SNVSBP3B May 2020 – June 2021 LM62435-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 EN Uses for Enable and VIN UVLO
- 8.3.2 MODE/SYNC Pin Operation
- 8.3.3 PGOOD Output Operation
- 8.3.4 Internal LDO, VCC UVLO, and BIAS Input
- 8.3.5 Bootstrap Voltage and VCBOOT-UVLO (CBOOT Pin)
- 8.3.6 Adjustable SW Node Slew Rate
- 8.3.7 Spread Spectrum
- 8.3.8 Soft Start and Recovery From Dropout
- 8.3.9 Output Voltage Setting
- 8.3.10 Overcurrent and Short Circuit Protection
- 8.3.11 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.12 Input Supply Current
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RJR|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.2.3 Clock Locking
Once a valid synchronization signal is detected, a clock locking procedure is initiated. The LM62435-Q1 receives this signal over the MODE/SYNC pin. After approximately 2048 pulses, the clock frequency completes a smooth transition to the frequency of the synchronization signal without output variation. Note that while the frequency is adjusted suddenly, phase is maintained so the clock cycle that lies between operation at the default frequency and at the synchronization frequency is of intermediate length. This eliminates very long or very short pulses. Once frequency is adjusted, phase is adjusted over a few tens of cycles so that rising synchronization edges correspond to rising SW node pulses.
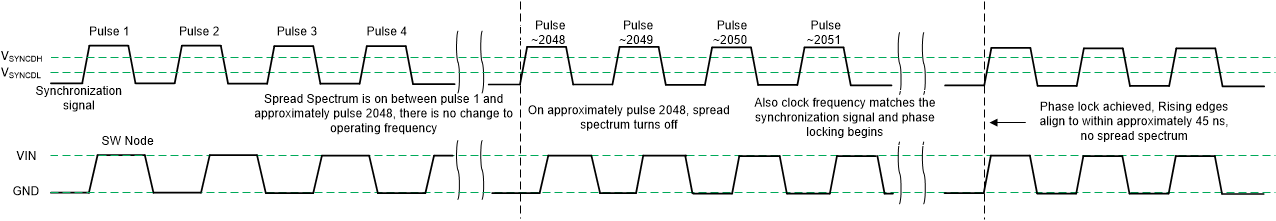
Also note that the LM62435-Q1 turns on spread spectrum after the first edge in the synchronization pulse. See the MODE/SYNC pin description in the Section 6. Upon adjustment of frequency on the approximate 2048th pulse, spread spectrum is turned off. Finally, if the part runs at reduced frequency due to low or high input voltage or during current limit, frequency lock does not occur until the condition causing low frequency operation has been removed.