SBOS556D June 2011 – August 2020 OPA171-Q1 , OPA2171-Q1 , OPA4171-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|5
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.3 Capacitive Load and Stability
The dynamic characteristics of the OPAx171-Q1 family of devices are optimized for commonly encountered operating conditions. The combination of low closed-loop gain and high capacitive loads decreases the phase margin of the amplifier and can lead to gain peaking or oscillations. As a result, heavier capacitive loads must be isolated from the output. The simplest way to achieve this isolation is to add a small resistor (for example, ROUT equal to 50 Ω) in series with the output. Figure 7-2 and Figure 7-3 shows small-signal overshoot versus capacitive load for several values of ROUT. For details of analysis techniques and application circuits, see Applications Bulletin AB-028, available for download from TI.com.
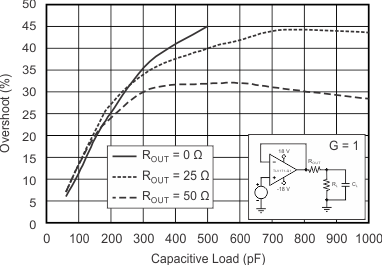 Figure 7-2 Small-Signal Overshoot versus Capacitive Load (100-mV Output Step)
Figure 7-2 Small-Signal Overshoot versus Capacitive Load (100-mV Output Step)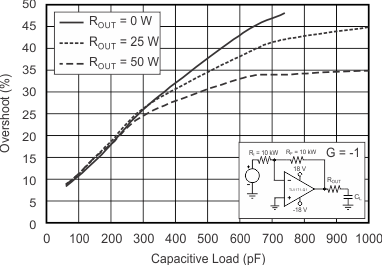 Figure 7-3 Small-Signal Overshoot versus Capacitive Load (100-mV Output Step)
Figure 7-3 Small-Signal Overshoot versus Capacitive Load (100-mV Output Step)