SBOS350B December 2006 – December 2024 OPA4830
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Related Products
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics VS = ±5V
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics VS = 5V
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics VS = 3V
- 6.8 Typical Characteristics: VS = ±5V
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics: VS = ±5V, Differential Configuration
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics: VS = 5V
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics: VS = 5V, Differential Configuration
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics: VS = 3V
- 6.13 Typical Characteristics: VS = 3V, Differential Configuration
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1 Wideband Voltage-Feedback Operation
- 8.1.2 DC Level-Shifting
- 8.1.3 AC-Coupled Output Video Line Driver
- 8.1.4 Noninverting Amplifier With Reduced Peaking
- 8.1.5 Single-Supply Active Filter
- 8.1.6 Differential Interface Applications
- 8.1.7 DC-Coupled Single-to-Differential Conversion
- 8.1.8 Low-Power, Differential I/O, 4th-Order Active Filter
- 8.1.9 Dual-Channel, Differential ADC Driver
- 8.1.10 Video Line Driving
- 8.1.11 4-Channel DAC Transimpedance Amplifier
- 8.1.12 Operating Suggestions: Optimizing Resistor Values
- 8.1.13 Bandwidth vs Gain: Noninverting Operation
- 8.1.14 Inverting Amplifier Operation
- 8.1.15 Output Current and Voltages
- 8.1.16 Driving Capacitive Loads
- 8.1.17 Distortion Performance
- 8.1.18 Noise Performance
- 8.1.19 DC Accuracy and Offset Control
- 8.2 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.3 Layout
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PW|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.1.3 AC-Coupled Output Video Line Driver
Low-power and low-cost video line drivers often buffer digital-to-analog converter (DAC) outputs with a gain of 2V/V into a doubly-terminated line. Those interfaces typically require a dc blocking capacitor. For a simple design, that interface often has used a very large value blocking capacitor (220μF) to limit tilt, or SAG, across the frames. Figure 8-5 shows one approach to creating a very low high-pass pole location using much lower capacitor values. This circuit gives a voltage gain of 2 at the output pin with a high-pass pole at 8Hz. Given the 150Ω load, a simple blocking capacitor approach requires a 133μF value. The two much-lower-valued capacitors give this same low-pass pole using this simple SAG correction circuit of Figure 8-5.
 Figure 8-5 Video
Line Driver With SAG Correction
Figure 8-5 Video
Line Driver With SAG CorrectionThe input is shifted slightly positive in Figure 8-5 using the voltage divider from the positive supply. This configuration gives about a 200mV input dc offset that shows up at the output pin as a 400mV dc offset when the DAC output is at zero current during the sync tip portion of the video signal. This offset acts to hold the output in the linear operating region. This circuit then passes on any power-supply noise to the output with a gain of approximately –20dB, so good supply decoupling is recommended on the power-supply pin. Figure 8-6 shows the frequency response for the circuit of Figure 8-5. This plot shows the 8Hz low-frequency high-pass pole and a high-end cutoff at approximately 100MHz.
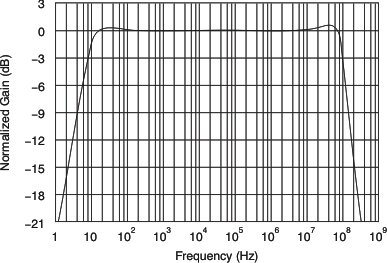 Figure 8-6 Video
Line Driver Response to Matched Load
Figure 8-6 Video
Line Driver Response to Matched Load