SBOS830I September 2017 – October 2021 OPA189 , OPA2189 , OPA4189
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DGK|8
Orderable Information
8.3.6 Electrical Overstress
Designers often ask questions about the capability of an operational amplifier to withstand electrical overstress. These questions tend to focus on the device inputs, but may involve the supply voltage pins or even the output pin. Each of these different pin functions have electrical stress limits determined by the voltage breakdown characteristics of the particular semiconductor fabrication process and specific circuits connected to the pin. Additionally, internal electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection is built into these circuits to protect from accidental ESD events both before and during product assembly.
Having a good understanding of this basic ESD circuitry and the relevance to an electrical overstress event is helpful. See Figure 8-4 for an illustration of the ESD circuits contained in the OPAx189 (indicated by the dashed line area). The ESD protection circuitry involves several current-steering diodes connected from the input and output pins and routed back to the internal power-supply lines, where the diodes meet at an absorption device internal to the operational amplifier. This protection circuitry is intended to remain inactive during normal circuit operation.
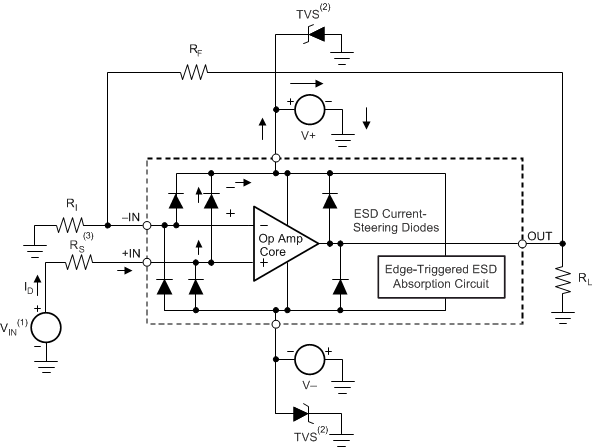
An ESD event produces a short-duration, high-voltage pulse that is transformed into a short-duration, high-current pulse while discharging through a semiconductor device. The ESD protection circuits are designed to provide a current path around the operational amplifier core to prevent damage. The energy absorbed by the protection circuitry is then dissipated as heat.
When an ESD voltage develops across two or more amplifier device pins, current flows through one or more steering diodes. Depending on the path that the current takes, the absorption device may activate. The absorption device has a trigger or threshold voltage that is above the normal operating voltage of the OPAx189 but below the device breakdown voltage level. When this threshold is exceeded, the absorption device quickly activates and clamps the voltage across the supply rails to a safe level.
When the operational amplifier connects into a circuit (as shown in Figure 8-4), the ESD protection components are intended to remain inactive and do not become involved in the application circuit operation. However, circumstances may arise where an applied voltage exceeds the operating voltage range of a given pin. Should this condition occur, there is a risk that some internal ESD protection circuits may be biased on, and conduct current. Any such current flow occurs through steering-diode paths and rarely involves the absorption device.
Figure 8-4 shows a specific example where the input voltage (VIN) exceeds the positive supply voltage (V+) by 500 mV or more. Much of what happens in the circuit depends on the supply characteristics. If V+ can sink the current, one of the upper input steering diodes conducts and directs current to +VS. Excessively high current levels can flow with increasingly higher VIN. As a result, the data sheet specifications recommend that applications limit the input current to 10 mA.
If the supply is not capable of sinking the current, VIN may begin sourcing current to the operational amplifier, and then take over as the source of positive supply voltage. The danger in this case is that the voltage can rise to levels that exceed the operational amplifier absolute maximum ratings.
Another common question involves what happens to the amplifier if an input signal is applied to the input while the power supplies V+ or V– are at 0 V. Again, this question depends on the supply characteristic while at 0 V, or at a level below the input signal amplitude. If the supplies appear as high impedance, then the operational amplifier supply current may be supplied by the input source through the current-steering diodes. This state is not a normal bias condition; the amplifier most likely does not operate normally. If the supplies are low impedance, then the current through the steering diodes can become quite high. The current level depends on the ability of the input source to deliver current, and any resistance in the input path.
If there is any uncertainty about the ability of the supply to absorb this current, external zener diodes must be added to the supply pins, as shown in Figure 8-4. The zener voltage must be selected such that the diode does not turn on during normal operation. However, the zener voltage must be low enough so that the zener diode conducts if the supply pin begins to rise above the safe operating supply voltage level.