SNVSBB6B December 2019 – December 2022 LMR36506
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Enable, Start-up, and Shutdown
- 8.3.2 Adjustable Switching Frequency (with RT)
- 8.3.3 Power-Good Output Operation
- 8.3.4 Internal LDO, VCC UVLO, and VOUT/BIAS Input
- 8.3.5 Bootstrap Voltage and VCBOOT-UVLO (CBOOT Terminal)
- 8.3.6 Output Voltage Selection
- 8.3.7 Soft Start and Recovery from Dropout
- 8.3.8 Current Limit and Short Circuit
- 8.3.9 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.10 Input Supply Current
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 9.3 Best Design Practices
- 9.4 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9.5 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RPE|9
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RPE|9
Orderable Information
8.3.2 Adjustable Switching Frequency (with RT)
The select variants in the LMR36506 family with the RT pin allow the power designers to set any desired operating frequency between 200 kHz and 2.2 MHz in their applications. See Figure 8-4 to determine the resistor value needed for the desired switching frequency. See Table 8-1 for selection on programming the RT pin.
Table 8-1 RT Pin Setting
| RT INPUT | SWITCHING FREQUENCY |
|---|---|
| VCC | 1 MHz |
| GND | 2.2 MHz |
| RT to GND | Adjustable according to Figure 8-4 |
| Float (Not Recommended) | No Switching |
Equation 1 can be used to calculate the value of RT for a desired frequency.
Equation 1. 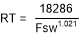
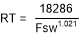
where
- RT is the frequency setting resistor value (kΩ).
- FSW is the switching frequency (kHz).
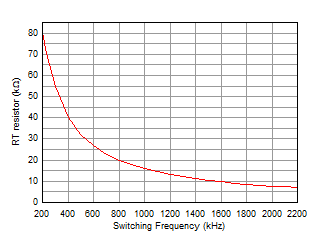 Figure 8-4 RT Values vs Frequency
Figure 8-4 RT Values vs Frequency