SNVSC11 May 2022 LM25143-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Input Voltage Range (VIN)
- 9.3.2 High-Voltage Bias Supply Regulator (VCC, VCCX, VDDA)
- 9.3.3 Enable (EN1, EN2)
- 9.3.4 Power-Good Monitor (PG1, PG2)
- 9.3.5 Switching Frequency (RT)
- 9.3.6 Clock Synchronization (DEMB)
- 9.3.7 Synchronization Out (SYNCOUT)
- 9.3.8 Spread Spectrum Frequency Modulation (DITH)
- 9.3.9 Configurable Soft Start (SS1, SS2)
- 9.3.10 Output Voltage Setpoint (FB1, FB2)
- 9.3.11 Minimum Controllable On Time
- 9.3.12 Error Amplifier and PWM Comparator (FB1, FB2, COMP1, COMP2)
- 9.3.13 Slope Compensation
- 9.3.14 Inductor Current Sense (CS1, VOUT1, CS2, VOUT2)
- 9.3.15 Hiccup Mode Current Limiting (RES)
- 9.3.16 High-Side and Low-Side Gate Drivers (HO1, HO2, LO1, LO2, HOL1, HOL2, LOL1, and LOL2)
- 9.3.17 Output Configurations (MODE, FB2)
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Applications
- 10.2.1 Design 1 – 5-V and 3.3-V Dual-Output Buck Regulator for Automotive Applications
- 10.2.2 Design 2 – Two-Phase, 15-A, 2.1-MHz Single-Output Buck Regulator for Automotive ADAS Applications
- 10.2.3 Design 3 – Two-Phase, 50-A, 300-kHz Single-Output Buck Regulator for High-Voltage Automotive Battery Applications
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHA|40
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHA|40
Orderable Information
9.3.15 Hiccup Mode Current Limiting (RES)
The LM25143-Q1 includes an optional hiccup mode protection function that is enabled when a capacitor is connected to the RES pin. In normal operation, the RES capacitor is discharged to ground. If 512 cycles of cycle-by-cycle current limiting occurs, SS is pulled low and the HO and LO outputs are disabled (see Figure 9-6). A 20-μA current source begins to charge the RES capacitor. When the RES voltage increases to 1.2 V, RES is pulled low and the SS capacitor begins to charge. The 512-cycle hiccup counter is reset if four consecutive switching cycles occur without exceeding the current limit threshold. Separate hiccup counters are provided for each channel, but the RES pin is shared by both channels. One channel can be in hiccup protection while the other operates normally. In the event that both channels are in an overcurrent condition triggering hiccup protection, the last hiccup counter to expire pulls RES low and starts the RES capacitor charging cycle. Both channels then restart together when VRES = 1.2 V. If RES is connected to VDDA at power up, the hiccup function is disabled for both channels.
Use Equation 13 to calculate the RES capacitance.
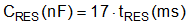
where
- tRES is the specified hiccup delay as shown in Figure 9-6.