SNAS724A February 2018 – April 2018 LMK05028
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Oscillator Input (XO_P/N)
- 9.3.2 TCXO/OCXO Input (TCXO_IN)
- 9.3.3 Reference Inputs (INx_P/N)
- 9.3.4 Clock Input Interfacing and Termination
- 9.3.5 Reference Input Mux Selection
- 9.3.6 Hitless Switching
- 9.3.7 Gapped Clock Support on Reference Inputs
- 9.3.8 Input Clock and PLL Monitoring, Status, and Interrupts
- 9.3.9
PLL Channels
- 9.3.9.1 PLL Frequency Relationships
- 9.3.9.2 Analog PLL (APLL)
- 9.3.9.3 APLL XO Doubler
- 9.3.9.4 APLL Phase Frequency Detector (PFD) and Charge Pump
- 9.3.9.5 APLL Loop Filter
- 9.3.9.6 APLL Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO)
- 9.3.9.7 APLL VCO Post-Dividers (P1, P2)
- 9.3.9.8 APLL Fractional N Divider (N) With SDM
- 9.3.9.9 REF-DPLL Reference Divider (R)
- 9.3.9.10 TCXO/OCXO Input Doubler and M Divider
- 9.3.9.11 TCXO Mux
- 9.3.9.12 REF-DPLL and TCXO-DPLL Time-to-Digital Converter (TDC)
- 9.3.9.13 REF-DPLL and TCXO-DPLL Loop Filter
- 9.3.9.14 REF-DPLL and TCXO-DPLL Feedback Dividers
- 9.3.10 Output Clock Distribution
- 9.3.11 Output Channel Muxes
- 9.3.12 Output Dividers
- 9.3.13 Clock Outputs (OUTx_P/N)
- 9.3.14 Glitchless Output Clock Start-Up
- 9.3.15 Clock Output Interfacing and Termination
- 9.3.16 Output Synchronization (SYNC)
- 9.3.17 Zero-Delay Mode (ZDM) Configuration
- 9.3.18 PLL Cascading With Internal VCO Loopback
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6 Register Maps
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGC|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.3.8.5 Tuning Word History
Each REF-DPLL domain has a tuning word history monitor block that determines the initial output frequency accuracy upon entry into holdover. The tuning word can be updated from one of three sources depending on the DPLL operating mode:
- Locked Mode: From the output of the digital loop filter when locked
- Holdover Mode: From the final output of the history monitor
- Free Run Mode: From the free-run tuning word register (user defined)
When the history monitor is enabled and the DPLL is locked, it effectively averages the reference input frequency by accumulating history from the digital loop filter output during a programmable averaging time (TAVG). Once the input becomes invalid, the final tuning word value is stored to determine the initial holdover frequency accuracy. Generally, a longer TAVG time will produce a more accurate initial holdover frequency. The stability of the 0-ppm reference clock (XO or TCXO input) determines the long-term stability and accuracy of the holdover output frequency.
There is also a separate programmable delay timer (TIGN) that can be set to ignore the history data that is corrupted just prior to entry into holdover. The history data could be corrupted if a tuning word update occurs while the input clock is failing and before it is detected by the input monitors. Both TAVG and TIGN times are programmable through the HISTCNT and HISTDLY register bits, respectively, and are related to the REF-TDC rate.
The tuning word history is initial cleared after a device hard reset or soft reset. The history monitor begins to accumulate history once the DPLL locks to a new reference. The previous history will be cleared when a switchover to a new reference occurs assuming the history persistence bit (HIST_HOLD) is not set. The history can be manually cleared by asserting the history soft reset bit (HIST_SW_RST). If the history persistence bit is set, the history monitor will not clear the previous history value during reference switchover, holdover exit, or history soft reset. Whenever the tuning word is cleared, the history monitor waits for the first TAVG timer to expire before storing the first tuning word value.
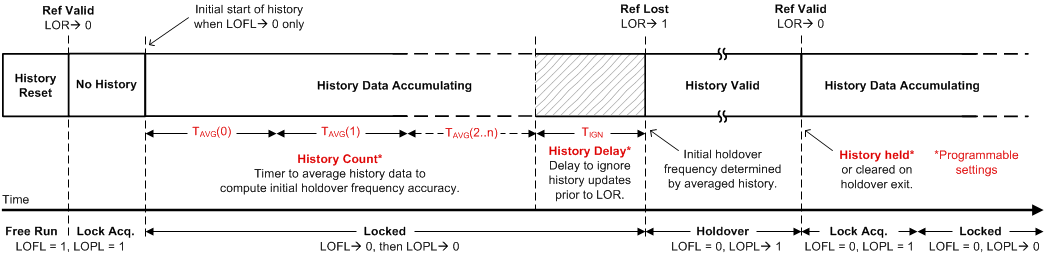 Figure 40. Tuning Word History Windows
Figure 40. Tuning Word History Windows If the TAVG period is set very long (minutes or hours) to obtain a more precise historical average frequency, it is possible for a switchover or holdover event to occur before the first tuning word is stored and available for use. To overcome this, there is an intermediate history update option (HIST_INTMD). If the history is reset, then the intermediate average can be updated at intervals of TAVG/2K , where K = HIST_INTMD to 0, during the first TAVG period only. If HIST_INTMD = 0, there is no intermediate update and the first average is stored after the first TAVG period. However, if HIST_INTMD = 4, then four intermediate averages are taken at TAVG/16, TAVG/8, TAVG/4, and TAVG/2, as well as at TAVG. After the first TAVG period, all subsequent history updates occur at the TAVG period.
When no tuning word history exists, the free-run tuning word value (TUNING_FREE_RUN) determines the initial holdover output frequency accuracy.