SBOS900B September 2018 – June 2019 OPA2156
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DGK|8
Orderable Information
8.1.1 Slew Rate Limit for Input Protection
In control systems for valves or motors, abrupt changes in voltages or currents can cause mechanical damages. By controlling the slew rate of the command voltages into the drive circuits, the load voltages ramps up and down at a safe rate. For symmetrical slew-rate applications (positive slew rate equals negative slew rate), one additional op amp provides slew-rate control for a given analog gain stage. The unique input protection and high output current and slew rate of the OPA2156 make the device an optimal amplifier to achieve slew rate control for both dual- and single-supply systems.Figure 45 shows the OPA2156 in a slew-rate limit design.
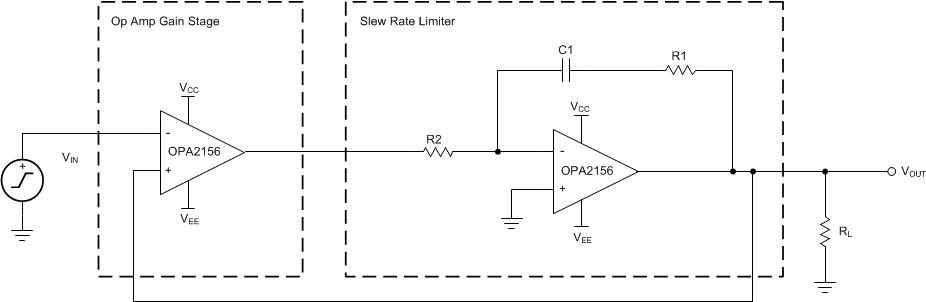 Figure 45. Slew Rate Limiter Uses One Op Amp
Figure 45. Slew Rate Limiter Uses One Op Amp
 |
For step-by-step design procedure, circuit schematics, bill of materials, PCB files, simulation results, and test results, refer to TI Precision Design TIDU026, Slew Rate Limiter Uses One Op Amp. |