SNVSB91C July 2019 – June 2020 LMR36506-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Enable, Start-up and Shutdown
- 8.3.2 External CLK SYNC (with MODE/SYNC)
- 8.3.3 Adjustable Switching Frequency (with RT)
- 8.3.4 Power-Good Output Operation
- 8.3.5 Internal LDO, VCC UVLO, and VOUT/BIAS Input
- 8.3.6 Bootstrap Voltage and VCBOOT-UVLO (CBOOT Terminal)
- 8.3.7 Output Voltage Selection
- 8.3.8 Spread Spectrum
- 8.3.9 Soft Start and Recovery from Dropout
- 8.3.10 Current Limit and Short Circuit
- 8.3.11 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.12 Input Supply Current
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 9.3 What to Do and What Not to Do
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RPE|9
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RPE|9
Orderable Information
8.3.1 Enable, Start-up and Shutdown
Voltage at the EN pin controls the start-up or remote shutdown of the LMR36506-Q1 family of devices. The part stays shut down as long as the EN pin voltage is less than VEN-WAKE = 0.4 V. During the shutdown, the input current drawn by the device typically drops down to 0.5 µA (VIN = 13.5 V). With the voltage at the EN pin greater than the VEN-WAKE, the device enters the device standby mode, the internal LDO powers up to generate VCC. As the EN voltage increases further, approaching VEN-VOUT, the device finally starts to switch, entering the start-up mode, with a soft start. During the device shutdown process, when the EN input voltage measures less than (VEN-VOUT – VEN-HYST), the regulator stops switching and re-enters the device standby mode. Any further decrease in the EN pin voltage, below VEN-WAKE, the device is then firmly shut down. The high-voltage compliant EN input pin can be connected directly to the VIN input pin if remote precision control is not needed. The EN input pin must not be allowed to float. The various EN threshold parameters and their values are listed in the Electrical Characteristics. Figure 8 shows the precision enable behavior, Figure 9 depicting a typical remote EN start-up waveform in an application. Once EN goes high, after a delay of about 1 ms, the output voltage begins to rise with a soft start and reaches close to the final value in about 2.67 ms (tss). After a delay of about 2 ms (tPGOOD_ACT), the PGOOD flag goes high. During start-up, the device is not allowed to enter FPWM mode until the soft-start time has elapsed. This time is measured from the rising edge of EN. Check External UVLO section for component selection.
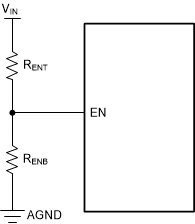 Figure 7. VIN UVLO Using the EN pin
Figure 7. VIN UVLO Using the EN pin 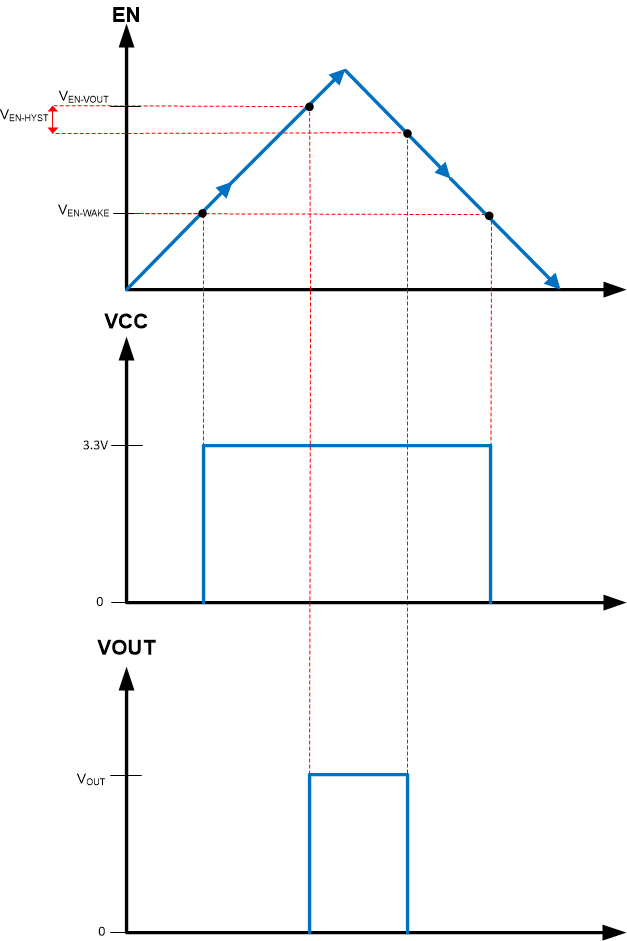 Figure 8. Precision Enable Behavior
Figure 8. Precision Enable Behavior 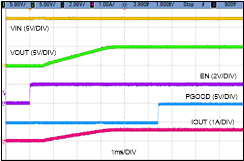 Figure 9. Enable Start-up
Figure 9. Enable Start-up
VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 5 V, IOUT = 600 mA