SNVSBP3B May 2020 – June 2021 LM62435-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 EN Uses for Enable and VIN UVLO
- 8.3.2 MODE/SYNC Pin Operation
- 8.3.3 PGOOD Output Operation
- 8.3.4 Internal LDO, VCC UVLO, and BIAS Input
- 8.3.5 Bootstrap Voltage and VCBOOT-UVLO (CBOOT Pin)
- 8.3.6 Adjustable SW Node Slew Rate
- 8.3.7 Spread Spectrum
- 8.3.8 Soft Start and Recovery From Dropout
- 8.3.9 Output Voltage Setting
- 8.3.10 Overcurrent and Short Circuit Protection
- 8.3.11 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.12 Input Supply Current
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RJR|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.1 EN Uses for Enable and VIN UVLO
Start-up and shutdown are controlled by the EN input and VIN UVLO. For the device to remain in shutdown mode, apply a voltage below VEN_WAKE (0.4 V) to the EN pin. In shutdown mode, the quiescent current drops to 0.6 µA (typical). At a voltage above VEN_WAKE and below VEN, VCC is active and the SW node is inactive. Once the EN voltage is above VEN, the chip begins to switch normally, provided the input voltage is above 3 V.
The EN pin cannot be left floating. The simplest way to enable the operation is to connect the EN pin to VIN, allowing self-start-up of the LM62435-Q1 when VIN drives the internal VCC above its UVLO level. However, many applications benefit from the employment of an enable divider network as shown in Figure 8-1, which establishes a precision input undervoltage lockout (UVLO). This can be used for sequencing, preventing re-triggering of the device when used with long input cables, or reducing the occurrence of deep discharge of a battery power source. Note that the precision enable threshold, VEN, has a 5% tolerance. Hysteresis must be enough to prevent re-triggering. External logic output of another IC can also be used to drive the EN pin, allowing system power sequencing.
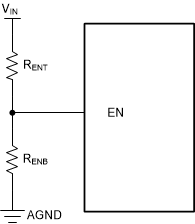 Figure 8-1 VIN UVLO Using the EN pin
Figure 8-1 VIN UVLO Using the EN pinResistor values can be calculated using Equation 1. See Section 9.2.2.11 for additional information.
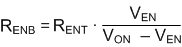
where
- VON is the desired typical start-up input voltage for the circuit being designed