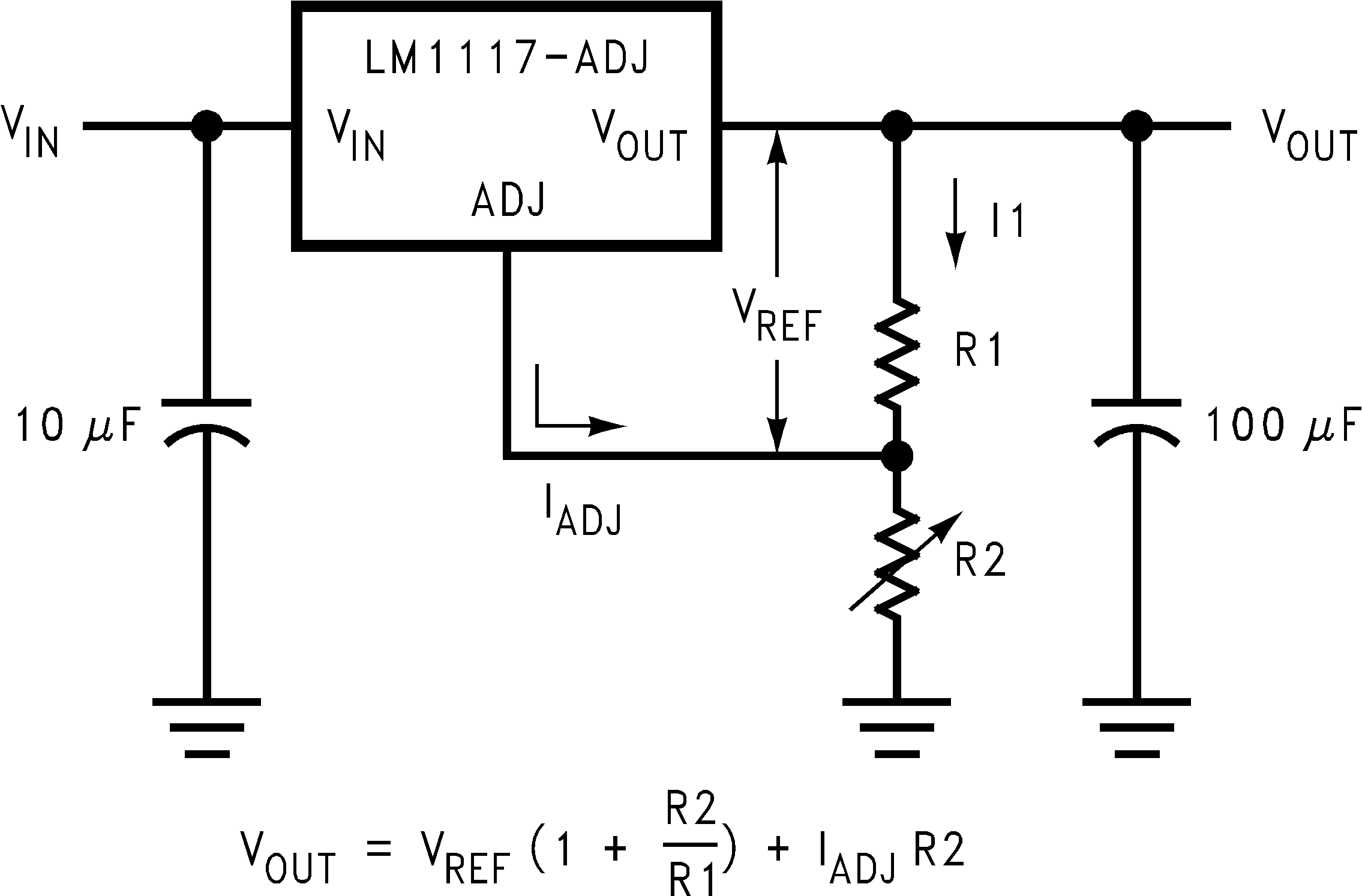 Figure 8-1 Basic Adjustable Regulator
Figure 8-1 Basic Adjustable Regulator