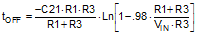SNVS726F July 2011 – March 2018 LM25118
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 R7 = RT
- 8.2.2.3 Inductor Selection – L1
- 8.2.2.4 R13 = RSENSE
- 8.2.2.5 C15 = CRAMP
- 8.2.2.6 Inductor Current Limit Calculation
- 8.2.2.7 C9 - C12 = Output Capacitors
- 8.2.2.8 D1
- 8.2.2.9 D4
- 8.2.2.10 C1 – C5 = Input Capacitors
- 8.2.2.11 C20
- 8.2.2.12 C8
- 8.2.2.13 C16 = CSS
- 8.2.2.14 R8, R9
- 8.2.2.15 R1, R3, C21
- 8.2.2.16 R2
- 8.2.2.17 Snubber
- 8.2.2.18 Error Amplifier Configuration
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Orderable Information
8.2.2.15 R1, R3, C21
A voltage divider can be connected to the UVLO pin to set a minimum operating voltage VIN(UVLO) for the regulator. If this feature is required, the easiest approach to select the divider resistor values is to choose a value for R1 between 10 kΩ and 100 kΩ, while observing the minimum value of R1 necessary to allow the UVLO switch to pull the UVLO pin low. This value is:
R1 ≥ 1000 × VIN(MAX)
R1 ≥ 75 k
R3 is then calculated from:

Because VIN(MIN) for our example is 5 V, set VIN(UVLO) to 4 V for some margin in component tolerances and input ripple.
R1 = 75 k is chosen because it is a standard value
R3 = 29.332 k is calculated from Equation 44. 29.4 k was used because it is a standard value
Capacitor C21 provides filtering for the divider and the off time of the hiccup duty cycle during current limit. The voltage at the UVLO pin should never exceed 15 V when using an external set-point divider. It may be necessary to clamp the UVLO pin at high input voltages.
Knowing the desired off time during hiccup current limit, the value of C21 is given by:
Notice that tOFF varies with VIN
In this example, C21 was chosen to be 0.1 µF. This will set the tOFF time to 723 µs with VIN = 12 V.